Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing the secret itself, enhancing privacy and security in cryptographic protocols. Digital signatures authenticate the sender's identity and ensure message integrity, relying on asymmetric key pairs for verification. Explore the distinct applications and advantages of zero-knowledge proofs versus digital signatures to understand their impact on modern technology.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero-knowledge proofs and digital signatures is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity and privacy in digital communications. Zero-knowledge proofs allow one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, boosting data confidentiality. Digital signatures ensure data integrity and authenticate the sender's identity, protecting against forgery. Mastery of both cryptographic tools supports the development of secure authentication and verification systems in blockchain technology and secure transactions.
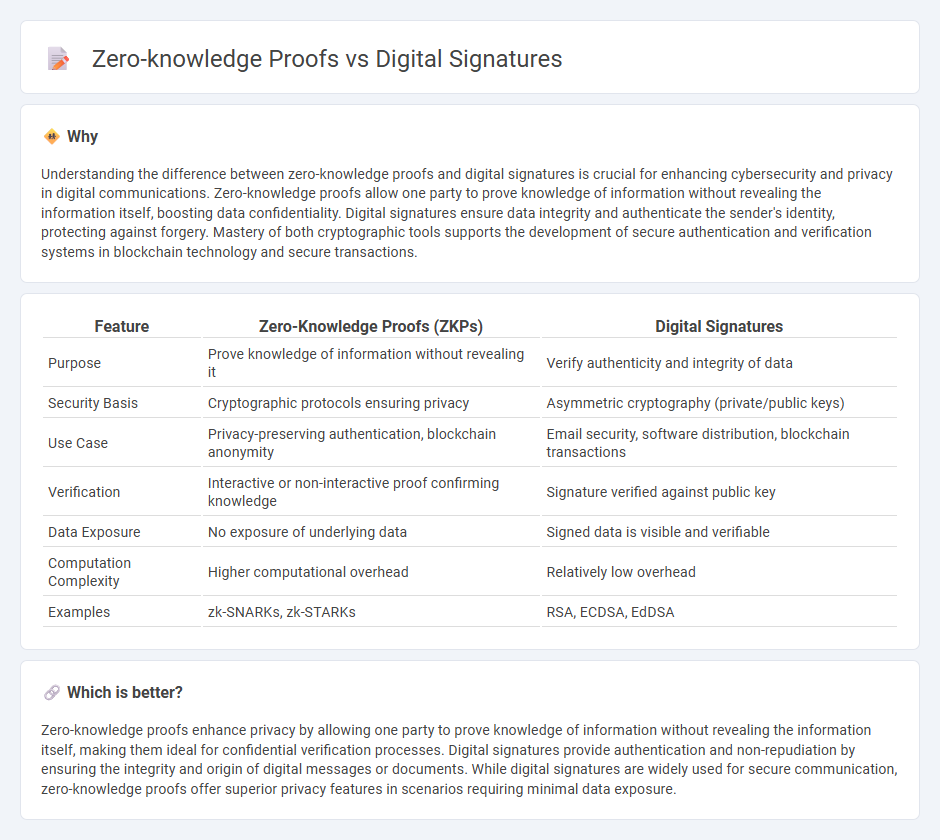
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) | Digital Signatures |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prove knowledge of information without revealing it | Verify authenticity and integrity of data |
| Security Basis | Cryptographic protocols ensuring privacy | Asymmetric cryptography (private/public keys) |
| Use Case | Privacy-preserving authentication, blockchain anonymity | Email security, software distribution, blockchain transactions |
| Verification | Interactive or non-interactive proof confirming knowledge | Signature verified against public key |
| Data Exposure | No exposure of underlying data | Signed data is visible and verifiable |
| Computation Complexity | Higher computational overhead | Relatively low overhead |
| Examples | zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs | RSA, ECDSA, EdDSA |
Which is better?
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge of information without revealing the information itself, making them ideal for confidential verification processes. Digital signatures provide authentication and non-repudiation by ensuring the integrity and origin of digital messages or documents. While digital signatures are widely used for secure communication, zero-knowledge proofs offer superior privacy features in scenarios requiring minimal data exposure.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to verify the validity of information without revealing the information itself, enhancing privacy in digital interactions. Digital signatures rely on cryptographic algorithms to authenticate the identity of the sender and ensure message integrity. The connection lies in zero-knowledge proofs providing a framework to verify signatures or transactions confidentially, thereby strengthening security in blockchain and cryptographic systems.
Key Terms
Authentication
Digital signatures authenticate users by verifying the origin and integrity of messages through cryptographic keys, providing non-repudiation in communication. Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing the secret itself, enhancing privacy during authentication processes. Explore how these technologies transform secure access and identity verification in modern systems.
Privacy
Digital signatures provide authentication and data integrity by verifying the identity of the sender without revealing the content. Zero-knowledge proofs enhance privacy by allowing one party to prove knowledge of specific information without disclosing the information itself, ensuring confidentiality in sensitive transactions. Explore how zero-knowledge proofs revolutionize privacy beyond traditional digital signature capabilities.
Cryptographic Protocols
Digital signatures rely on asymmetric cryptography to authenticate the origin and integrity of a message, ensuring non-repudiation through public-private key pairs. Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to prove knowledge of a secret without revealing the secret itself, enhancing privacy within cryptographic protocols. Explore the nuances between these techniques to understand their unique applications in secure communications.
Source and External Links
What is a Digital Signature? | DigiCert FAQ - A digital signature cryptographically binds a digital signature certificate to a document using public key infrastructure (PKI), validating signer identity and document integrity to ensure the signer is authentic and the content unchanged.
What is a Digital Signature? | Definition from TechTarget - A digital signature is a mathematical method based on public key cryptography that authenticates the origin and integrity of digital documents, providing a legally binding equivalent to handwritten signatures in many countries.
Understanding digital signatures | Docusign - Digital signatures use a pair of cryptographic keys (private key to sign, public key to verify) managed under PKI, ensuring document validity and signer identity by invalidating signatures if the document changes after signing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com