Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused urban land to increase housing density while preserving existing neighborhood character, often supported by local zoning policies and urban planning initiatives. Gentrification describes the socioeconomic shift where an influx of higher-income residents leads to rising property values and displacement of lower-income communities, frequently observed in historically marginalized urban areas. Explore the nuances and impacts of both processes to better understand urban transformation dynamics.
Why it is important
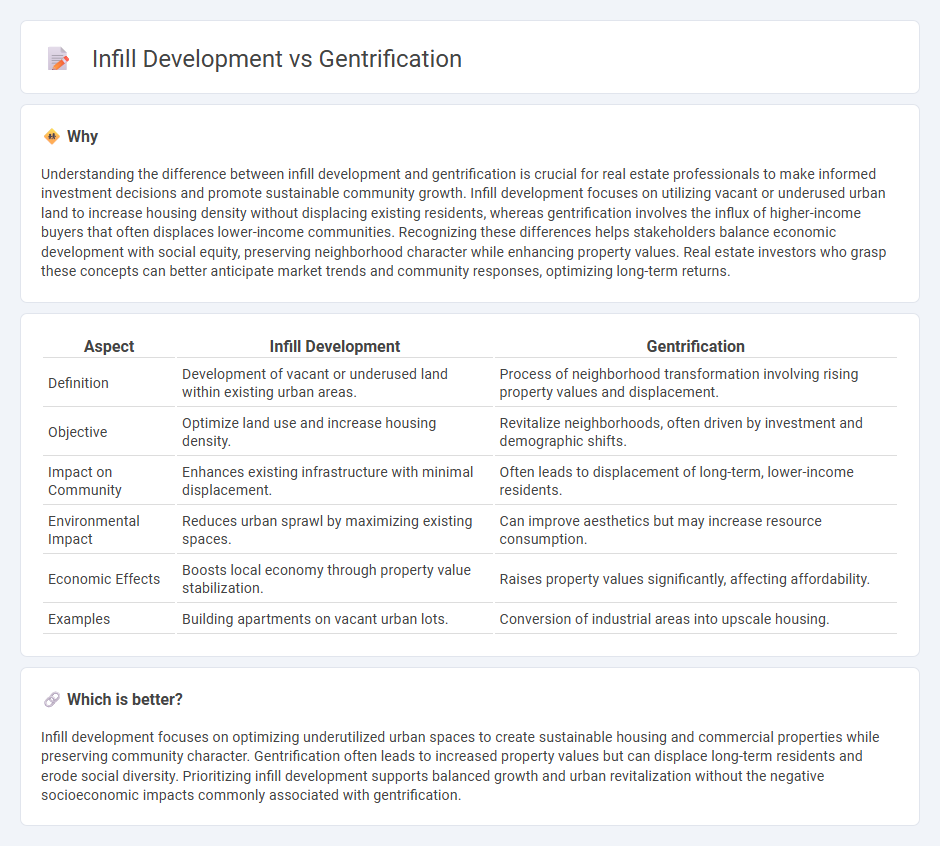
Understanding the difference between infill development and gentrification is crucial for real estate professionals to make informed investment decisions and promote sustainable community growth. Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused urban land to increase housing density without displacing existing residents, whereas gentrification involves the influx of higher-income buyers that often displaces lower-income communities. Recognizing these differences helps stakeholders balance economic development with social equity, preserving neighborhood character while enhancing property values. Real estate investors who grasp these concepts can better anticipate market trends and community responses, optimizing long-term returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Infill Development | Gentrification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development of vacant or underused land within existing urban areas. | Process of neighborhood transformation involving rising property values and displacement. |
| Objective | Optimize land use and increase housing density. | Revitalize neighborhoods, often driven by investment and demographic shifts. |
| Impact on Community | Enhances existing infrastructure with minimal displacement. | Often leads to displacement of long-term, lower-income residents. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces urban sprawl by maximizing existing spaces. | Can improve aesthetics but may increase resource consumption. |
| Economic Effects | Boosts local economy through property value stabilization. | Raises property values significantly, affecting affordability. |
| Examples | Building apartments on vacant urban lots. | Conversion of industrial areas into upscale housing. |
Which is better?
Infill development focuses on optimizing underutilized urban spaces to create sustainable housing and commercial properties while preserving community character. Gentrification often leads to increased property values but can displace long-term residents and erode social diversity. Prioritizing infill development supports balanced growth and urban revitalization without the negative socioeconomic impacts commonly associated with gentrification.
Connection
Infill development often drives gentrification by attracting higher-income residents to underutilized or vacant urban spaces, leading to increased property values and displacement of long-term, lower-income residents. The redevelopment of centrally located parcels promotes densification and modernization, which reshapes neighborhood demographics and local economies. This connection highlights the complex interplay between urban growth strategies and social equity challenges in real estate markets.
Key Terms
Displacement
Gentrification often leads to the displacement of long-term residents due to rising property values and increased living costs, disproportionately affecting low-income communities. Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused urban land to increase density, potentially reducing displacement by preserving existing neighborhoods. Explore how strategic urban planning balances growth with community stability to learn more.
Urban Renewal
Gentrification reshapes urban neighborhoods by increasing property values and attracting higher-income residents, often displacing long-term communities, while infill development maximizes the use of underutilized land within existing urban areas to meet housing demands without extensive displacement. Urban renewal strategies leveraging infill development promote sustainable growth, improved infrastructure, and enhanced community services, contrasting with gentrification's potential socio-economic disruptions. Explore more about how urban renewal balances these approaches to create inclusive, thriving cities.
Density
Gentrification often leads to increased density through the renovation of existing structures and the influx of higher-income residents, which can displace lower-income communities. Infill development increases urban density by building on vacant or underutilized land within existing neighborhoods without necessarily changing the socio-economic makeup. Explore more to understand how these approaches impact urban density and community dynamics.
Source and External Links
Gentrification - Gentrification is the process whereby the character of a neighborhood changes due to the influx of more affluent residents and investment, often controversial due to its impact on existing residents.
Understanding Gentrification and Displacement - This page explains gentrification as a process affecting historically marginalized neighborhoods with higher-income residents moving in, leading to increased housing costs and displacement.
What Are Gentrification and Displacement - Gentrification involves economic and demographic changes in historically disinvested neighborhoods through real estate investment and the influx of higher-income residents, affecting community dynamics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com