Passkey authentication leverages cryptographic key pairs stored securely on devices, providing a phishing-resistant and user-friendly way to verify identity without passwords. Certificate-based authentication uses digital certificates issued by trusted authorities to confirm user or device legitimacy, commonly employed in enterprise environments for robust access control. Explore how these authentication methods compare in security, usability, and deployment scenarios to choose the best fit for your needs.
Why it is important
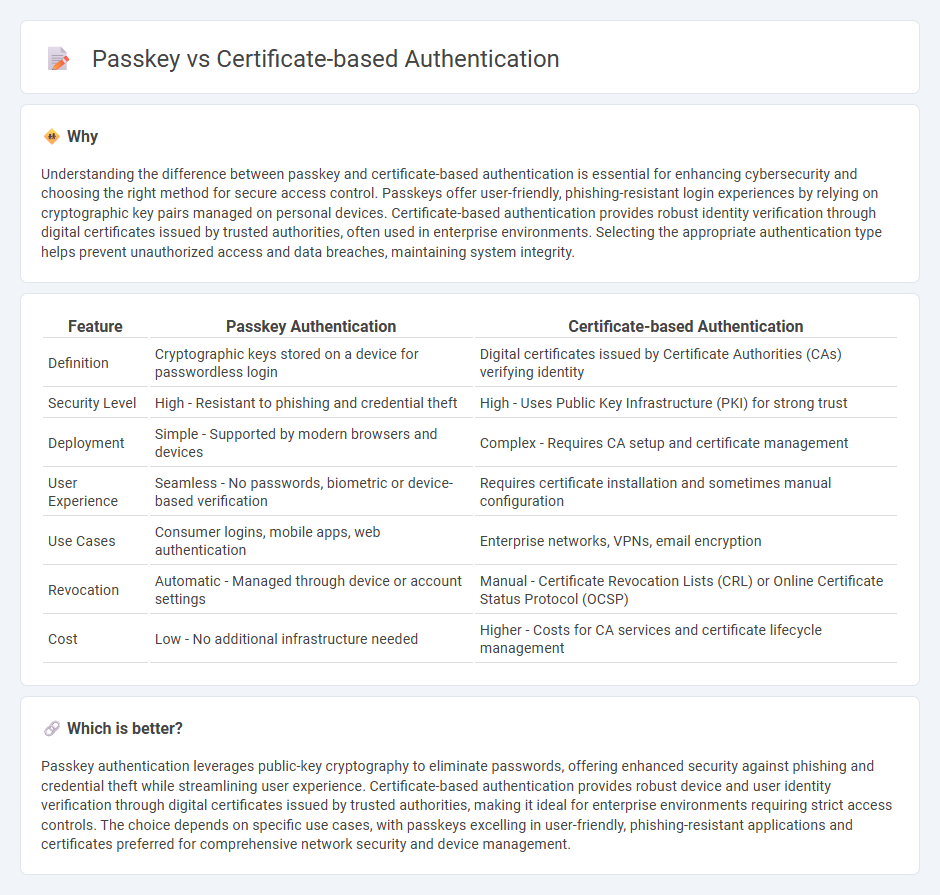
Understanding the difference between passkey and certificate-based authentication is essential for enhancing cybersecurity and choosing the right method for secure access control. Passkeys offer user-friendly, phishing-resistant login experiences by relying on cryptographic key pairs managed on personal devices. Certificate-based authentication provides robust identity verification through digital certificates issued by trusted authorities, often used in enterprise environments. Selecting the appropriate authentication type helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches, maintaining system integrity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Passkey Authentication | Certificate-based Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic keys stored on a device for passwordless login | Digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) verifying identity |
| Security Level | High - Resistant to phishing and credential theft | High - Uses Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for strong trust |
| Deployment | Simple - Supported by modern browsers and devices | Complex - Requires CA setup and certificate management |
| User Experience | Seamless - No passwords, biometric or device-based verification | Requires certificate installation and sometimes manual configuration |
| Use Cases | Consumer logins, mobile apps, web authentication | Enterprise networks, VPNs, email encryption |
| Revocation | Automatic - Managed through device or account settings | Manual - Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) |
| Cost | Low - No additional infrastructure needed | Higher - Costs for CA services and certificate lifecycle management |
Which is better?
Passkey authentication leverages public-key cryptography to eliminate passwords, offering enhanced security against phishing and credential theft while streamlining user experience. Certificate-based authentication provides robust device and user identity verification through digital certificates issued by trusted authorities, making it ideal for enterprise environments requiring strict access controls. The choice depends on specific use cases, with passkeys excelling in user-friendly, phishing-resistant applications and certificates preferred for comprehensive network security and device management.
Connection
Passkey and certificate-based authentication both leverage cryptographic principles to enhance security by verifying user identities without transmitting passwords. Passkeys use asymmetric key pairs stored securely on user devices to authenticate, similar to digital certificates that bind public keys to identities within certificate authorities. This connection ensures robust, phishing-resistant authentication frameworks crucial for modern cybersecurity infrastructures.
Key Terms
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Certificate-based authentication leverages Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) by issuing digital certificates that bind a public key to an entity's identity, ensuring secure verification through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Passkeys, built on asymmetric cryptography and often underpinned by PKI principles, replace passwords with cryptographic key pairs stored on devices, providing phishing-resistant and user-friendly authentication. Explore how PKI enhances security frameworks by comparing these methods for stronger identity protection.
Cryptographic Keys
Certificate-based authentication relies on asymmetric cryptographic keys where a digital certificate binds a public key to an entity, ensuring identity verification through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Passkeys leverage public-key cryptography as well but are designed for passwordless login, storing private keys securely on devices while facilitating seamless, phishing-resistant authentication. Discover more about the distinct cryptographic foundations and security benefits of each method.
FIDO2
FIDO2 leverages certificate-based authentication by utilizing public key cryptography, where a unique key pair is generated and the certificate verifies the public key's authenticity without transmitting passwords. Passkeys, built on FIDO2 standards, offer a phishing-resistant and passwordless experience by securely storing cryptographic credentials on the device using biometric or PIN verification. Explore the nuances of FIDO2's implementation for enhanced digital security and user convenience.
Source and External Links
What is Certificate-based Authentication? - GeeksforGeeks - Certificate-based authentication uses digital certificates and public key cryptography, signed by a trusted certificate authority, to verify the identity of users, machines, or devices without relying on passwords, providing stronger security and convenience.
What is Certificate-Based Authentication | Yubico - This phishing-resistant method allows computers to securely identify each other using digital certificates, which are stored locally with a private key, enabling automatic authentication for various systems and endpoints including IoT devices.
Boost Security with Certificate-Based Authentication - Ping Identity - Certificate-based authentication verifies identity by confirming ownership of a unique private key that corresponds to a public key in a certificate, ensuring only the rightful owner can access protected resources and that the certificate is signed by a trusted authority.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com