Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property prices based on market demand, competitor rates, and seasonal trends to maximize revenue. Cost-plus pricing calculates prices by adding a fixed percentage or amount to the total cost of property development or acquisition, ensuring profitability. Explore how these pricing strategies impact real estate investment returns and sales efficiency.
Why it is important
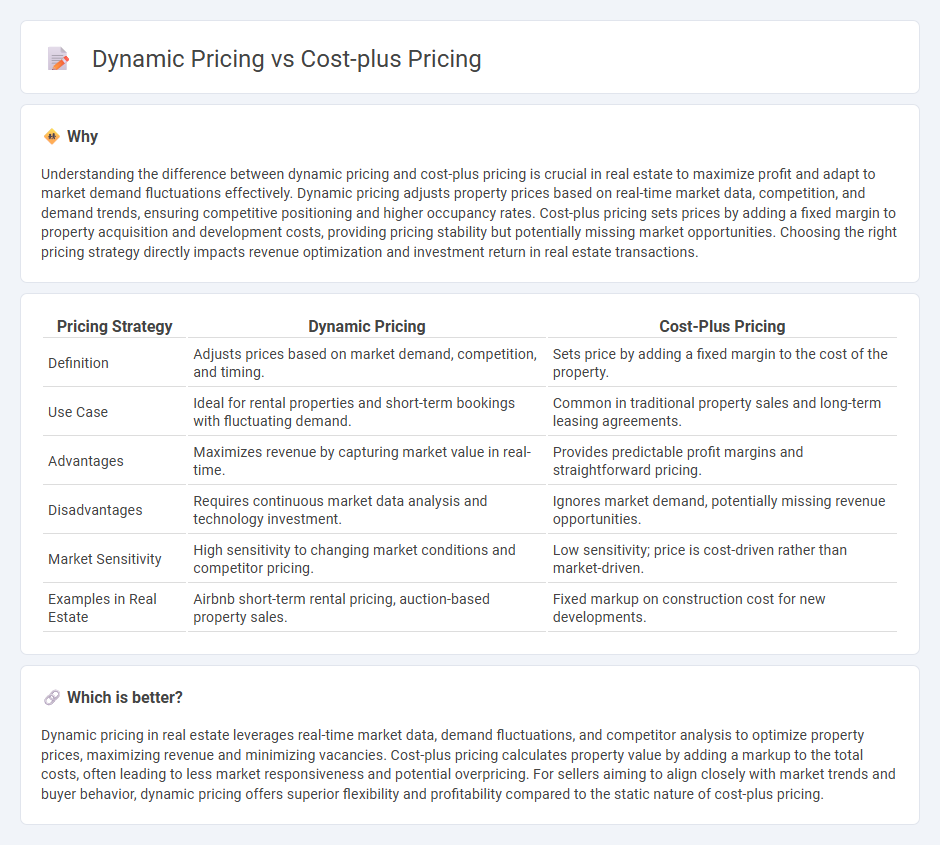
Understanding the difference between dynamic pricing and cost-plus pricing is crucial in real estate to maximize profit and adapt to market demand fluctuations effectively. Dynamic pricing adjusts property prices based on real-time market data, competition, and demand trends, ensuring competitive positioning and higher occupancy rates. Cost-plus pricing sets prices by adding a fixed margin to property acquisition and development costs, providing pricing stability but potentially missing market opportunities. Choosing the right pricing strategy directly impacts revenue optimization and investment return in real estate transactions.
Comparison Table
| Pricing Strategy | Dynamic Pricing | Cost-Plus Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusts prices based on market demand, competition, and timing. | Sets price by adding a fixed margin to the cost of the property. |
| Use Case | Ideal for rental properties and short-term bookings with fluctuating demand. | Common in traditional property sales and long-term leasing agreements. |
| Advantages | Maximizes revenue by capturing market value in real-time. | Provides predictable profit margins and straightforward pricing. |
| Disadvantages | Requires continuous market data analysis and technology investment. | Ignores market demand, potentially missing revenue opportunities. |
| Market Sensitivity | High sensitivity to changing market conditions and competitor pricing. | Low sensitivity; price is cost-driven rather than market-driven. |
| Examples in Real Estate | Airbnb short-term rental pricing, auction-based property sales. | Fixed markup on construction cost for new developments. |
Which is better?
Dynamic pricing in real estate leverages real-time market data, demand fluctuations, and competitor analysis to optimize property prices, maximizing revenue and minimizing vacancies. Cost-plus pricing calculates property value by adding a markup to the total costs, often leading to less market responsiveness and potential overpricing. For sellers aiming to align closely with market trends and buyer behavior, dynamic pricing offers superior flexibility and profitability compared to the static nature of cost-plus pricing.
Connection
Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property prices based on real-time market demand, supply conditions, and competitor analysis, while cost-plus pricing sets prices by adding a fixed margin to the total property development or acquisition costs. Both pricing strategies integrate cost factors, but dynamic pricing incorporates market fluctuations and buyer behavior, resulting in optimized revenue potential. Leveraging cost data within dynamic pricing models enhances accuracy and profitability in property value assessments.
Key Terms
Construction Costs (Cost-plus pricing)
Cost-plus pricing in construction determines the project price by adding a fixed percentage or fee to the actual construction costs, ensuring coverage of materials, labor, and overhead while maintaining profit margins. This method provides transparency and reduces financial risk during fluctuating material prices but can limit competitive pricing flexibility. Explore further to understand how cost-plus pricing can optimize budgeting and risk management in construction projects.
Market Demand (Dynamic pricing)
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor prices, and customer behavior, optimizing revenue during peak and off-peak periods. In contrast, cost-plus pricing sets prices by adding a fixed markup to production costs, ignoring fluctuations in market demand and competitor strategies. Explore how leveraging market demand data for dynamic pricing can significantly boost profitability and competitiveness.
Price Adjustment Mechanism
Cost-plus pricing calculates prices by adding a fixed markup to production costs, ensuring predictable profit margins and straightforward price adjustments based on cost fluctuations. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time according to market demand, competitor actions, or inventory levels, enabling flexible responses to external factors but requiring sophisticated data analytics and algorithms. Explore detailed comparisons of price adjustment mechanisms to determine the optimal strategy for your business goals.
Source and External Links
Cost-Plus Pricing Strategy | Formula + Calculator - Wall Street Prep - Cost-plus pricing sets the selling price by adding a fixed markup percentage to the total cost per unit, ensuring all costs are covered and a target profit margin is met.
Cost-plus pricing - Wikipedia - This pricing method determines the sale price by calculating the total cost of production, dividing by the number of units to get unit cost, and then adding a fixed markup percentage to achieve the desired rate of return.
What is Cost Plus Pricing? - DealHub - Cost-plus pricing is a straightforward approach where businesses add a set profit margin to their product or service costs, making it easy to anticipate profitability but not always responsive to customer demand or market competition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com