Passkey authentication uses cryptographic keys stored on a device for secure access, eliminating the need for traditional passwords. Biometric authentication relies on unique physical traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition to verify identity. Explore the advantages and challenges of passkey and biometric authentication to understand which technology best suits your security needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between passkey and biometric authentication is crucial for enhancing digital security by choosing the most appropriate method for different applications. Passkeys offer a cryptographic, phishing-resistant means of authentication without relying on traditional passwords, while biometric authentication uses unique physical traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition for identity verification. Knowing the strengths and vulnerabilities of each helps organizations prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data effectively. This knowledge supports secure user experiences and reduces the risk of cyberattacks in modern technology environments.
Comparison Table
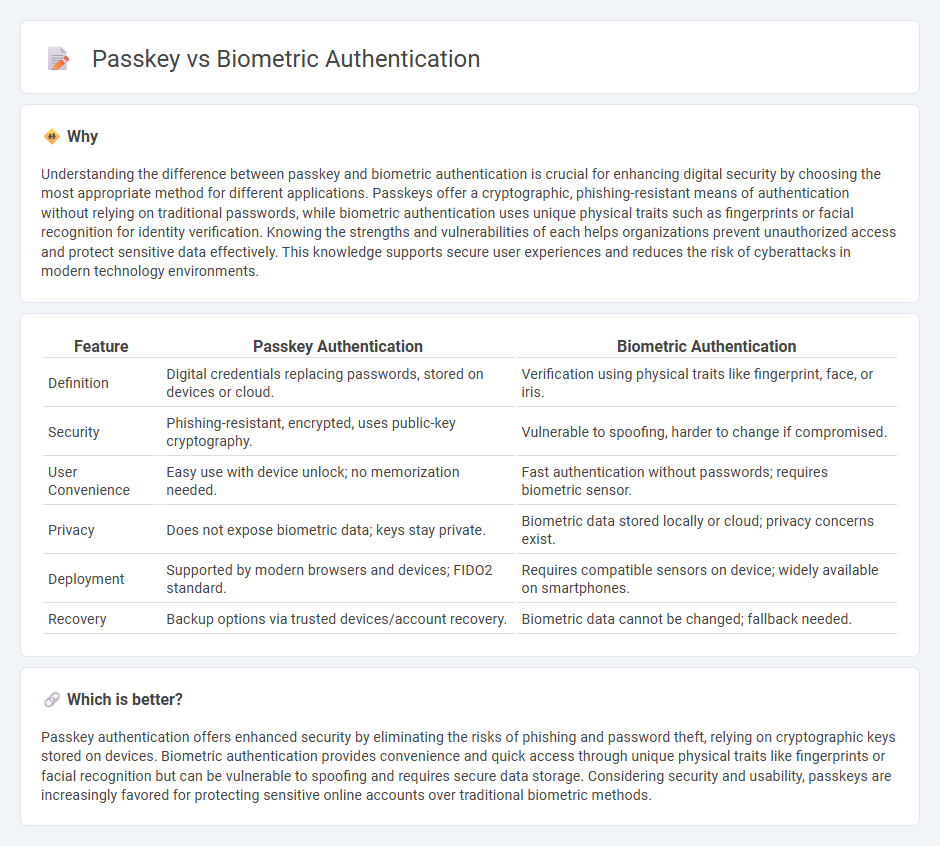
| Feature | Passkey Authentication | Biometric Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital credentials replacing passwords, stored on devices or cloud. | Verification using physical traits like fingerprint, face, or iris. |
| Security | Phishing-resistant, encrypted, uses public-key cryptography. | Vulnerable to spoofing, harder to change if compromised. |
| User Convenience | Easy use with device unlock; no memorization needed. | Fast authentication without passwords; requires biometric sensor. |
| Privacy | Does not expose biometric data; keys stay private. | Biometric data stored locally or cloud; privacy concerns exist. |
| Deployment | Supported by modern browsers and devices; FIDO2 standard. | Requires compatible sensors on device; widely available on smartphones. |
| Recovery | Backup options via trusted devices/account recovery. | Biometric data cannot be changed; fallback needed. |
Which is better?
Passkey authentication offers enhanced security by eliminating the risks of phishing and password theft, relying on cryptographic keys stored on devices. Biometric authentication provides convenience and quick access through unique physical traits like fingerprints or facial recognition but can be vulnerable to spoofing and requires secure data storage. Considering security and usability, passkeys are increasingly favored for protecting sensitive online accounts over traditional biometric methods.
Connection
Passkey and biometric authentication are interconnected through their reliance on cryptographic security and user verification methods to enhance digital identity protection. Passkeys utilize biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition to securely unlock cryptographic keys, eliminating the need for traditional passwords. This integration reduces phishing risks and simplifies authentication by combining device-based biometrics with asymmetric key cryptography for seamless user access.
Key Terms
Identity Verification
Biometric authentication uses unique biological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans to verify identity, offering high security through intrinsic user characteristics. Passkeys, based on cryptographic key pairs stored on devices, provide phishing-resistant, passwordless login experiences by securely binding identity verification to the user's hardware. Discover how these identity verification methods enhance security protocols and user convenience in modern digital authentication.
Cryptographic Keys
Biometric authentication relies on unique biological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition, which are converted into cryptographic keys to securely verify identity without transmitting actual biometric data. Passkey systems use asymmetric cryptography, generating a pair of cryptographic keys--one public and one private--to authenticate users across devices with enhanced security and phishing resistance. Explore how these cryptographic key mechanisms fundamentally reshape digital security.
User Experience
Biometric authentication leverages unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition for seamless, fast access, enhancing convenience and security without memorization. Passkeys replace traditional passwords with cryptographic keys stored on devices, minimizing phishing risks and streamlining login processes across platforms. Explore how these technologies compare in real-world applications to optimize your user experience.
Source and External Links
What is Biometric Authentication and How Does It Work? - LoginTC - Biometric authentication verifies a user's identity using unique biological traits like fingerprints, voice, retina, or facial features, offering higher security than traditional password-based methods.
What is Biometric Authentication? - GeeksforGeeks - This method safeguards sensitive information by confirming identity through physical attributes such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial and voice recognition, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult.
What is Biometric Authentication? Use Cases, Pros & Cons | OneSpan - Biometric authentication uses a data-generated model of an individual's unique physical or behavioral traits to securely grant access to applications and network resources, combining strong security with user convenience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com