Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming with residential living, offering homebuyers access to fresh produce and green spaces while fostering community engagement. Tiny house communities prioritize minimalistic, affordable housing solutions, attracting residents who value simplicity and reduced environmental impact. Explore how these innovative real estate trends shape modern living by discovering more about agrihoods and tiny house communities.
Why it is important
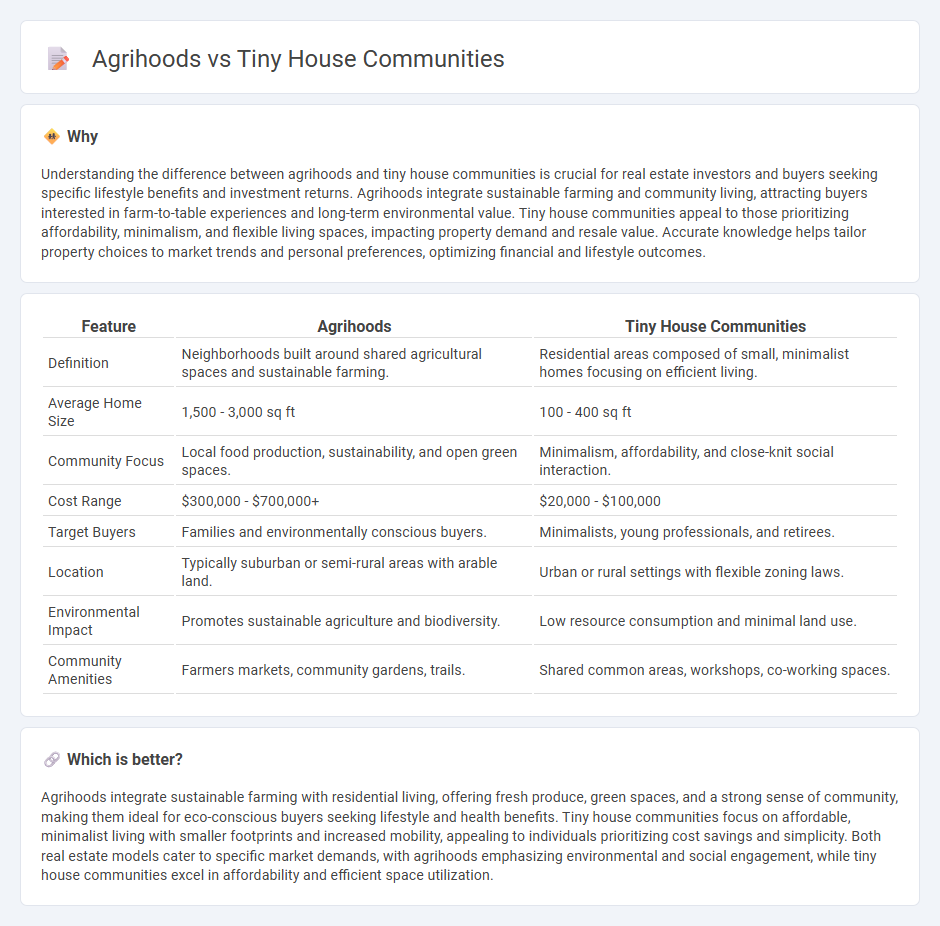
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and tiny house communities is crucial for real estate investors and buyers seeking specific lifestyle benefits and investment returns. Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming and community living, attracting buyers interested in farm-to-table experiences and long-term environmental value. Tiny house communities appeal to those prioritizing affordability, minimalism, and flexible living spaces, impacting property demand and resale value. Accurate knowledge helps tailor property choices to market trends and personal preferences, optimizing financial and lifestyle outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Agrihoods | Tiny House Communities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Neighborhoods built around shared agricultural spaces and sustainable farming. | Residential areas composed of small, minimalist homes focusing on efficient living. |
| Average Home Size | 1,500 - 3,000 sq ft | 100 - 400 sq ft |
| Community Focus | Local food production, sustainability, and open green spaces. | Minimalism, affordability, and close-knit social interaction. |
| Cost Range | $300,000 - $700,000+ | $20,000 - $100,000 |
| Target Buyers | Families and environmentally conscious buyers. | Minimalists, young professionals, and retirees. |
| Location | Typically suburban or semi-rural areas with arable land. | Urban or rural settings with flexible zoning laws. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainable agriculture and biodiversity. | Low resource consumption and minimal land use. |
| Community Amenities | Farmers markets, community gardens, trails. | Shared common areas, workshops, co-working spaces. |
Which is better?
Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming with residential living, offering fresh produce, green spaces, and a strong sense of community, making them ideal for eco-conscious buyers seeking lifestyle and health benefits. Tiny house communities focus on affordable, minimalist living with smaller footprints and increased mobility, appealing to individuals prioritizing cost savings and simplicity. Both real estate models cater to specific market demands, with agrihoods emphasizing environmental and social engagement, while tiny house communities excel in affordability and efficient space utilization.
Connection
Agrihoods and tiny house communities both emphasize sustainable living and intentional community design, integrating agriculture and eco-friendly housing to promote self-sufficiency and reduced environmental impact. Agrihoods revolve around communal farming and green spaces, while tiny house communities focus on minimizing living footprints and maximizing efficient use of space. Together, they attract residents seeking affordable, eco-conscious housing solutions with a strong connection to nature and local food production.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations for tiny house communities often classify them under residential or accessory dwelling unit (ADU) categories, with restrictions on minimum square footage and occupancy, impacting their feasibility. Agrihoods face zoning challenges centered around integrating agricultural activities within residential zones, requiring allowances for farming, livestock, and community gardens while maintaining land-use balance. Explore local zoning codes and ordinances to understand how they shape the development and sustainability of both tiny house communities and agrihoods.
Community Amenities
Tiny house communities often feature shared amenities such as communal kitchens, co-working spaces, and recreational areas designed to foster social interaction among residents. Agrihoods prioritize agricultural amenities like community gardens, farmers' markets, and farm-to-table dining experiences, promoting sustainable living and local food production. Explore the unique community amenities offered by both options to discover which lifestyle suits your preferences.
Land Use
Tiny house communities capitalize on compact land use, maximizing residential density with minimal environmental impact by clustering small, efficient homes. Agrihoods integrate residential living with active farmland, promoting sustainable agriculture and green spaces that enhance community well-being and biodiversity. Explore how land use strategies in these models create distinct lifestyles and environmental benefits.
Source and External Links
Discover Tiny Home Communities In The USA - Highlights several tiny house communities like Mountain Haven in Virginia with outdoor amenities, Cape Charles Tiny Livin' offering historic-modern tiny homes, and Autumn Sun Community focused on sustainable living and cooperation.
The Top Tiny House Communities to Consider in the USA - Discusses benefits of tiny house communities including cost savings, environmental impact, social interaction, simplified lifestyle, mobility, security, and health/wellness advantages provided by communal living environments.
Tiny House Communities - Features Escalante Village in Durango, Colorado, which offers affordable tiny home ownership beside a riverfront with city access, customization options, community gardens, and proximity to outdoor recreation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com