Real estate crowdfunding allows investors to pool funds online to purchase properties, offering lower entry costs and diversified portfolios compared to direct property ownership. Direct ownership provides full control over the property and potential tax benefits but requires significant capital and management responsibilities. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to determine the best investment strategy for you.
Why it is important
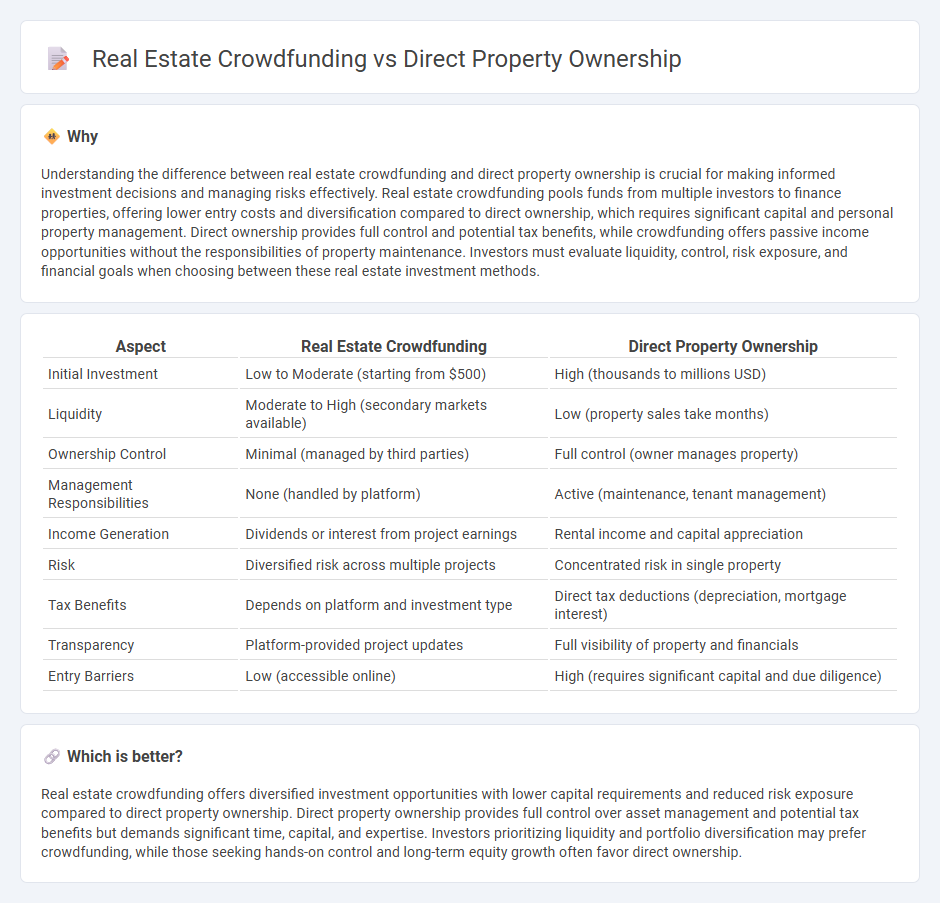
Understanding the difference between real estate crowdfunding and direct property ownership is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing risks effectively. Real estate crowdfunding pools funds from multiple investors to finance properties, offering lower entry costs and diversification compared to direct ownership, which requires significant capital and personal property management. Direct ownership provides full control and potential tax benefits, while crowdfunding offers passive income opportunities without the responsibilities of property maintenance. Investors must evaluate liquidity, control, risk exposure, and financial goals when choosing between these real estate investment methods.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Real Estate Crowdfunding | Direct Property Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to Moderate (starting from $500) | High (thousands to millions USD) |
| Liquidity | Moderate to High (secondary markets available) | Low (property sales take months) |
| Ownership Control | Minimal (managed by third parties) | Full control (owner manages property) |
| Management Responsibilities | None (handled by platform) | Active (maintenance, tenant management) |
| Income Generation | Dividends or interest from project earnings | Rental income and capital appreciation |
| Risk | Diversified risk across multiple projects | Concentrated risk in single property |
| Tax Benefits | Depends on platform and investment type | Direct tax deductions (depreciation, mortgage interest) |
| Transparency | Platform-provided project updates | Full visibility of property and financials |
| Entry Barriers | Low (accessible online) | High (requires significant capital and due diligence) |
Which is better?
Real estate crowdfunding offers diversified investment opportunities with lower capital requirements and reduced risk exposure compared to direct property ownership. Direct property ownership provides full control over asset management and potential tax benefits but demands significant time, capital, and expertise. Investors prioritizing liquidity and portfolio diversification may prefer crowdfunding, while those seeking hands-on control and long-term equity growth often favor direct ownership.
Connection
Real estate crowdfunding and direct property ownership both provide avenues for investing in real estate, allowing investors to gain exposure to property markets without traditional barriers. Crowdfunding platforms pool funds from multiple investors to acquire or develop properties, while direct ownership involves purchasing and managing individual properties outright. Both methods offer potential returns through rental income and property appreciation, but differ in terms of control, liquidity, and required capital investment.
Key Terms
Title Deed
Direct property ownership grants investors full control and legal title via a title deed, ensuring exclusive rights to the property and straightforward asset transfer. Real estate crowdfunding offers fractional ownership without issuing individual title deeds, relying on pooled funds and contractual agreements to secure investor stakes. Explore the distinctions further to understand how title deed implications impact your investment choice.
Fractional Ownership
Direct property ownership involves purchasing entire real estate assets, granting full control, equity, and responsibilities like maintenance and financing. Real estate crowdfunding offers fractional ownership, allowing multiple investors to pool funds and share in property profits and risks with lower capital commitment and minimal management duties. Explore the benefits and challenges of fractional ownership to make informed investment decisions.
Platform Fees
Direct property ownership typically involves upfront costs, such as down payments, closing fees, and ongoing expenses like maintenance and property management fees. Real estate crowdfunding platforms charge platform fees ranging from 1% to 3% of the invested amount, which cover administrative and operational costs but eliminate the need for direct management responsibilities. Explore more details on how platform fees impact your overall real estate investment returns.
Source and External Links
The Different Types of Property Ownership - This article discusses the concept of direct property ownership, involving the purchase and management of physical real estate assets like houses or commercial buildings, offering total control and potential for rental income and capital gains.
Real Estate Syndication vs. Direct Ownership - This article compares real estate syndication and direct ownership, highlighting that direct ownership involves purchasing and managing properties independently, while syndication involves pooled investments managed by professionals.
DST vs. Direct Property Ownership - This article explores the differences between direct property ownership and Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs), focusing on control versus passive investment strategies for tax-efficient real estate investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com