Adaptive reuse transforms existing buildings for new purposes while preserving their historic or architectural significance, often reducing environmental impact and construction costs. Repurposing involves modifying structures or materials for different uses without necessarily maintaining original features, emphasizing flexibility and functionality. Explore the advantages and distinctions between adaptive reuse and repurposing to optimize your real estate investments.
Why it is important
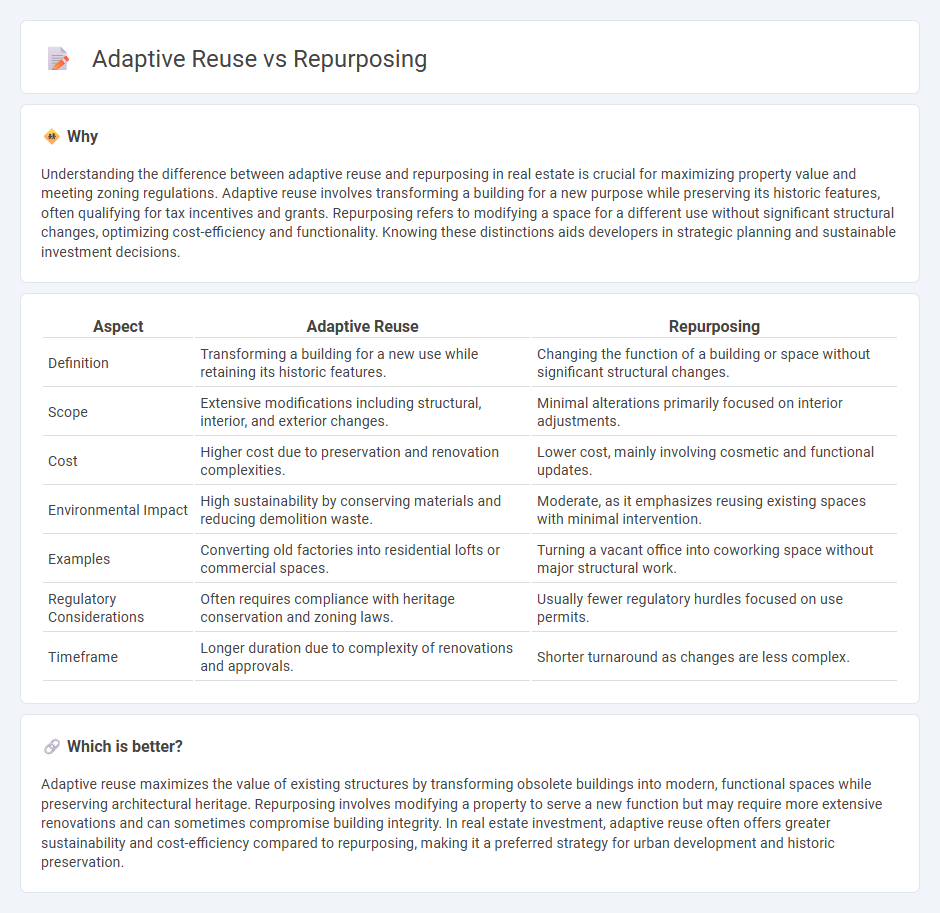
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and repurposing in real estate is crucial for maximizing property value and meeting zoning regulations. Adaptive reuse involves transforming a building for a new purpose while preserving its historic features, often qualifying for tax incentives and grants. Repurposing refers to modifying a space for a different use without significant structural changes, optimizing cost-efficiency and functionality. Knowing these distinctions aids developers in strategic planning and sustainable investment decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse | Repurposing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming a building for a new use while retaining its historic features. | Changing the function of a building or space without significant structural changes. |
| Scope | Extensive modifications including structural, interior, and exterior changes. | Minimal alterations primarily focused on interior adjustments. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to preservation and renovation complexities. | Lower cost, mainly involving cosmetic and functional updates. |
| Environmental Impact | High sustainability by conserving materials and reducing demolition waste. | Moderate, as it emphasizes reusing existing spaces with minimal intervention. |
| Examples | Converting old factories into residential lofts or commercial spaces. | Turning a vacant office into coworking space without major structural work. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Often requires compliance with heritage conservation and zoning laws. | Usually fewer regulatory hurdles focused on use permits. |
| Timeframe | Longer duration due to complexity of renovations and approvals. | Shorter turnaround as changes are less complex. |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse maximizes the value of existing structures by transforming obsolete buildings into modern, functional spaces while preserving architectural heritage. Repurposing involves modifying a property to serve a new function but may require more extensive renovations and can sometimes compromise building integrity. In real estate investment, adaptive reuse often offers greater sustainability and cost-efficiency compared to repurposing, making it a preferred strategy for urban development and historic preservation.
Connection
Adaptive reuse and repurposing in real estate both involve transforming existing structures to serve new functions, optimizing resource efficiency and reducing construction waste. These strategies preserve architectural heritage while meeting contemporary market demands, enhancing property value and sustainability. They contribute to urban revitalization by converting obsolete buildings into vibrant residential, commercial, or mixed-use spaces.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in distinguishing repurposing from adaptive reuse by determining permissible land uses and building modifications within specific zones. Repurposing often requires compliance with existing zoning laws, while adaptive reuse may necessitate zoning variances or changes to accommodate new functions in old structures. Discover how zoning impacts redevelopment strategies and compliance requirements in urban planning.
Building Code Compliance
Repurposing of buildings involves changing a building's function without extensive structural modifications, whereas adaptive reuse entails significant alterations to meet updated building codes and new usage requirements. Building code compliance in adaptive reuse often requires upgrades to fire safety systems, accessibility standards, and structural reinforcements to ensure occupant safety and regulatory adherence. Explore deeper insights on how these processes impact design strategies and regulatory challenges in construction projects.
Historic Preservation
Repurposing involves modifying historic structures for entirely new functions while Adaptive Reuse retains a building's historic character by integrating new uses with original elements, preserving architectural heritage and cultural significance. Both approaches support sustainable development by extending building lifespans, reducing waste, and maintaining the historic fabric of communities. Explore more about how these strategies balance innovation and preservation in historic preservation projects.
Source and External Links
The Difference Between Upcycling and Repurposing - Repurposing means using an item again but for a different purpose, such as turning old clothing into rags or an old fridge into a wine cooler, helping save money and reduce waste by reusing what would otherwise be discarded.
Repurposing - Wikipedia - Repurposing is the process of transforming an object with one functional use into another use, often involving materials considered junk or obsolete, such as using tires for building insulation or worn clothes as rags.
Repurposing Content: A 101 Guide - In content marketing, repurposing refers to reusing existing content by refreshing, rewriting, or converting it into new formats to reach different audiences and extend the value of the original assets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com