Co-living developments offer shared living spaces designed to foster community and affordability, targeting young professionals and digital nomads seeking flexibility. Multifamily apartments provide private units within larger residential buildings, appealing to families and long-term residents valuing privacy and conventional amenities. Explore more insights on how these housing options shape urban living trends and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
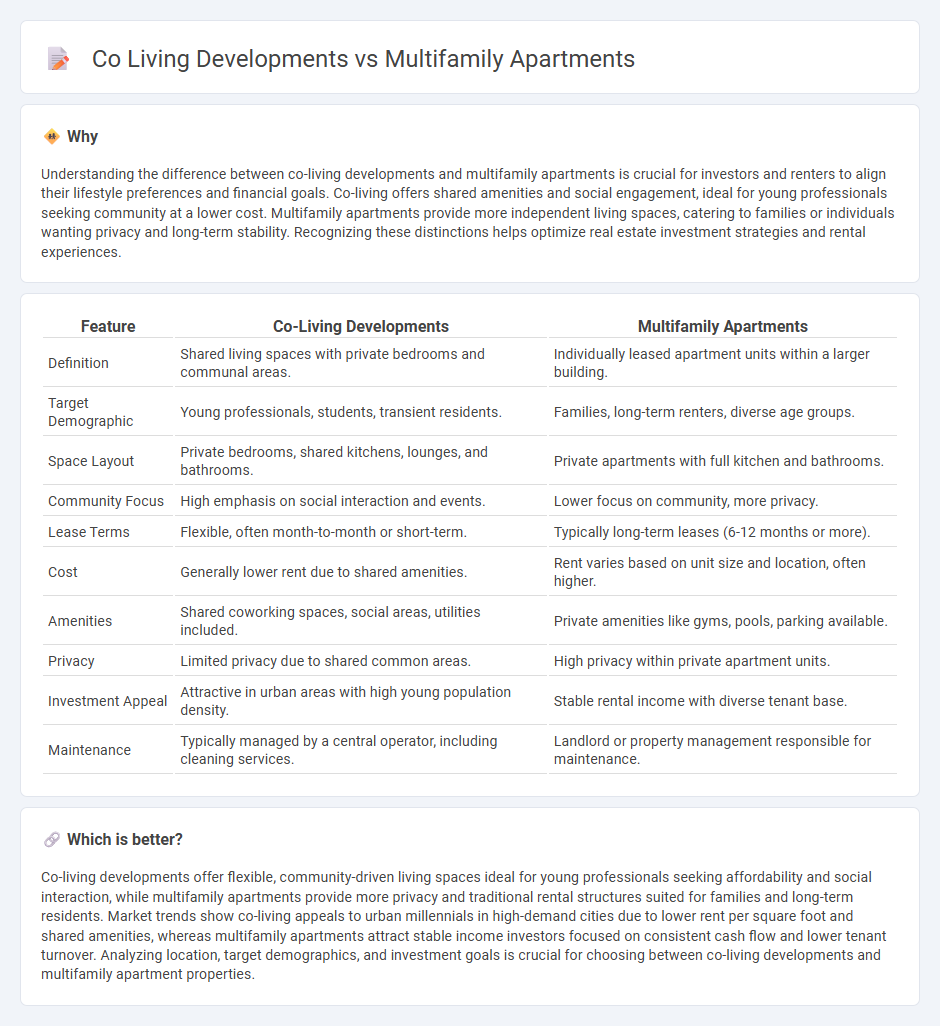
Understanding the difference between co-living developments and multifamily apartments is crucial for investors and renters to align their lifestyle preferences and financial goals. Co-living offers shared amenities and social engagement, ideal for young professionals seeking community at a lower cost. Multifamily apartments provide more independent living spaces, catering to families or individuals wanting privacy and long-term stability. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize real estate investment strategies and rental experiences.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Co-Living Developments | Multifamily Apartments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared living spaces with private bedrooms and communal areas. | Individually leased apartment units within a larger building. |
| Target Demographic | Young professionals, students, transient residents. | Families, long-term renters, diverse age groups. |
| Space Layout | Private bedrooms, shared kitchens, lounges, and bathrooms. | Private apartments with full kitchen and bathrooms. |
| Community Focus | High emphasis on social interaction and events. | Lower focus on community, more privacy. |
| Lease Terms | Flexible, often month-to-month or short-term. | Typically long-term leases (6-12 months or more). |
| Cost | Generally lower rent due to shared amenities. | Rent varies based on unit size and location, often higher. |
| Amenities | Shared coworking spaces, social areas, utilities included. | Private amenities like gyms, pools, parking available. |
| Privacy | Limited privacy due to shared common areas. | High privacy within private apartment units. |
| Investment Appeal | Attractive in urban areas with high young population density. | Stable rental income with diverse tenant base. |
| Maintenance | Typically managed by a central operator, including cleaning services. | Landlord or property management responsible for maintenance. |
Which is better?
Co-living developments offer flexible, community-driven living spaces ideal for young professionals seeking affordability and social interaction, while multifamily apartments provide more privacy and traditional rental structures suited for families and long-term residents. Market trends show co-living appeals to urban millennials in high-demand cities due to lower rent per square foot and shared amenities, whereas multifamily apartments attract stable income investors focused on consistent cash flow and lower tenant turnover. Analyzing location, target demographics, and investment goals is crucial for choosing between co-living developments and multifamily apartment properties.
Connection
Co-living developments and multifamily apartments both address urban housing demand by offering communal living spaces designed for affordability and flexibility. Multifamily apartments provide traditional private units within a single building, while co-living emphasizes shared amenities and social interaction among residents. This connection drives innovation in residential design, enhancing community engagement and optimizing space utilization in densely populated cities.
Key Terms
Lease Structure
Multifamily apartments typically offer traditional lease structures with fixed terms ranging from six to twelve months, providing tenants with long-term stability and predictable payments. Co-living developments adopt flexible lease agreements that often include shorter terms, room rentals, and shared amenities, catering to transient populations such as young professionals and students. Explore the key differences in lease structures to determine the best living arrangement for your lifestyle and investment goals.
Common Areas
Multifamily apartments typically provide private living spaces with limited shared amenities, focusing on individual unit comfort rather than extensive common areas. Co-living developments emphasize communal living with expansive shared spaces such as kitchens, lounges, and work areas designed to foster social interaction and community engagement. Discover how the design and functionality of common areas impact resident experiences in both housing models.
Tenant Demographics
Multifamily apartments predominantly attract established renters such as families and professionals seeking long-term leases and stable living environments. Co-living developments appeal mainly to younger demographics, including millennials and remote workers, who prioritize affordability, flexibility, and community-oriented spaces. Explore further to understand how these tenant demographics shape the future of residential property markets.
Source and External Links
Multifamily residential - Wikipedia - Multifamily residential, also known as multidwelling unit (MDU), refers to housing where multiple separate housing units exist within one building or complex, including apartments and condominiums, with units side-by-side or stacked vertically.
What is multifamily housing and what are the benefits? - Multifamily housing includes residential real estate with two or more household units such as apartments and condominiums, often rented to tenants sharing walls and communal spaces, and ranging from small buildings to large high-rises.
Multifamily Housing - Home for All San Mateo County - Multifamily housing can vary from low-rise duplexes to high-rise apartments, providing medium to high density dwelling options that are essential for affordable housing and can include amenities and resident services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com