Modular construction offers faster build times and enhanced quality control by fabricating sections in a factory setting, reducing onsite labor and weather delays. Stick-built construction allows for greater design flexibility and customization, relying on traditional onsite framing methods that adapt to specific site conditions. Discover the advantages of each method to determine which best suits your real estate project needs.
Why it is important
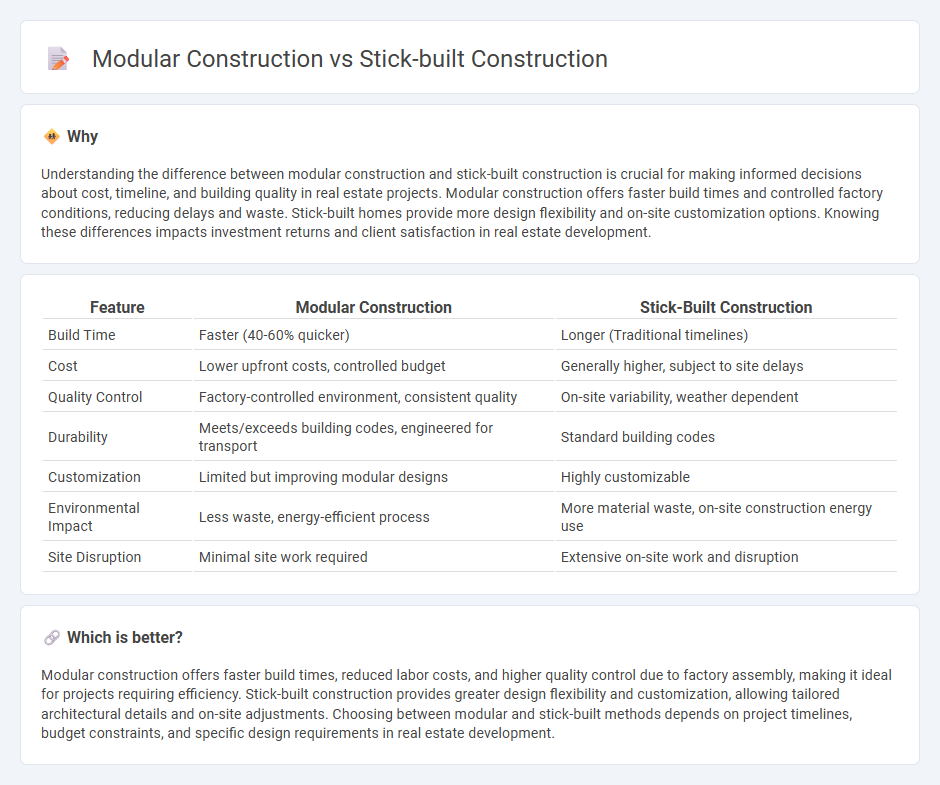
Understanding the difference between modular construction and stick-built construction is crucial for making informed decisions about cost, timeline, and building quality in real estate projects. Modular construction offers faster build times and controlled factory conditions, reducing delays and waste. Stick-built homes provide more design flexibility and on-site customization options. Knowing these differences impacts investment returns and client satisfaction in real estate development.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Construction | Stick-Built Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Build Time | Faster (40-60% quicker) | Longer (Traditional timelines) |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs, controlled budget | Generally higher, subject to site delays |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled environment, consistent quality | On-site variability, weather dependent |
| Durability | Meets/exceeds building codes, engineered for transport | Standard building codes |
| Customization | Limited but improving modular designs | Highly customizable |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste, energy-efficient process | More material waste, on-site construction energy use |
| Site Disruption | Minimal site work required | Extensive on-site work and disruption |
Which is better?
Modular construction offers faster build times, reduced labor costs, and higher quality control due to factory assembly, making it ideal for projects requiring efficiency. Stick-built construction provides greater design flexibility and customization, allowing tailored architectural details and on-site adjustments. Choosing between modular and stick-built methods depends on project timelines, budget constraints, and specific design requirements in real estate development.
Connection
Modular construction and stick-built construction both utilize standardized building materials and comply with local building codes to ensure structural integrity and safety. Modular construction involves assembling pre-fabricated modules off-site, which are then transported and installed on-site, while stick-built construction is traditionally built entirely on-site from individual components. Both methods aim to optimize efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customization options in real estate development projects.
Key Terms
On-site Construction
Stick-built construction involves assembling building components directly on-site, allowing for greater customization and adaptation to unique site conditions. Modular construction fabricates sections in a controlled factory environment, which reduces on-site build time and limits weather-related delays during assembly. Explore further to understand how on-site construction dynamics influence project budgets, timelines, and overall quality in both methods.
Prefabrication
Prefabrication in modular construction allows precise off-site manufacturing of building components, resulting in reduced construction time and minimized material waste compared to traditional stick-built methods. Stick-built construction involves assembling materials on-site piece by piece, which can lead to longer build times and greater exposure to weather-related delays. Explore how prefabrication advances efficiency and sustainability in modern construction by learning more about modular versus stick-built techniques.
Building Codes
Building codes for stick-built construction require on-site inspections at multiple stages, ensuring compliance with localized safety and zoning regulations. Modular construction must meet the same building codes, but modules are pre-fabricated in controlled factory environments and undergo rigorous quality inspections before delivery. Explore detailed code comparison and compliance strategies to optimize your construction project.
Source and External Links
Stick-built construction - A stick-built home is a wooden house constructed largely or entirely on-site, using traditional methods with lumber framing for walls and roof, as opposed to factory-built modular or manufactured homes.
What Does 'Stick Built' Mean and Why Does it Matter? - Stick building is a traditional framing method where lumber is assembled piece-by-piece on-site, allowing flexibility and custom designs, often perceived as higher quality by industry and consumers.
What Is a Stick-built Home? - Stick-built homes offer high customization, can incorporate energy-efficient features, and allow homeowners to build equity since the home is constructed on a permanent foundation, unlike modular or manufactured homes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com