Smart contracts revolutionize real estate transactions by automating agreements and reducing the need for physical signatures, enhancing efficiency and security. These digital contracts provide transparent, immutable records stored on blockchain, minimizing fraud and errors compared to traditional paper-based methods. Explore how smart contracts can transform your real estate experience and streamline property deals.
Why it is important
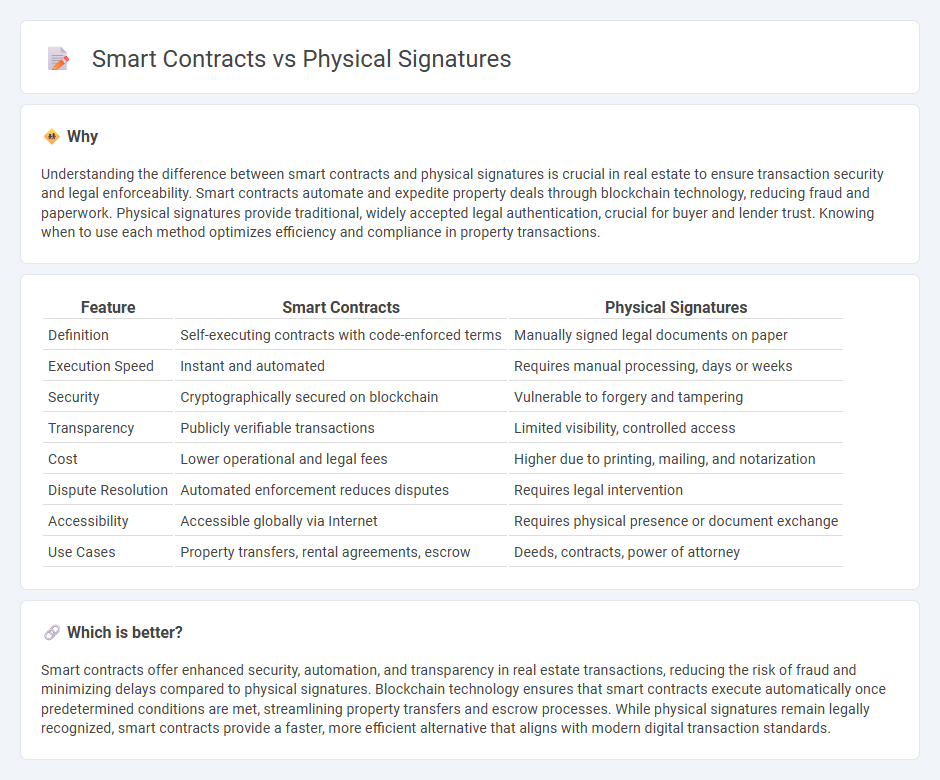
Understanding the difference between smart contracts and physical signatures is crucial in real estate to ensure transaction security and legal enforceability. Smart contracts automate and expedite property deals through blockchain technology, reducing fraud and paperwork. Physical signatures provide traditional, widely accepted legal authentication, crucial for buyer and lender trust. Knowing when to use each method optimizes efficiency and compliance in property transactions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Contracts | Physical Signatures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-executing contracts with code-enforced terms | Manually signed legal documents on paper |
| Execution Speed | Instant and automated | Requires manual processing, days or weeks |
| Security | Cryptographically secured on blockchain | Vulnerable to forgery and tampering |
| Transparency | Publicly verifiable transactions | Limited visibility, controlled access |
| Cost | Lower operational and legal fees | Higher due to printing, mailing, and notarization |
| Dispute Resolution | Automated enforcement reduces disputes | Requires legal intervention |
| Accessibility | Accessible globally via Internet | Requires physical presence or document exchange |
| Use Cases | Property transfers, rental agreements, escrow | Deeds, contracts, power of attorney |
Which is better?
Smart contracts offer enhanced security, automation, and transparency in real estate transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and minimizing delays compared to physical signatures. Blockchain technology ensures that smart contracts execute automatically once predetermined conditions are met, streamlining property transfers and escrow processes. While physical signatures remain legally recognized, smart contracts provide a faster, more efficient alternative that aligns with modern digital transaction standards.
Connection
Smart contracts automate and enforce real estate agreements by digitally executing terms without intermediaries, while physical signatures provide legally recognized authentication for traditional contract validation. Combining smart contracts with physical signatures enhances transaction security, ensuring both automated execution and compliance with regulatory standards. This integration streamlines property transfers, reduces fraud risk, and accelerates deal closures in real estate transactions.
Key Terms
Wet Ink Signatures
Wet ink signatures provide a tangible and legally recognized method for authenticating documents, widely accepted in traditional contracts and notarizations. Smart contracts automate agreements through blockchain technology, ensuring self-execution and immutability but may lack universal legal acceptance compared to wet ink signatures. Explore the evolving legal landscape and practical applications of both methods to understand their strengths and limitations.
Digital Authentication
Digital authentication enhances security by replacing physical signatures with smart contracts that use cryptographic methods to verify identity and transaction integrity. Smart contracts automate contract execution on blockchain networks, reducing fraud and providing immutable records for transparency. Discover more about how digital authentication transforms legal agreements and business processes.
Blockchain Ledger
Physical signatures provide a tangible method of authentication in traditional contracts, while smart contracts automate agreement execution on a blockchain ledger through coded protocols. Blockchain ledger technology enhances transparency, immutability, and security, ensuring all contract terms are self-executed without intermediaries or manual verification. Explore how integrating smart contracts with blockchain can revolutionize contract management and legal processes.
Source and External Links
Legal Signatures: Everything You Need to Know - Physical signatures are made in person, usually with a pen, and sometimes require witness verification or notarization for important documents.
Digital Signature vs. Wet Signature: What's the Difference? - Wet signatures are traditional, physical marks made with ink on paper, serving as a unique, legally binding representation of a person's identity.
The Difference Between Wet, Digital & Electronic Signatures - A wet signature is created when a person physically marks a document, typically with ink, and may be styled as a cursive name, an "X," or a seal, depending on the culture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com