Adaptive reuse properties transform existing structures into functional spaces, maximizing sustainability and preserving architectural heritage while reducing construction waste. Modular construction involves prefabricating building sections off-site, accelerating project timelines and improving quality control with less environmental impact. Explore how these innovative real estate strategies can redefine urban development and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and modular construction is crucial for real estate investors seeking strategic asset management. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings, enhancing sustainability and preserving historical value, while modular construction uses prefabricated modules for faster, cost-effective new builds. Knowing these distinctions helps investors optimize project timelines, budgets, and regulatory compliance. Real estate developers can leverage adaptive reuse for urban revitalization or choose modular construction to accelerate delivery and reduce labor costs.
Comparison Table
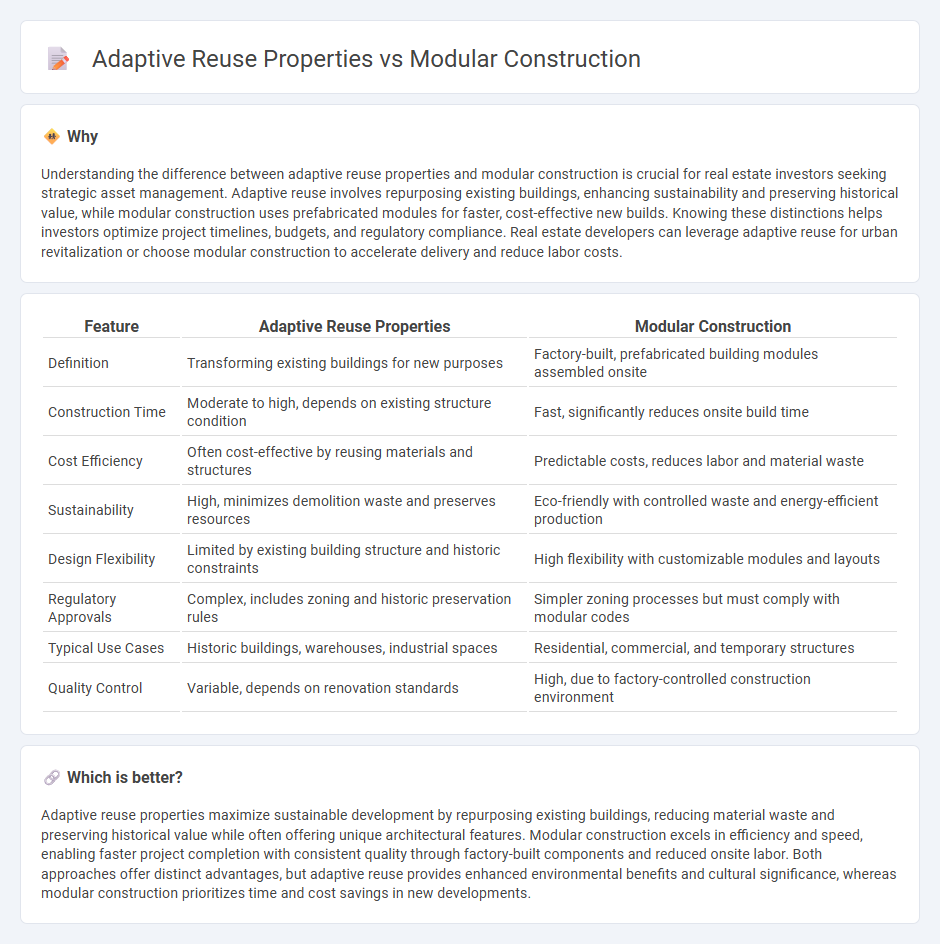
| Feature | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Modular Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming existing buildings for new purposes | Factory-built, prefabricated building modules assembled onsite |
| Construction Time | Moderate to high, depends on existing structure condition | Fast, significantly reduces onsite build time |
| Cost Efficiency | Often cost-effective by reusing materials and structures | Predictable costs, reduces labor and material waste |
| Sustainability | High, minimizes demolition waste and preserves resources | Eco-friendly with controlled waste and energy-efficient production |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by existing building structure and historic constraints | High flexibility with customizable modules and layouts |
| Regulatory Approvals | Complex, includes zoning and historic preservation rules | Simpler zoning processes but must comply with modular codes |
| Typical Use Cases | Historic buildings, warehouses, industrial spaces | Residential, commercial, and temporary structures |
| Quality Control | Variable, depends on renovation standards | High, due to factory-controlled construction environment |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties maximize sustainable development by repurposing existing buildings, reducing material waste and preserving historical value while often offering unique architectural features. Modular construction excels in efficiency and speed, enabling faster project completion with consistent quality through factory-built components and reduced onsite labor. Both approaches offer distinct advantages, but adaptive reuse provides enhanced environmental benefits and cultural significance, whereas modular construction prioritizes time and cost savings in new developments.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and modular construction intersect through their shared focus on sustainability and efficiency in real estate development. Adaptive reuse revitalizes existing structures by repurposing them for new uses, while modular construction facilitates faster assembly of building components, often compatible with retrofitting projects. Integrating modular construction methods in adaptive reuse projects enhances resource efficiency, reduces construction timelines, and minimizes environmental impact within urban real estate markets.
Key Terms
Prefabrication
Modular construction leverages prefabrication by manufacturing building components off-site in controlled environments, enhancing quality control, reducing waste, and accelerating project timelines. Adaptive reuse properties often incorporate prefabricated elements to retrofit and modernize existing structures while maintaining historical integrity and minimizing disruption. Explore the advantages and applications of prefabrication in both modular construction and adaptive reuse to optimize building efficiency.
Historic preservation
Modular construction offers efficient building methods but often lacks the authentic materials and craftsmanship essential for historic preservation, whereas adaptive reuse preserves the original architectural elements and cultural significance of historic properties. Adaptive reuse reduces environmental impact by maintaining existing structures and can often qualify for historic tax credits, making it a sustainable choice for preserving heritage. Explore how adaptive reuse balances modern needs and historic integrity for sustainable preservation projects.
Building codes
Modular construction often benefits from streamlined compliance with modern building codes due to factory-built components designed to meet specific standards before onsite assembly. Adaptive reuse projects must navigate existing structural limitations and retrofit requirements to satisfy current codes, often involving extensive inspections and customized solutions. Explore detailed comparisons to understand code implications for each method and optimize your construction strategy.
Source and External Links
Modular Building - Wikipedia - Provides information on modular buildings, which are prefabricated structures composed of modules that are assembled off-site and then installed at the intended site.
What is Modular Construction - Explains modular construction as a process where buildings are constructed off-site under controlled conditions, offering advantages such as faster completion times and reduced waste.
Off-Site and Modular Construction Explained - Describes modular manufacturing as an inside-out process where frames are constructed and finished from the inside to eliminate weather and site delays.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com