Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated content, utilizing machine learning algorithms to spot deepfakes, manipulated videos, or altered images by analyzing inconsistencies and anomalies. Media provenance emphasizes tracing the origin and history of digital content through cryptographic methods, blockchain technology, and metadata verification to establish authenticity and trustworthiness. Explore the latest advancements in detecting synthetic media and ensuring content provenance to enhance digital security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and media provenance is crucial for combating misinformation and ensuring content authenticity. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated or manipulated content, while media provenance tracks the origin and history of media files. Accurate distinction enhances digital security by preventing the spread of deepfakes and verifying legitimate news sources. This knowledge empowers users and organizations to maintain trust in digital communications.
Comparison Table
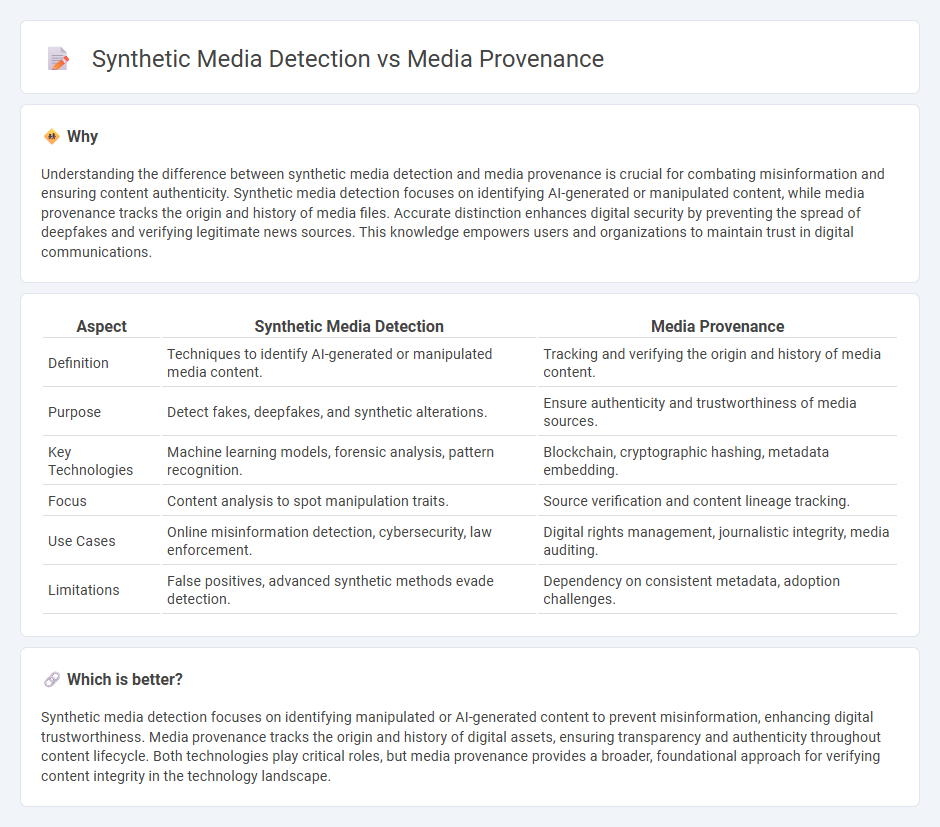
| Aspect | Synthetic Media Detection | Media Provenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques to identify AI-generated or manipulated media content. | Tracking and verifying the origin and history of media content. |
| Purpose | Detect fakes, deepfakes, and synthetic alterations. | Ensure authenticity and trustworthiness of media sources. |
| Key Technologies | Machine learning models, forensic analysis, pattern recognition. | Blockchain, cryptographic hashing, metadata embedding. |
| Focus | Content analysis to spot manipulation traits. | Source verification and content lineage tracking. |
| Use Cases | Online misinformation detection, cybersecurity, law enforcement. | Digital rights management, journalistic integrity, media auditing. |
| Limitations | False positives, advanced synthetic methods evade detection. | Dependency on consistent metadata, adoption challenges. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content to prevent misinformation, enhancing digital trustworthiness. Media provenance tracks the origin and history of digital assets, ensuring transparency and authenticity throughout content lifecycle. Both technologies play critical roles, but media provenance provides a broader, foundational approach for verifying content integrity in the technology landscape.
Connection
Synthetic media detection identifies manipulated or AI-generated content by analyzing digital fingerprints and inconsistencies, while media provenance tracks the origin and history of media files through secure metadata and blockchain technologies. Both technologies are crucial for verifying authenticity and combating misinformation in digital environments. Enhanced collaboration between detection algorithms and provenance tracing strengthens trust in media integrity across online platforms.
Key Terms
Digital Watermarking
Media provenance techniques establish the origin and history of digital content, crucial for verifying authenticity through embedded digital watermarks that carry metadata about creation and edits. Synthetic media detection relies primarily on analyzing digital artifacts and inconsistencies, complementing watermarking by identifying manipulated or AI-generated content. Explore how digital watermarking enhances trust across media provenance and synthetic media detection to safeguard digital integrity.
Deepfake Detection
Deepfake detection methods are central to distinguishing synthetic media from authentic content by analyzing inconsistencies in visual and audio data, leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms. Media provenance involves tracking and verifying the origin and history of digital content through metadata, cryptographic signatures, and blockchain technology to ensure authenticity and trustworthiness. Explore the latest advancements in deepfake detection techniques and the role of media provenance for more insights.
Content Authenticity Initiative
The Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) advances media provenance by embedding verifiable metadata across digital content to trace its origin and modifications. This approach contrasts with synthetic media detection, which employs AI algorithms to identify manipulated or fabricated visuals without metadata reliance. Explore the CAI's strategies and tools to understand their role in enhancing digital content trust.
Source and External Links
A new era for the media industry: placing value in content provenance - Content provenance in digital media is the practice of verifying the origin and authenticity of content, such as images and videos, to combat misinformation and establish accountability in an increasingly manipulated digital landscape.
The Importance of Understanding Multimedia Provenance - Understanding media provenance involves tracking the creation and editing history of multimedia files using embedded cryptographic metadata, which helps law enforcement, agencies, and corporations ensure authenticity and build digital trust.
The Value of Content Provenance in the Media Landscape - Provenance refers to the documented history of a digital media asset, and standards like those from the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) enable secure, verifiable trails of origin and edits, directly impacting the perceived value and trustworthiness of media content.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com