Single family rentals offer flexible living spaces ideal for families seeking privacy and customization, while senior housing provides specialized amenities and medical support tailored to older adults' needs. Market trends show increasing demand for single family rentals in suburban areas, whereas senior housing is expanding rapidly due to aging populations worldwide. Discover more about the benefits and challenges of each housing option to make an informed real estate decision.
Why it is important
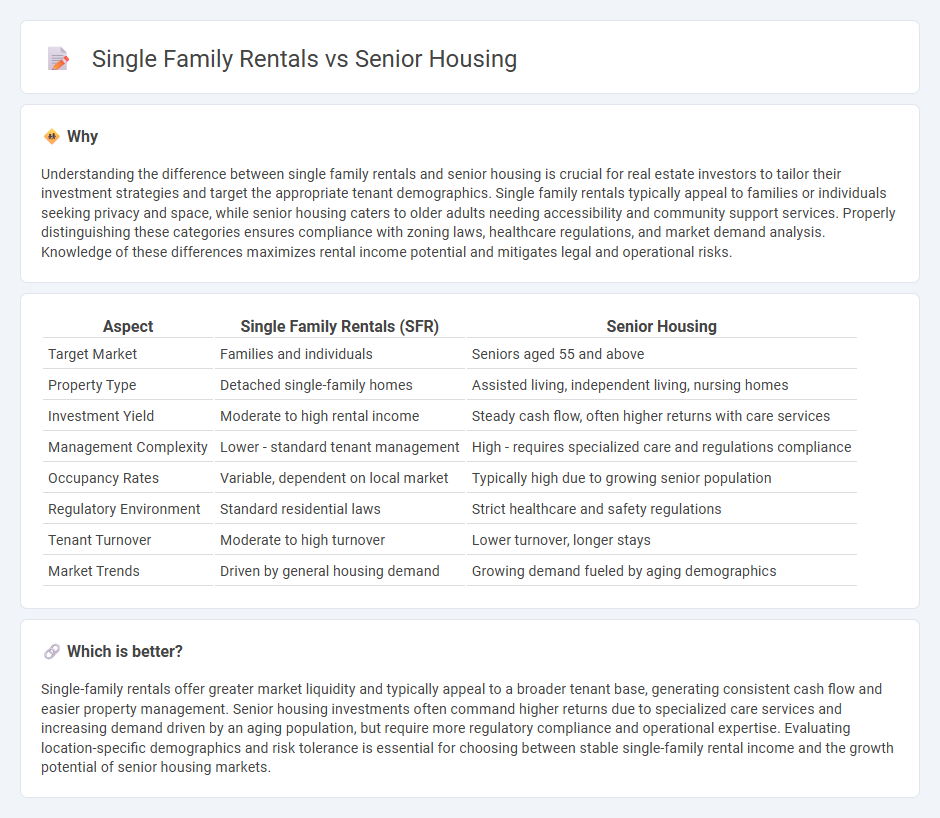
Understanding the difference between single family rentals and senior housing is crucial for real estate investors to tailor their investment strategies and target the appropriate tenant demographics. Single family rentals typically appeal to families or individuals seeking privacy and space, while senior housing caters to older adults needing accessibility and community support services. Properly distinguishing these categories ensures compliance with zoning laws, healthcare regulations, and market demand analysis. Knowledge of these differences maximizes rental income potential and mitigates legal and operational risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Single Family Rentals (SFR) | Senior Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Target Market | Families and individuals | Seniors aged 55 and above |
| Property Type | Detached single-family homes | Assisted living, independent living, nursing homes |
| Investment Yield | Moderate to high rental income | Steady cash flow, often higher returns with care services |
| Management Complexity | Lower - standard tenant management | High - requires specialized care and regulations compliance |
| Occupancy Rates | Variable, dependent on local market | Typically high due to growing senior population |
| Regulatory Environment | Standard residential laws | Strict healthcare and safety regulations |
| Tenant Turnover | Moderate to high turnover | Lower turnover, longer stays |
| Market Trends | Driven by general housing demand | Growing demand fueled by aging demographics |
Which is better?
Single-family rentals offer greater market liquidity and typically appeal to a broader tenant base, generating consistent cash flow and easier property management. Senior housing investments often command higher returns due to specialized care services and increasing demand driven by an aging population, but require more regulatory compliance and operational expertise. Evaluating location-specific demographics and risk tolerance is essential for choosing between stable single-family rental income and the growth potential of senior housing markets.
Connection
Single family rentals and senior housing intersect through the increasing demand for accessible, affordable living options tailored to aging populations. Both sectors benefit from suburban locations that offer space, safety, and community amenities preferred by seniors seeking independent lifestyles. Investment trends show growing capital flow into these categories, driven by demographic shifts such as the aging Baby Boomer generation and rising homeownership barriers.
Key Terms
Occupancy Rate
Senior housing consistently achieves higher occupancy rates compared to single family rentals, often exceeding 90% due to specialized services and community appeal tailored to aging populations. Single family rentals typically experience more variability in occupancy, influenced by broader market conditions and tenant turnover. Explore detailed data and trends to understand how occupancy rates impact investment strategies in these housing sectors.
Lease Structure
Senior housing leases often feature flexible terms tailored to residents' unique needs, including service fees and optional care packages that impact monthly costs. Single family rentals typically have fixed lease durations, usually one year, with consistent rent payments and fewer variable charges. Explore how lease structures influence tenant experience and investment returns in both housing sectors.
Resident Demographics
Senior housing primarily serves adults aged 65 and older, offering tailored amenities and healthcare support suited to their lifestyle and health needs. In contrast, single-family rentals attract a diverse demographic, including young professionals, families with children, and retirees, reflecting varied housing preferences and economic backgrounds. Discover more about how resident demographics influence housing development and investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Affordable Housing - New York Foundation for Senior Citizens - Provides subsidized housing options for older adults to age in place, offering social services and supportive environments.
Senior Housing - HPD - Offers affordable rental apartments for seniors through the Senior Affordable Rental Apartments (SARA) program, providing low-interest loans for housing development.
Housing | Office for the Aging - NY.gov - Lists various housing options for older adults, including independent living, assisted living, and skilled nursing facilities across New York State.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com