Upzoning increases allowable building density and height, enabling developers to maximize land use and address housing shortages. Overlay zoning imposes specific regulations on top of base zoning to achieve targeted community goals such as historic preservation or environmental protection. Explore the impacts and benefits of upzoning versus overlay zoning to understand their roles in urban planning.
Why it is important
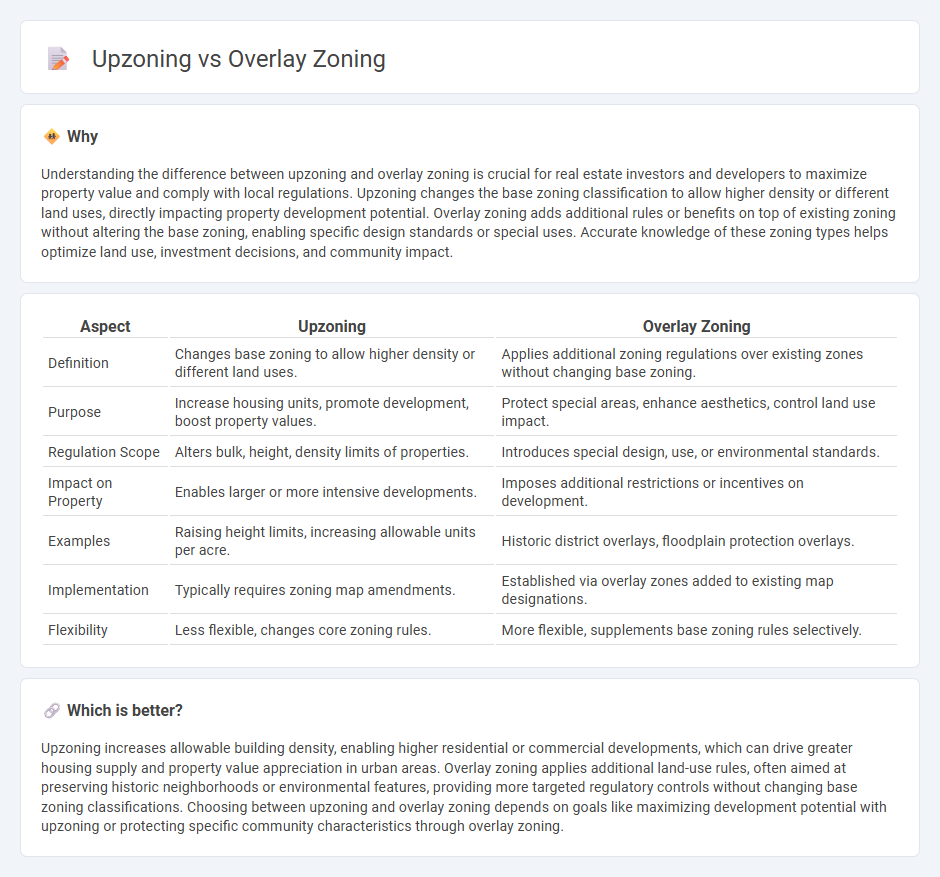
Understanding the difference between upzoning and overlay zoning is crucial for real estate investors and developers to maximize property value and comply with local regulations. Upzoning changes the base zoning classification to allow higher density or different land uses, directly impacting property development potential. Overlay zoning adds additional rules or benefits on top of existing zoning without altering the base zoning, enabling specific design standards or special uses. Accurate knowledge of these zoning types helps optimize land use, investment decisions, and community impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Overlay Zoning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changes base zoning to allow higher density or different land uses. | Applies additional zoning regulations over existing zones without changing base zoning. |
| Purpose | Increase housing units, promote development, boost property values. | Protect special areas, enhance aesthetics, control land use impact. |
| Regulation Scope | Alters bulk, height, density limits of properties. | Introduces special design, use, or environmental standards. |
| Impact on Property | Enables larger or more intensive developments. | Imposes additional restrictions or incentives on development. |
| Examples | Raising height limits, increasing allowable units per acre. | Historic district overlays, floodplain protection overlays. |
| Implementation | Typically requires zoning map amendments. | Established via overlay zones added to existing map designations. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, changes core zoning rules. | More flexible, supplements base zoning rules selectively. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases allowable building density, enabling higher residential or commercial developments, which can drive greater housing supply and property value appreciation in urban areas. Overlay zoning applies additional land-use rules, often aimed at preserving historic neighborhoods or environmental features, providing more targeted regulatory controls without changing base zoning classifications. Choosing between upzoning and overlay zoning depends on goals like maximizing development potential with upzoning or protecting specific community characteristics through overlay zoning.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density or height in a specific area, while overlay zoning applies additional regulatory layers to existing zones for targeted improvements. Overlay zoning often incorporates upzoning provisions to promote transit-oriented development, affordable housing, or historic preservation within designated districts. Together, they strategically guide urban growth by balancing increased development capacity with specific planning goals.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Overlay zoning introduces additional regulations on top of existing base zoning, allowing for specific land use adjustments without altering the underlying zoning classification. Upzoning changes the base zoning designation to allow for higher density or different land uses, often increasing building heights or allowable occupancy. Explore more about how these zoning strategies impact urban development and community planning.
Density
Overlay zoning allows additional regulations on top of base zoning to increase density selectively, often targeting specific areas for growth without altering the underlying zoning districts. Upzoning changes the base zoning itself, typically permitting higher density, greater building heights, or reduced setbacks across a broader area to encourage more intensive land use. Discover how these zoning strategies influence urban density and development potential in your community.
Land use
Overlay zoning enhances existing land use regulations by adding extra requirements or incentives without changing the underlying zoning, often targeting specific goals like historic preservation or environmental protection. Upzoning increases allowable density or changes land use categories to permit more intensive development, such as converting low-density residential areas to mixed-use or commercial zones. Explore how these zoning strategies impact urban growth and development by learning more about their applications and effects.
Source and External Links
Overlay zoning districts can be a valuable tool - An overlay zone adds an additional layer of regulations to one or more existing zoning districts, often streamlining the process for specific community goals or environmental protections.
Property Topics and Concepts - Overlay zones are used to protect special features or promote specific developments by adding stricter standards over existing zoning districts.
What Is an Overlay District? - An overlay district superimposes additional regulations over existing zoning districts to address specific conditions, such as environmental protection or historic preservation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com