Blockchain oracles serve as trusted entities that provide external data to smart contracts, enabling them to execute based on real-world information. Data feeds supply continuous streams of data, often from multiple sources, to maintain accuracy and reliability within decentralized applications. Explore how blockchain oracles and data feeds transform data integrity and accessibility in the evolving tech landscape.
Why it is important
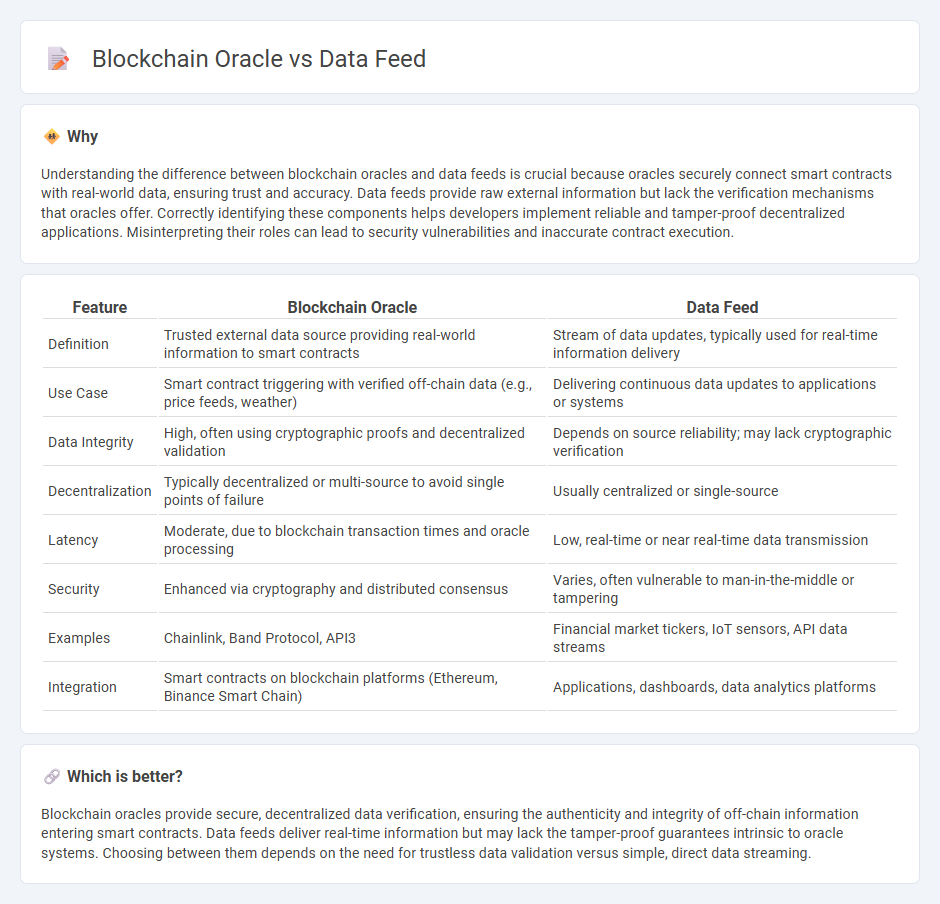
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and data feeds is crucial because oracles securely connect smart contracts with real-world data, ensuring trust and accuracy. Data feeds provide raw external information but lack the verification mechanisms that oracles offer. Correctly identifying these components helps developers implement reliable and tamper-proof decentralized applications. Misinterpreting their roles can lead to security vulnerabilities and inaccurate contract execution.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Data Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trusted external data source providing real-world information to smart contracts | Stream of data updates, typically used for real-time information delivery |
| Use Case | Smart contract triggering with verified off-chain data (e.g., price feeds, weather) | Delivering continuous data updates to applications or systems |
| Data Integrity | High, often using cryptographic proofs and decentralized validation | Depends on source reliability; may lack cryptographic verification |
| Decentralization | Typically decentralized or multi-source to avoid single points of failure | Usually centralized or single-source |
| Latency | Moderate, due to blockchain transaction times and oracle processing | Low, real-time or near real-time data transmission |
| Security | Enhanced via cryptography and distributed consensus | Varies, often vulnerable to man-in-the-middle or tampering |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol, API3 | Financial market tickers, IoT sensors, API data streams |
| Integration | Smart contracts on blockchain platforms (Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain) | Applications, dashboards, data analytics platforms |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles provide secure, decentralized data verification, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of off-chain information entering smart contracts. Data feeds deliver real-time information but may lack the tamper-proof guarantees intrinsic to oracle systems. Choosing between them depends on the need for trustless data validation versus simple, direct data streaming.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as trusted intermediaries that provide external real-world data feeds to blockchain smart contracts, enabling them to execute based on real-time information. Data feeds supply continuous, reliable streams of external information such as price indexes, weather data, or event outcomes that oracles integrate and verify before delivering to decentralized applications. This connection ensures smart contracts operate with accurate, tamper-proof data, bridging on-chain and off-chain environments for complex automated processes.
Key Terms
Real-time Data
Data feeds provide real-time data streams crucial for applications requiring up-to-the-minute information, delivering continuously updated data directly from sources. Blockchain oracles act as trusted intermediaries that bridge external real-time data with smart contracts on the blockchain, ensuring accurate execution based on dynamic external conditions. Explore in detail how these technologies enhance decentralized applications with real-time data integration.
Trustless Verification
Data feeds provide external information to blockchain applications but rely on centralized sources, which introduces trust concerns. Blockchain oracles enable trustless verification by securely fetching and validating off-chain data through decentralized protocols, reducing reliance on single points of failure. Explore how trustless oracles enhance data integrity and transparency in smart contracts.
External Data Integration
Data feeds provide structured external data directly into applications, enabling real-time access to market prices, weather updates, and financial statistics essential for decision-making. Blockchain oracles act as trusted intermediaries, transmitting verified external data onto blockchain networks to facilitate smart contract execution with external information. Explore how these technologies uniquely enable seamless external data integration to enhance system reliability and automation.
Source and External Links
Data feed - Wikipedia - A data feed is a mechanism to receive updated, structured data from sources, commonly used in real-time applications and web feeds, including news, product information, and financial markets, often utilizing formats like CSV, RSS, RDF, or OWL for semantic data feeds.
Analytics Data Feed Overview - Adobe Experience League - Data feeds from Adobe Analytics provide raw data batches regularly, which can be exported and used in external platforms, requiring specific configurations and permissions to access and manage.
What is a data feed? | Definition from TechTarget - A data feed is an ongoing structured data stream delivering updated information from one or more sources to devices or software, either continuously or on demand, enabling timely updates and automation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com