Adaptive reuse projects transform existing buildings into functional spaces, preserving architectural heritage while reducing environmental impact. Ground-up development involves constructing new structures from the foundation, offering complete design flexibility and modern amenities. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to determine the best strategy for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse projects and ground-up development is crucial because adaptive reuse transforms existing structures, often reducing costs and environmental impact, while ground-up development involves building from scratch, offering complete design freedom and potentially higher long-term value. Adaptive reuse can preserve historic character and leverage existing infrastructure, making it attractive in urban areas with zoning restrictions. Ground-up development allows for modern, energy-efficient designs tailored to specific needs, which can maximize functionality and market appeal. Knowing these distinctions helps investors, developers, and planners make informed decisions that align with financial goals, sustainability, and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
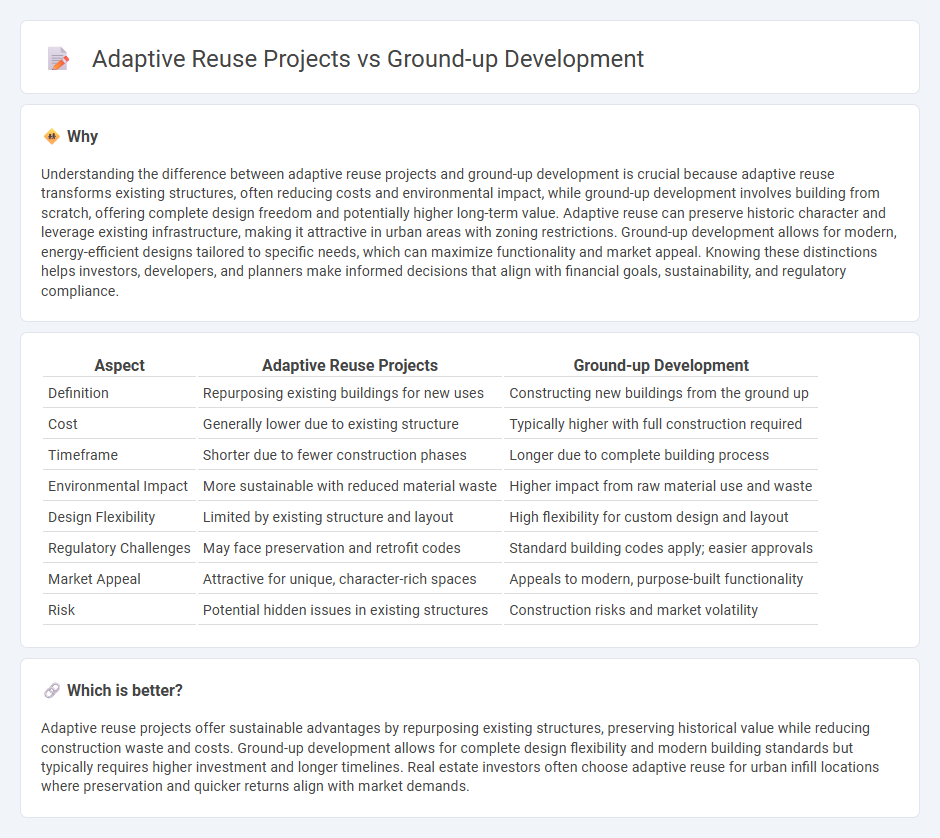
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse Projects | Ground-up Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Constructing new buildings from the ground up |
| Cost | Generally lower due to existing structure | Typically higher with full construction required |
| Timeframe | Shorter due to fewer construction phases | Longer due to complete building process |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable with reduced material waste | Higher impact from raw material use and waste |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by existing structure and layout | High flexibility for custom design and layout |
| Regulatory Challenges | May face preservation and retrofit codes | Standard building codes apply; easier approvals |
| Market Appeal | Attractive for unique, character-rich spaces | Appeals to modern, purpose-built functionality |
| Risk | Potential hidden issues in existing structures | Construction risks and market volatility |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse projects offer sustainable advantages by repurposing existing structures, preserving historical value while reducing construction waste and costs. Ground-up development allows for complete design flexibility and modern building standards but typically requires higher investment and longer timelines. Real estate investors often choose adaptive reuse for urban infill locations where preservation and quicker returns align with market demands.
Connection
Adaptive reuse projects and ground-up development both contribute to urban revitalization by optimizing land use and meeting evolving market demands. Adaptive reuse transforms existing structures into functional spaces, while ground-up development creates new buildings tailored to current needs, together enhancing real estate value and sustainability. Both approaches leverage strategic planning and design to address housing shortages and promote economic growth in dynamic urban environments.
Key Terms
Entitlements
Ground-up development projects require securing entitlements from scratch, including zoning approvals, permits, and environmental reviews, which can be time-consuming and complex. Adaptive reuse projects often benefit from existing entitlements or can leverage historic preservation incentives, but must navigate restrictions tied to the original structure's status and current zoning codes. Explore how strategic entitlement management can streamline your development process and unlock value in both project types.
Zoning
Zoning regulations play a critical role in both ground-up development and adaptive reuse projects by dictating land use, building height, density, and setbacks. Ground-up development often faces strict compliance with current zoning codes, while adaptive reuse projects may seek variances or special permits to repurpose existing structures. Explore how zoning impacts project feasibility, timelines, and costs to make informed development decisions.
Site Selection
Site selection for ground-up development prioritizes undeveloped land with optimal zoning, infrastructure access, and minimal environmental constraints to maximize design flexibility and construction efficiency. In adaptive reuse projects, the emphasis is on existing structures' location advantages, historic significance, and integration with urban fabric, balancing preservation goals with functional upgrades. Explore comprehensive strategies to identify the best site for your next project's success.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Ground Up Development Process - Ground up real estate development involves constructing a new building or development on a vacant or undeveloped piece of land, starting from scratch.
What Are the Stages of Ground-Up Construction? - Ground-up construction is a process that begins with a vacant site and ends with a new, ready-to-use structure, managed by the project owner and general contractor.
Ground-up Development - Ground-up development involves constructing a real estate asset from scratch, starting with raw land or completely tearing down existing structures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com