Adaptive reuse properties transform underutilized buildings into functional living spaces, preserving historical architecture while promoting sustainability and urban regeneration. Co-housing initiatives foster community-centric living through shared spaces and collaborative management, enhancing social interactions and reducing individual living costs. Discover how these innovative real estate solutions reshape urban lifestyles and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
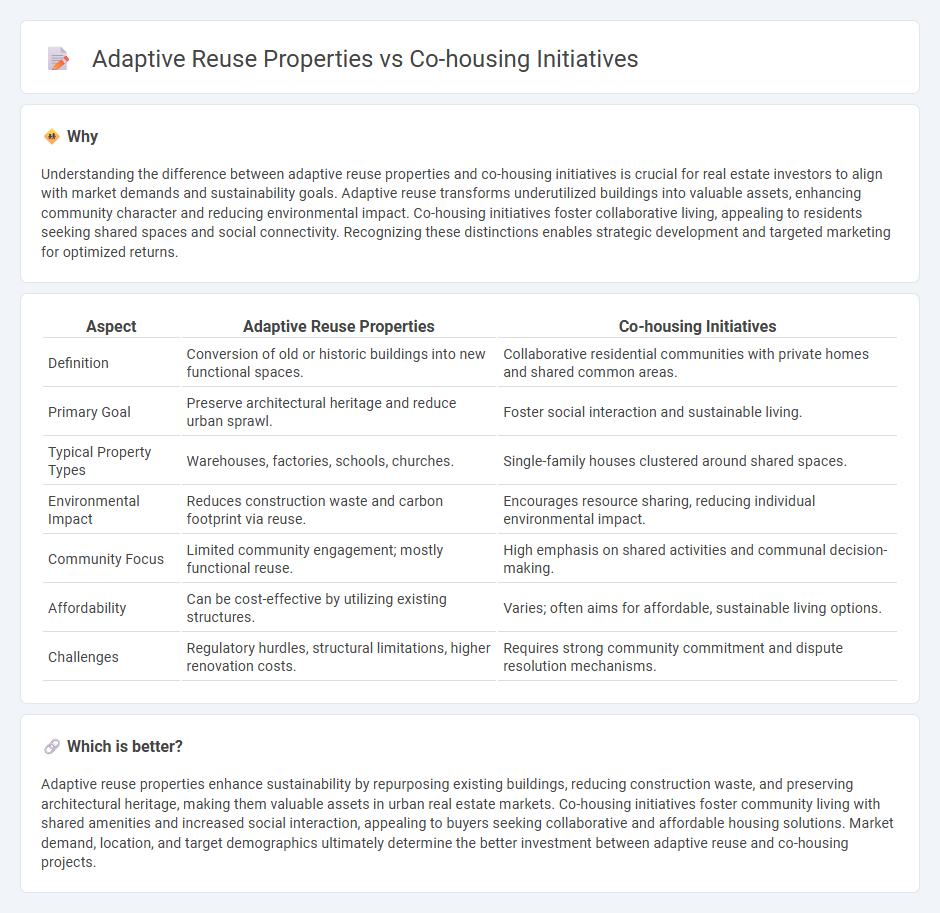
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and co-housing initiatives is crucial for real estate investors to align with market demands and sustainability goals. Adaptive reuse transforms underutilized buildings into valuable assets, enhancing community character and reducing environmental impact. Co-housing initiatives foster collaborative living, appealing to residents seeking shared spaces and social connectivity. Recognizing these distinctions enables strategic development and targeted marketing for optimized returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Co-housing Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion of old or historic buildings into new functional spaces. | Collaborative residential communities with private homes and shared common areas. |
| Primary Goal | Preserve architectural heritage and reduce urban sprawl. | Foster social interaction and sustainable living. |
| Typical Property Types | Warehouses, factories, schools, churches. | Single-family houses clustered around shared spaces. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces construction waste and carbon footprint via reuse. | Encourages resource sharing, reducing individual environmental impact. |
| Community Focus | Limited community engagement; mostly functional reuse. | High emphasis on shared activities and communal decision-making. |
| Affordability | Can be cost-effective by utilizing existing structures. | Varies; often aims for affordable, sustainable living options. |
| Challenges | Regulatory hurdles, structural limitations, higher renovation costs. | Requires strong community commitment and dispute resolution mechanisms. |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties enhance sustainability by repurposing existing buildings, reducing construction waste, and preserving architectural heritage, making them valuable assets in urban real estate markets. Co-housing initiatives foster community living with shared amenities and increased social interaction, appealing to buyers seeking collaborative and affordable housing solutions. Market demand, location, and target demographics ultimately determine the better investment between adaptive reuse and co-housing projects.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties transform obsolete buildings into modern living spaces, aligning with co-housing initiatives that emphasize communal living and shared amenities. Both approaches promote sustainability by reducing new construction and fostering community engagement, addressing urban housing shortages efficiently. Integrating adaptive reuse with co-housing models maximizes resource utilization while enhancing social interaction among residents.
Key Terms
**Co-housing initiatives:**
Co-housing initiatives foster collaborative living by combining private homes with shared community spaces, enhancing social interaction and sustainable living. These projects emphasize resident participation in design and management, promoting a strong sense of community and mutual support. Explore how co-housing initiatives transform urban living with innovative, socially-driven housing solutions.
Shared amenities
Co-housing initiatives prioritize communal living with shared amenities such as kitchens, recreational spaces, and gardens designed to foster social interaction and resource efficiency. Adaptive reuse properties often incorporate existing structures to create mixed-use spaces that balance shared facilities with private areas, optimizing sustainability and historic preservation. Explore how these models redefine community engagement and sustainability in residential development.
Community governance
Co-housing initiatives emphasize resident-led community governance structures that foster collaboration, shared decision-making, and collective responsibility in managing common spaces. Adaptive reuse properties typically incorporate governance models influenced by existing regulatory frameworks and property management, often limiting direct resident control. Explore how these governance approaches impact social cohesion and resident empowerment in diverse housing models for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
Co-Living - Housing - This webpage discusses co-living initiatives, including private sleeping quarters with communal facilities, and examples like Altair EcoVillage and Thistledown Co-Living House.
Affordable Housing Initiative - The Cooperative Development Foundation's initiative focuses on community-driven solutions for affordable housing, including shared equity models like cooperatives and community land trusts.
Co-housing communities: A guide for social workers - This guide provides strategies for fostering community and collaboration within co-housing settings, emphasizing shared responsibilities and community-building activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com