Tiny home villages offer compact, eco-friendly living spaces designed for affordability and community engagement, while mobile home parks provide a broader range of modular housing options with established infrastructure. Both real estate models address housing shortages through cost-effective solutions but differ in property size, mobility, and zoning regulations. Explore the key differences and benefits of tiny home villages and mobile home parks to determine which suits your investment or living needs.
Why it is important
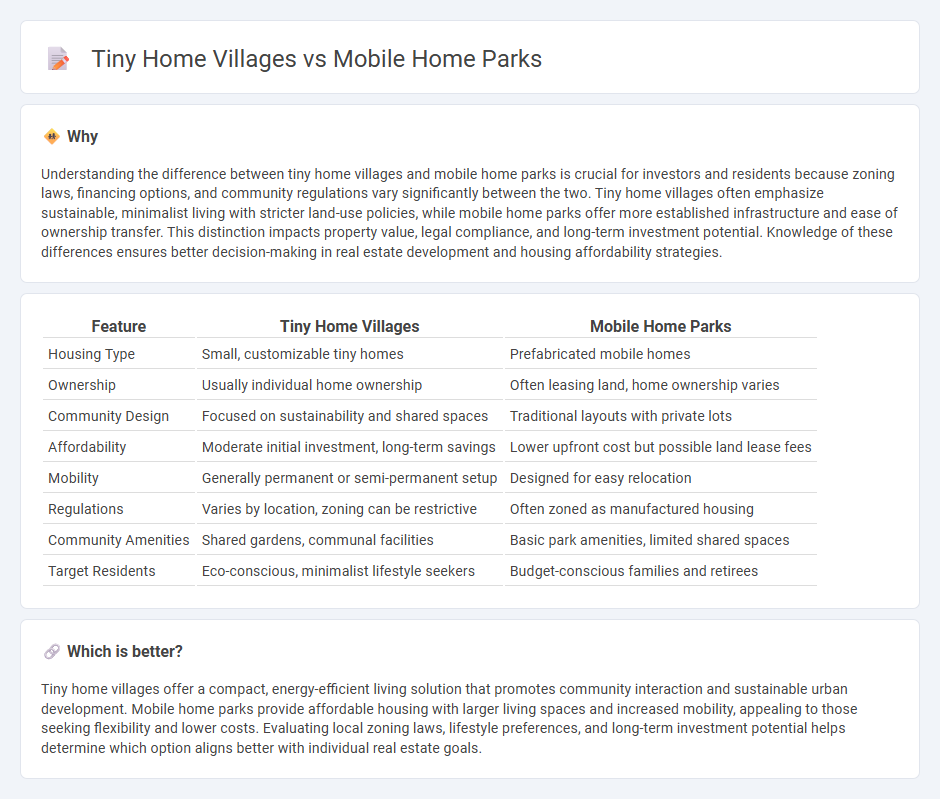
Understanding the difference between tiny home villages and mobile home parks is crucial for investors and residents because zoning laws, financing options, and community regulations vary significantly between the two. Tiny home villages often emphasize sustainable, minimalist living with stricter land-use policies, while mobile home parks offer more established infrastructure and ease of ownership transfer. This distinction impacts property value, legal compliance, and long-term investment potential. Knowledge of these differences ensures better decision-making in real estate development and housing affordability strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny Home Villages | Mobile Home Parks |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Small, customizable tiny homes | Prefabricated mobile homes |
| Ownership | Usually individual home ownership | Often leasing land, home ownership varies |
| Community Design | Focused on sustainability and shared spaces | Traditional layouts with private lots |
| Affordability | Moderate initial investment, long-term savings | Lower upfront cost but possible land lease fees |
| Mobility | Generally permanent or semi-permanent setup | Designed for easy relocation |
| Regulations | Varies by location, zoning can be restrictive | Often zoned as manufactured housing |
| Community Amenities | Shared gardens, communal facilities | Basic park amenities, limited shared spaces |
| Target Residents | Eco-conscious, minimalist lifestyle seekers | Budget-conscious families and retirees |
Which is better?
Tiny home villages offer a compact, energy-efficient living solution that promotes community interaction and sustainable urban development. Mobile home parks provide affordable housing with larger living spaces and increased mobility, appealing to those seeking flexibility and lower costs. Evaluating local zoning laws, lifestyle preferences, and long-term investment potential helps determine which option aligns better with individual real estate goals.
Connection
Tiny home villages and mobile home parks both address affordable housing shortages by providing compact, cost-effective living spaces within community-oriented environments. These developments maximize land use efficiency through clustered housing designs, shared amenities, and streamlined zoning regulations. Integrating tiny homes into mobile home parks expands housing options while benefiting from existing infrastructure and communal support systems.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations for mobile home parks often classify them under manufactured housing zones, allowing for more lenient land use and infrastructure requirements compared to tiny home villages, which frequently face stricter residential zoning constraints due to their non-traditional structure and smaller footprint. Mobile home parks benefit from established legal frameworks enabling higher density and efficient utility hookups, while tiny home villages must navigate varying local ordinances that may limit their size, placement, and permanence. Explore detailed zoning regulations and compliance strategies to better understand the development potential for both housing options.
Infrastructure Requirements
Mobile home parks require extensive infrastructure including water, sewage, electrical systems, and road maintenance to support larger units and higher occupancy rates. Tiny home villages often have scaled-down infrastructure needs, prioritizing sustainable solutions like shared utilities and green energy systems to accommodate smaller living spaces. Explore detailed comparisons on infrastructure requirements to determine the best option for your housing project.
Ownership Structure
Mobile home parks typically operate under a landlord-tenant model where residents rent lots from the park owner, often facing limited control over property rules and potential rent increases. Tiny home villages often emphasize cooperative or community land trust ownership, granting residents collective control and equity in the land, fostering long-term stability and shared governance. Explore the nuances of ownership structures to understand which model aligns with your housing and investment goals.
Source and External Links
What Is a Mobile Home Park? - Discusses the concept of mobile home parks, including their layout and benefits like affordability and community-driven environments.
Mobile Home Parks | Find the Perfect Community - Offers a platform to search for mobile home parks with various amenities and community types.
Why & How To Invest In Mobile Home Parks - Provides insights into investing in mobile home parks, highlighting benefits like low costs and high demand.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com