Last mile logistics hubs are strategically located distribution centers designed to expedite the delivery of goods to end consumers, optimizing urban supply chains and reducing transit times. Cold storage facilities specialize in preserving perishable products such as food and pharmaceuticals by maintaining controlled temperature environments, ensuring product freshness and safety during storage and transport. Explore how these distinct real estate assets drive efficiency in supply chain management and meet diverse industry needs.
Why it is important
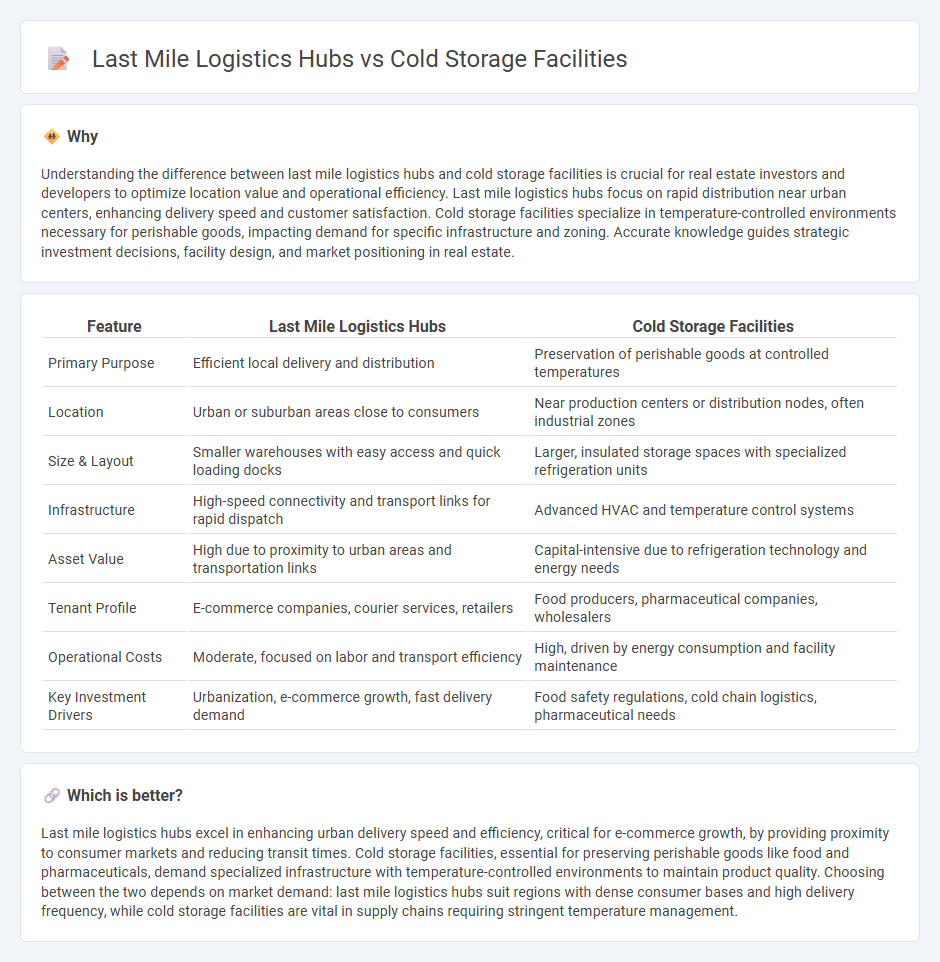
Understanding the difference between last mile logistics hubs and cold storage facilities is crucial for real estate investors and developers to optimize location value and operational efficiency. Last mile logistics hubs focus on rapid distribution near urban centers, enhancing delivery speed and customer satisfaction. Cold storage facilities specialize in temperature-controlled environments necessary for perishable goods, impacting demand for specific infrastructure and zoning. Accurate knowledge guides strategic investment decisions, facility design, and market positioning in real estate.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Last Mile Logistics Hubs | Cold Storage Facilities |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Efficient local delivery and distribution | Preservation of perishable goods at controlled temperatures |
| Location | Urban or suburban areas close to consumers | Near production centers or distribution nodes, often industrial zones |
| Size & Layout | Smaller warehouses with easy access and quick loading docks | Larger, insulated storage spaces with specialized refrigeration units |
| Infrastructure | High-speed connectivity and transport links for rapid dispatch | Advanced HVAC and temperature control systems |
| Asset Value | High due to proximity to urban areas and transportation links | Capital-intensive due to refrigeration technology and energy needs |
| Tenant Profile | E-commerce companies, courier services, retailers | Food producers, pharmaceutical companies, wholesalers |
| Operational Costs | Moderate, focused on labor and transport efficiency | High, driven by energy consumption and facility maintenance |
| Key Investment Drivers | Urbanization, e-commerce growth, fast delivery demand | Food safety regulations, cold chain logistics, pharmaceutical needs |
Which is better?
Last mile logistics hubs excel in enhancing urban delivery speed and efficiency, critical for e-commerce growth, by providing proximity to consumer markets and reducing transit times. Cold storage facilities, essential for preserving perishable goods like food and pharmaceuticals, demand specialized infrastructure with temperature-controlled environments to maintain product quality. Choosing between the two depends on market demand: last mile logistics hubs suit regions with dense consumer bases and high delivery frequency, while cold storage facilities are vital in supply chains requiring stringent temperature management.
Connection
Last mile logistics hubs and cold storage facilities are interconnected through temperature-controlled supply chains that ensure perishable goods, such as pharmaceuticals and fresh food, maintain their quality during transit. Real estate developments integrate cold storage units within or near logistics hubs to optimize distribution efficiency and reduce delivery times for temperature-sensitive products. Strategic placement of these facilities enhances urban logistics networks, driving demand for specialized industrial real estate spaces.
Key Terms
Temperature Control
Cold storage facilities maintain precise temperature ranges from -25degC to 5degC to ensure perishable goods like pharmaceuticals, seafood, and fresh produce remain fresh. Last mile logistics hubs primarily focus on rapid, temperature-monitored transfers within 2-8degC for cold chain compliance during final delivery stages. Explore the latest innovations in temperature control technologies to enhance supply chain efficiency and product quality.
Proximity to End-User
Cold storage facilities require strategic placement near production or distribution centers to maintain product integrity, while last mile logistics hubs prioritize proximity to end-users to ensure rapid delivery. The closer last mile hubs are to consumers, the faster and more efficient the final delivery, reducing transit time and enhancing customer satisfaction. Explore detailed comparisons on how location impacts efficiency for cold storage and last mile logistics solutions.
Inventory Turnover
Cold storage facilities enhance inventory turnover by preserving perishable goods, reducing spoilage, and enabling faster product rotation. Last mile logistics hubs streamline distribution by minimizing delivery time and improving order accuracy, which accelerates inventory replenishment cycles. Discover the key strategies to optimize inventory turnover through effective use of cold storage and last mile logistics hubs.
Source and External Links
Cold Storage Warehouse - A cold storage warehouse is a specialized facility equipped with temperature-controlled environments to store perishable goods efficiently.
Cold Storage Warehouses - This guide explains how cold storage warehouses maintain specific temperatures using insulation and HVAC systems to preserve sensitive goods.
Cold Storage Facilities - Cold storage facilities use advanced refrigeration systems to maintain low temperatures for storing perishable goods in various industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com