Agrihood communities integrate sustainable farming and green spaces within residential areas, promoting local food production and environmental stewardship. Suburban subdivisions typically prioritize uniform housing developments with limited access to agricultural elements and communal green infrastructure. Explore how these distinct real estate models impact lifestyle, community engagement, and property value.
Why it is important
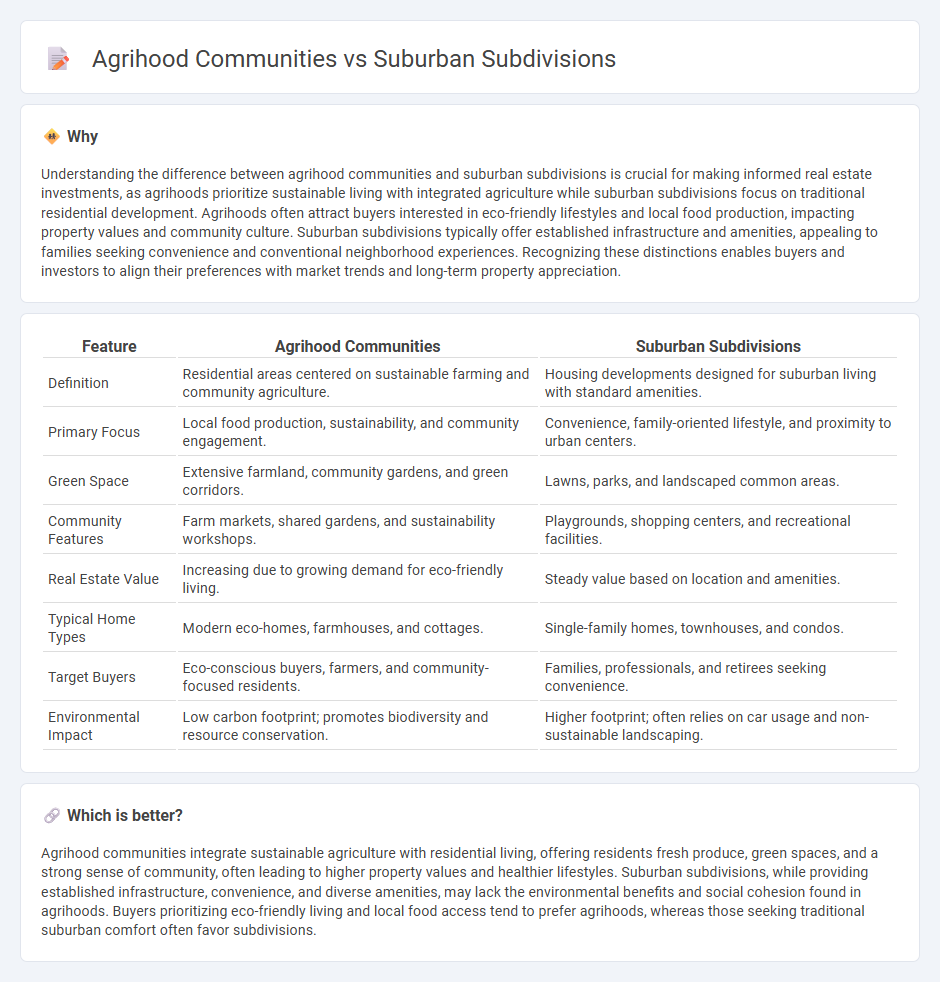
Understanding the difference between agrihood communities and suburban subdivisions is crucial for making informed real estate investments, as agrihoods prioritize sustainable living with integrated agriculture while suburban subdivisions focus on traditional residential development. Agrihoods often attract buyers interested in eco-friendly lifestyles and local food production, impacting property values and community culture. Suburban subdivisions typically offer established infrastructure and amenities, appealing to families seeking convenience and conventional neighborhood experiences. Recognizing these distinctions enables buyers and investors to align their preferences with market trends and long-term property appreciation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Agrihood Communities | Suburban Subdivisions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential areas centered on sustainable farming and community agriculture. | Housing developments designed for suburban living with standard amenities. |
| Primary Focus | Local food production, sustainability, and community engagement. | Convenience, family-oriented lifestyle, and proximity to urban centers. |
| Green Space | Extensive farmland, community gardens, and green corridors. | Lawns, parks, and landscaped common areas. |
| Community Features | Farm markets, shared gardens, and sustainability workshops. | Playgrounds, shopping centers, and recreational facilities. |
| Real Estate Value | Increasing due to growing demand for eco-friendly living. | Steady value based on location and amenities. |
| Typical Home Types | Modern eco-homes, farmhouses, and cottages. | Single-family homes, townhouses, and condos. |
| Target Buyers | Eco-conscious buyers, farmers, and community-focused residents. | Families, professionals, and retirees seeking convenience. |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint; promotes biodiversity and resource conservation. | Higher footprint; often relies on car usage and non-sustainable landscaping. |
Which is better?
Agrihood communities integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, offering residents fresh produce, green spaces, and a strong sense of community, often leading to higher property values and healthier lifestyles. Suburban subdivisions, while providing established infrastructure, convenience, and diverse amenities, may lack the environmental benefits and social cohesion found in agrihoods. Buyers prioritizing eco-friendly living and local food access tend to prefer agrihoods, whereas those seeking traditional suburban comfort often favor subdivisions.
Connection
Agrihood communities integrate agricultural spaces within suburban subdivisions, creating a blend of rural farming lifestyles and modern suburban living. These developments prioritize local food production, community gardens, and sustainable land use, attracting homeowners seeking a connection to nature without sacrificing suburban amenities. The synergy between agrihoods and suburban subdivisions enhances property values by promoting healthier living environments and fostering a strong sense of community engagement.
Key Terms
Zoning
Suburban subdivisions often rely on conventional residential zoning that separates single-family homes from commercial and agricultural uses, creating distinct neighborhoods with limited integration of green spaces. Agrihood communities typically utilize mixed-use zoning or agricultural overlay zones that blend residential living with active farmland, promoting sustainability and local food production. Explore the zoning regulations that shape these unique community models and their impact on lifestyle and environment.
Amenities
Suburban subdivisions typically offer standard amenities such as playgrounds, community pools, and sidewalks designed for family-friendly living. Agrihood communities prioritize farm-to-table experiences, featuring organic gardens, livestock areas, and communal farming spaces that promote sustainability and connection to nature. Discover the benefits of each lifestyle and find the perfect community that caters to your interests.
Land Use
Suburban subdivisions typically prioritize residential density with uniform lot sizes and minimal green space, emphasizing efficient land use for housing development. Agrihood communities integrate actively managed agricultural land, such as farms and community gardens, into the residential layout, promoting sustainable land use and local food production. Explore how land use strategies create distinct lifestyles and environmental impacts in these community types.
Source and External Links
Suburbs in The U.S - Describes suburban communities as primarily single-family homes arranged into neighborhoods with some local businesses and schools, often developed around car transportation post-World War II.
Suburb - Provides an overview of suburbs as areas within metropolitan regions, often associated with suburbanization and influenced by historical factors like the automobile and streetcar lines.
Suburban Neighborhoods - Discusses suburban areas as clusters of largely residential properties that are quieter than cities but more developed than rural areas, offering a balance between city and country living.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com