Spatial computing transforms digital interactions by integrating virtual elements into physical environments, enabling immersive experiences through augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies. Human-computer interaction (HCI) focuses on optimizing user interfaces and experiences through studying behaviors, usability, and ergonomic designs to enhance effectiveness and accessibility. Explore the evolving landscape of how spatial computing reshapes human-computer interaction to unlock new possibilities in technology.
Why it is important
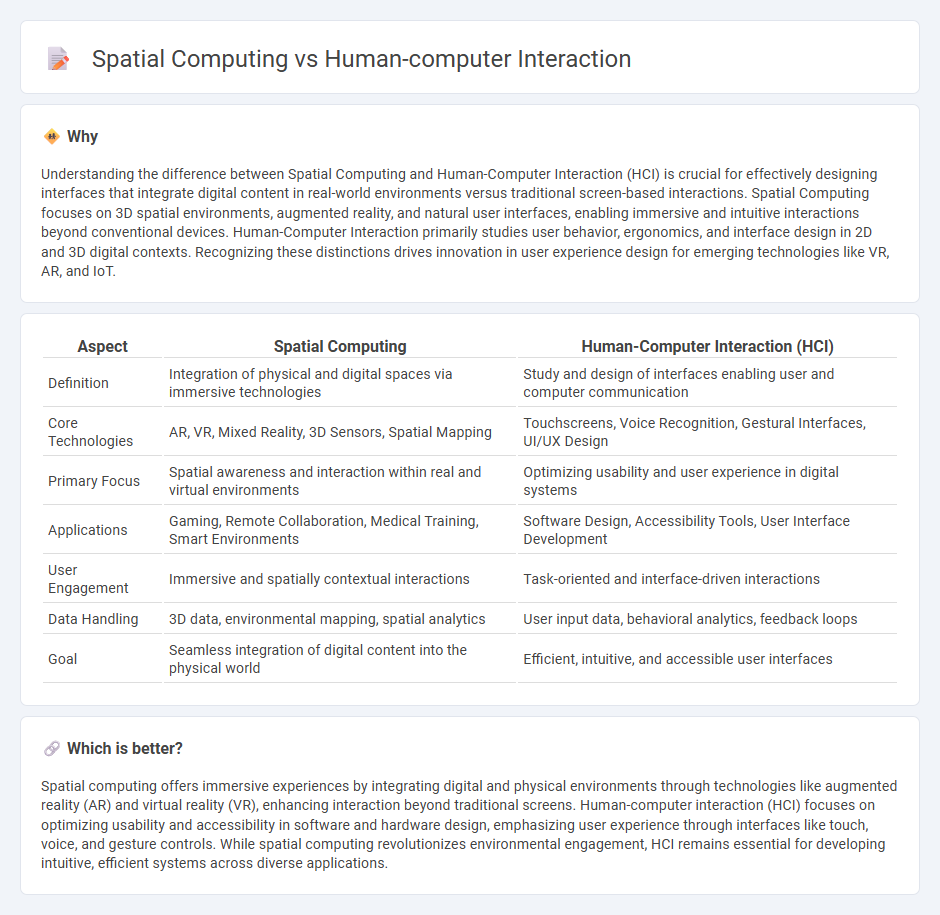
Understanding the difference between Spatial Computing and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is crucial for effectively designing interfaces that integrate digital content in real-world environments versus traditional screen-based interactions. Spatial Computing focuses on 3D spatial environments, augmented reality, and natural user interfaces, enabling immersive and intuitive interactions beyond conventional devices. Human-Computer Interaction primarily studies user behavior, ergonomics, and interface design in 2D and 3D digital contexts. Recognizing these distinctions drives innovation in user experience design for emerging technologies like VR, AR, and IoT.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spatial Computing | Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of physical and digital spaces via immersive technologies | Study and design of interfaces enabling user and computer communication |
| Core Technologies | AR, VR, Mixed Reality, 3D Sensors, Spatial Mapping | Touchscreens, Voice Recognition, Gestural Interfaces, UI/UX Design |
| Primary Focus | Spatial awareness and interaction within real and virtual environments | Optimizing usability and user experience in digital systems |
| Applications | Gaming, Remote Collaboration, Medical Training, Smart Environments | Software Design, Accessibility Tools, User Interface Development |
| User Engagement | Immersive and spatially contextual interactions | Task-oriented and interface-driven interactions |
| Data Handling | 3D data, environmental mapping, spatial analytics | User input data, behavioral analytics, feedback loops |
| Goal | Seamless integration of digital content into the physical world | Efficient, intuitive, and accessible user interfaces |
Which is better?
Spatial computing offers immersive experiences by integrating digital and physical environments through technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), enhancing interaction beyond traditional screens. Human-computer interaction (HCI) focuses on optimizing usability and accessibility in software and hardware design, emphasizing user experience through interfaces like touch, voice, and gesture controls. While spatial computing revolutionizes environmental engagement, HCI remains essential for developing intuitive, efficient systems across diverse applications.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates digital information with the physical environment, enabling more natural and immersive human-computer interaction (HCI) through technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). HCI leverages spatial computing to enhance user experience by interpreting gestures, eye movements, and spatial awareness, facilitating intuitive communication between humans and machines. This synergy drives advancements in fields such as gaming, healthcare, and remote collaboration by creating seamless, context-aware interfaces.
Key Terms
**Human-computer interaction:**
Human-computer interaction (HCI) explores the design and use of computer technology, emphasizing the interfaces between people and computers to enhance usability and user experience. It incorporates aspects like user interface design, cognitive psychology, and ergonomics to create intuitive and efficient interactions. Discover how HCI innovations are transforming digital environments and shaping future technology experiences.
Usability
Human-computer interaction (HCI) emphasizes usability through intuitive interfaces and user-centered design, aiming to minimize cognitive load and maximize accessibility across diverse devices. Spatial computing integrates 3D environments and augmented reality, enhancing usability by leveraging natural gestures, eye tracking, and spatial awareness for immersive user experiences. Explore the latest advancements in usability within HCI and spatial computing to understand how these fields shape future interactions.
Interface design
Human-computer interaction (HCI) emphasizes user-centered interface design principles aimed at optimizing usability and accessibility across traditional screens and input devices. Spatial computing extends these principles by integrating 3D environments and spatial awareness, requiring interfaces that support immersive interaction through gestures, voice, and eye-tracking technologies. Explore the latest trends in interface design to understand how spatial computing is transforming user experiences in HCI.
Source and External Links
Human-computer interaction - Human-computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems, focusing on the design and use of computer technology and interfaces between humans and computers.
Human-Computer Interaction - Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is a multidisciplinary research area focused on designing, evaluating, and implementing interactive systems for effective communication between humans and computers.
Human-Computer Interaction - Human-computer interaction studies how users interact with technology, incorporating insights from computer science, cognitive science, and human factors to enhance user experience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com