Circular electronics focus on designing devices to be easily recyclable, extending product life cycles and reducing electronic waste through material recovery and reuse. Bio-based electronics utilize organic, biodegradable materials for components, aiming to minimize environmental impact and enhance sustainability in device manufacturing. Explore how these innovations are transforming the future of eco-friendly technology development.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and bio-based electronics is crucial for promoting sustainable technology solutions tailored to environmental impact reduction. Circular electronics focus on recycling and reusing electronic components to minimize e-waste, whereas bio-based electronics utilize renewable, biodegradable materials to reduce dependence on traditional plastics and metals. Differentiating these concepts helps in developing targeted policies and innovations for eco-friendly electronic products. This knowledge supports manufacturers and consumers in making informed choices that align with environmental sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
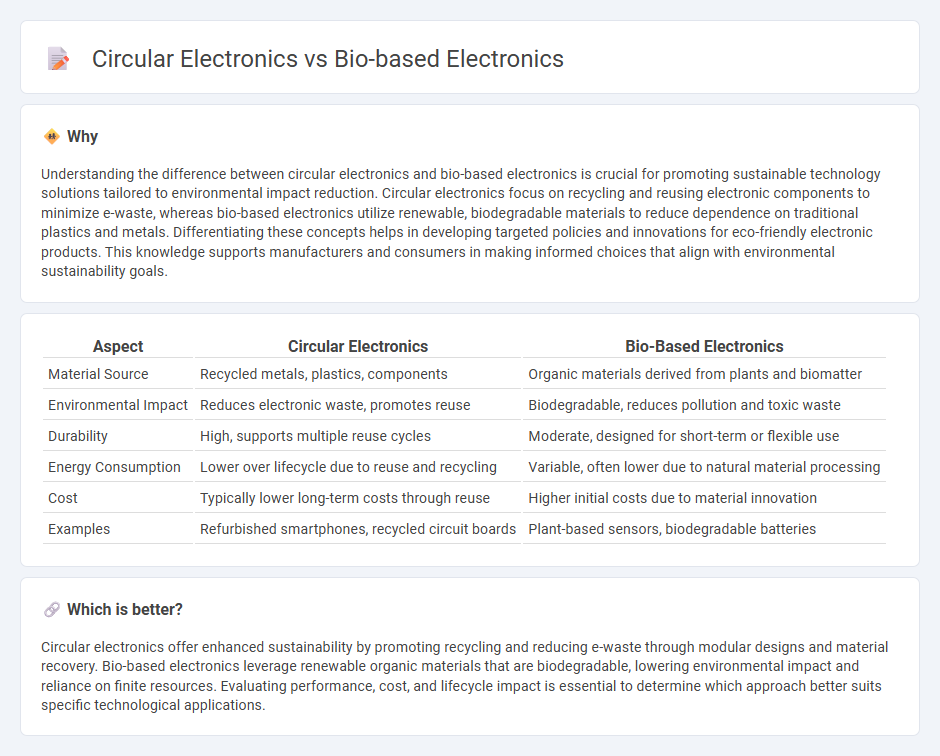
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Bio-Based Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Recycled metals, plastics, components | Organic materials derived from plants and biomatter |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces electronic waste, promotes reuse | Biodegradable, reduces pollution and toxic waste |
| Durability | High, supports multiple reuse cycles | Moderate, designed for short-term or flexible use |
| Energy Consumption | Lower over lifecycle due to reuse and recycling | Variable, often lower due to natural material processing |
| Cost | Typically lower long-term costs through reuse | Higher initial costs due to material innovation |
| Examples | Refurbished smartphones, recycled circuit boards | Plant-based sensors, biodegradable batteries |
Which is better?
Circular electronics offer enhanced sustainability by promoting recycling and reducing e-waste through modular designs and material recovery. Bio-based electronics leverage renewable organic materials that are biodegradable, lowering environmental impact and reliance on finite resources. Evaluating performance, cost, and lifecycle impact is essential to determine which approach better suits specific technological applications.
Connection
Circular electronics and bio-based electronics are interconnected through their shared focus on sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Circular electronics prioritize reuse, recycling, and extending the lifecycle of devices, while bio-based electronics utilize organic, biodegradable materials that support circular economy principles. This synergy advances eco-friendly innovation by minimizing electronic waste and promoting renewable resources in technology production.
Key Terms
Bio-based electronics:
Bio-based electronics utilize renewable organic materials such as cellulose, lignin, and proteins to create sustainable electronic components, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental impact. These materials offer biodegradability and lower carbon footprints, contributing to enhanced eco-friendly electronic design. Discover how bio-based electronics are revolutionizing sustainability in technology by exploring their innovative applications and benefits.
Biodegradable polymers
Biodegradable polymers in bio-based electronics offer eco-friendly alternatives by utilizing renewable resources to minimize electronic waste through natural decomposition. Circular electronics prioritize designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling, extending lifespan and reducing landfill accumulation. Explore how biodegradable polymers bridge sustainability goals in both bio-based and circular electronics for a greener future.
Organic semiconductors
Organic semiconductors in bio-based electronics leverage renewable biological materials to create sustainable, eco-friendly devices with reduced environmental impact. Circular electronics emphasize the reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of organic semiconductor components to minimize waste and extend product life cycles. Explore the advancements in organic semiconductor technologies reshaping bio-based and circular electronics.
Source and External Links
Bio-Based Electronics Innovation - Term - Bio-based electronics use materials from living organisms or renewable biological feedstocks--such as plant polymers, bacterial cellulose, proteins, or DNA--to create sustainable electronic components and devices.
Bio-Based Flexible PCBs: A New Frontier in Sustainable Electronics - Bio-based flexible printed circuit boards are emerging as eco-friendly alternatives for applications like wearables, IoT, and medical devices, offering biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint in manufacturing.
Bio-Based Chemicals Project: Homegrown Electronics for All - Research projects like MADE-PUBLIC are developing ways to convert plant biomass into printable, biodegradable inks for 3D-printed electronics, aiming for locally produced and compostable devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com