Retrofit for net zero focuses on upgrading buildings to achieve zero carbon emissions by maximizing energy efficiency and integrating renewable energy systems, while deep energy retrofit prioritizes major improvements to drastically reduce energy consumption, often exceeding 50% savings. Both approaches involve comprehensive measures such as enhanced insulation, high-performance windows, and advanced HVAC systems but differ in scope and end goals. Explore detailed strategies and benefits to determine the best retrofit path for your property.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between retrofit for net zero and deep energy retrofit is crucial in real estate to align renovation strategies with specific sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. Retrofit for net zero aims to achieve complete energy self-sufficiency by balancing energy consumption with on-site renewable energy production. Deep energy retrofit focuses on significantly reducing energy use, typically by 50% or more, through comprehensive upgrades but may not reach net zero status. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors and developers optimize building performance, comply with environmental standards, and maximize property value.
Comparison Table
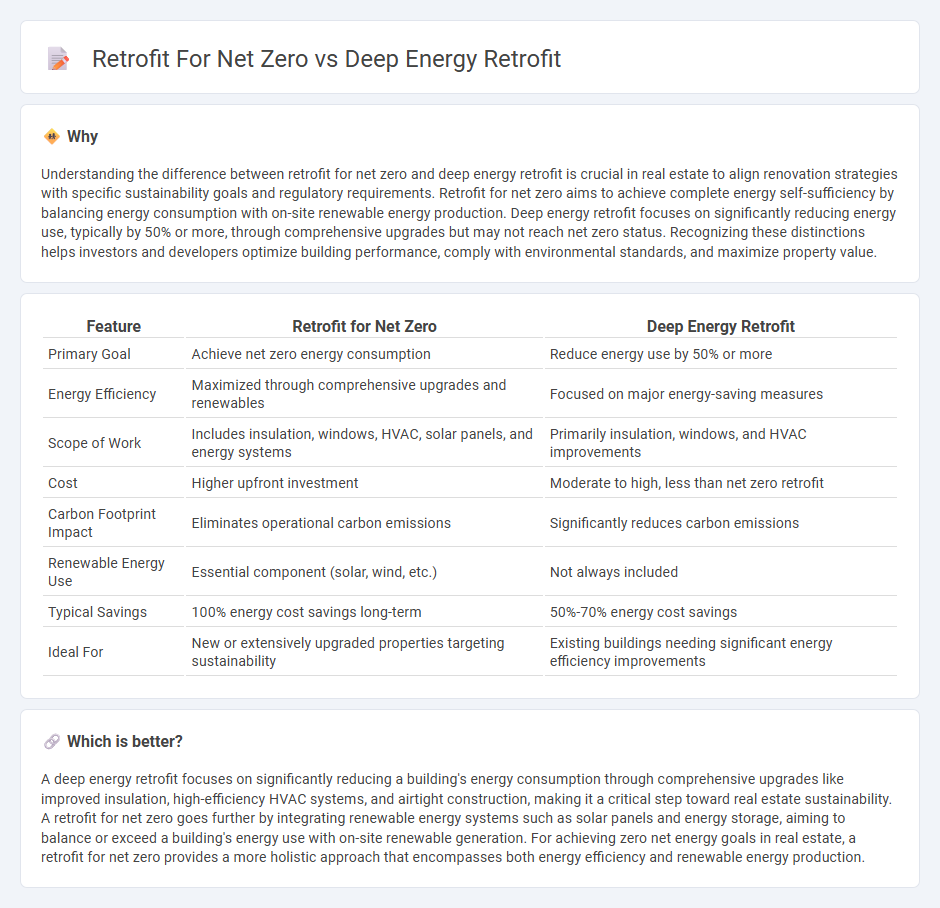
| Feature | Retrofit for Net Zero | Deep Energy Retrofit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Achieve net zero energy consumption | Reduce energy use by 50% or more |
| Energy Efficiency | Maximized through comprehensive upgrades and renewables | Focused on major energy-saving measures |
| Scope of Work | Includes insulation, windows, HVAC, solar panels, and energy systems | Primarily insulation, windows, and HVAC improvements |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment | Moderate to high, less than net zero retrofit |
| Carbon Footprint Impact | Eliminates operational carbon emissions | Significantly reduces carbon emissions |
| Renewable Energy Use | Essential component (solar, wind, etc.) | Not always included |
| Typical Savings | 100% energy cost savings long-term | 50%-70% energy cost savings |
| Ideal For | New or extensively upgraded properties targeting sustainability | Existing buildings needing significant energy efficiency improvements |
Which is better?
A deep energy retrofit focuses on significantly reducing a building's energy consumption through comprehensive upgrades like improved insulation, high-efficiency HVAC systems, and airtight construction, making it a critical step toward real estate sustainability. A retrofit for net zero goes further by integrating renewable energy systems such as solar panels and energy storage, aiming to balance or exceed a building's energy use with on-site renewable generation. For achieving zero net energy goals in real estate, a retrofit for net zero provides a more holistic approach that encompasses both energy efficiency and renewable energy production.
Connection
Retrofitting for net zero involves upgrading buildings to achieve zero carbon emissions by enhancing energy efficiency and integrating renewable energy sources. Deep energy retrofit focuses on comprehensive improvements that reduce energy consumption by 50% or more, targeting insulation, HVAC systems, and windows. Both approaches prioritize sustainability and cost savings, making them essential strategies in transforming existing real estate assets into low-carbon, energy-efficient properties.
Key Terms
Energy Performance
Deep energy retrofit significantly enhances building energy performance by improving insulation, sealing air leaks, and upgrading HVAC systems to reduce energy consumption by 50-75%. Retrofit for net zero integrates renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and energy storage, alongside efficiency measures to achieve net-zero energy balance. Explore detailed strategies and case studies to understand how these approaches optimize energy performance.
Building Envelope
Deep energy retrofit focuses on comprehensive upgrades to the building envelope, including enhanced insulation, high-performance windows, and airtight construction to drastically reduce energy consumption. Retrofit for net zero prioritizes integrating renewable energy systems with building envelope improvements to achieve a balance between energy use and on-site energy generation. Explore detailed strategies and technologies to optimize your building envelope for maximum energy efficiency and sustainability.
Renewable Energy Systems
Deep energy retrofits maximize building efficiency, significantly reducing energy consumption through advanced insulation, airtight construction, and high-performance HVAC upgrades, thereby lowering reliance on renewable energy systems. Retrofit for net zero goes further by integrating on-site renewable energy technologies such as solar PV, wind turbines, and geothermal heat pumps to achieve a balance between consumed and produced energy. Explore how combining deep energy retrofits with cutting-edge renewable energy systems can drive your building toward net zero emissions.
Source and External Links
Deep energy retrofit - Wikipedia - A deep energy retrofit is a whole-building process aiming to reduce energy use by 50% or more by integrating energy-saving technologies and remodeling for enhanced performance, indoor air quality, and comfort, applicable to residential and commercial buildings.
Deep Energy Retrofits - U.S. Department of Energy - Deep energy retrofits involve whole-building upgrades such as enhanced insulation and airtightness to reduce heating and cooling loads, enabling equipment downsizing and facilitating renewable energy integration and decarbonization.
The Retrofit Depot - Rocky Mountain Institute - Deep energy retrofits achieve energy cost savings sometimes exceeding 50% by adopting integrative design and phased implementation strategies, enhancing building efficiency, occupant desirability, and value through a multidisciplinary approach.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com