Adaptive reuse properties transform historic or underutilized buildings into modern living spaces, enhancing sustainability by preserving architectural heritage and reducing construction waste. Tiny home villages offer affordable, compact housing solutions that promote minimalism and community living, often addressing urban housing shortages with efficient land use. Explore the benefits and potential of both adaptive reuse projects and tiny home villages to discover innovative real estate development strategies.
Why it is important
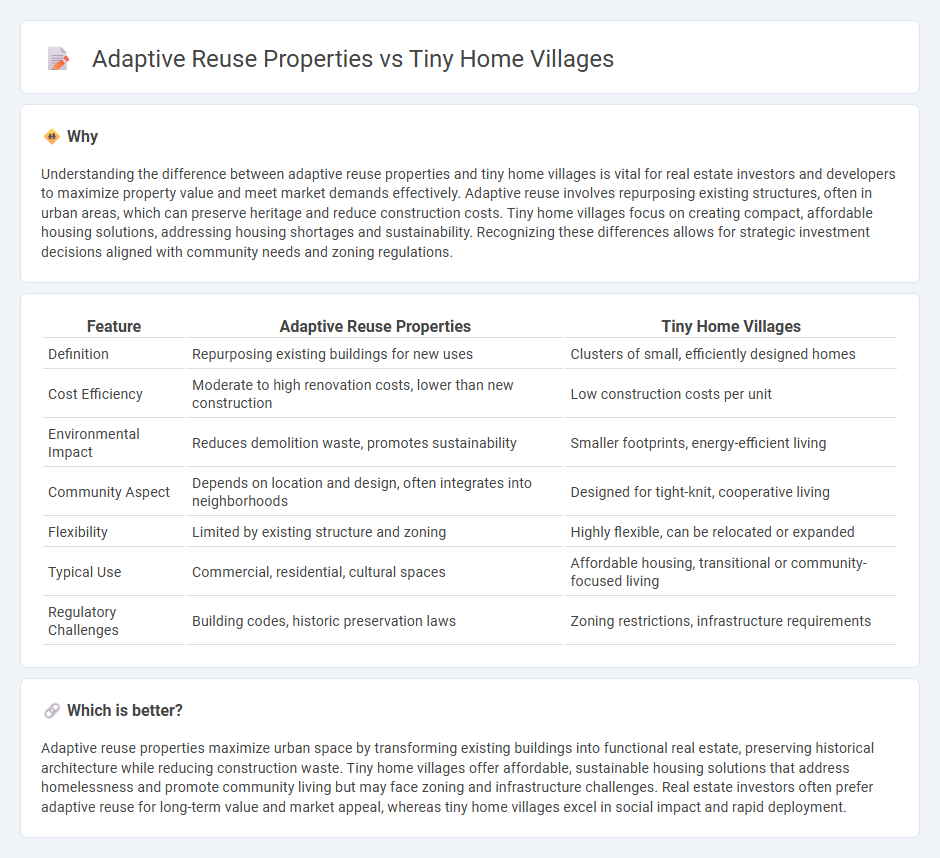
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and tiny home villages is vital for real estate investors and developers to maximize property value and meet market demands effectively. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing structures, often in urban areas, which can preserve heritage and reduce construction costs. Tiny home villages focus on creating compact, affordable housing solutions, addressing housing shortages and sustainability. Recognizing these differences allows for strategic investment decisions aligned with community needs and zoning regulations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Tiny Home Villages |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Clusters of small, efficiently designed homes |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate to high renovation costs, lower than new construction | Low construction costs per unit |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces demolition waste, promotes sustainability | Smaller footprints, energy-efficient living |
| Community Aspect | Depends on location and design, often integrates into neighborhoods | Designed for tight-knit, cooperative living |
| Flexibility | Limited by existing structure and zoning | Highly flexible, can be relocated or expanded |
| Typical Use | Commercial, residential, cultural spaces | Affordable housing, transitional or community-focused living |
| Regulatory Challenges | Building codes, historic preservation laws | Zoning restrictions, infrastructure requirements |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties maximize urban space by transforming existing buildings into functional real estate, preserving historical architecture while reducing construction waste. Tiny home villages offer affordable, sustainable housing solutions that address homelessness and promote community living but may face zoning and infrastructure challenges. Real estate investors often prefer adaptive reuse for long-term value and market appeal, whereas tiny home villages excel in social impact and rapid deployment.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and tiny home villages both focus on maximizing existing spaces by transforming underutilized structures into functional living areas, promoting sustainability in real estate. Repurposed buildings often provide the framework for tiny home communities, enabling affordable, eco-friendly housing solutions in urban environments. This connection reflects a growing trend in real estate to address housing shortages while reducing environmental impact through innovative redevelopment.
Key Terms
**Tiny home villages:**
Tiny home villages offer sustainable, low-cost housing solutions by efficiently utilizing small, prefabricated dwellings typically measuring 100 to 400 square feet. These communities foster social interaction and provide flexible zoning opportunities, making them ideal for addressing urban housing shortages and homelessness. Explore how tiny home villages can transform affordable living in your area.
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations critically impact the development of tiny home villages by often classifying them under accessory dwelling units (ADUs) or requiring special permits, which can limit placement and density. Adaptive reuse properties face regulations centered on preserving building character while adapting to new uses, often involving historic zoning overlays and compliance with building codes for safety and accessibility. Explore in-depth zoning challenges and strategies for both to maximize sustainable urban housing solutions.
Community amenities
Tiny home villages often feature shared community amenities such as gardens, communal kitchens, and recreational spaces designed to foster social interaction and sustainable living. Adaptive reuse properties typically incorporate existing structures retrofitted with modern amenities like coworking spaces, fitness centers, and bike storage to enhance urban living while preserving architectural heritage. Explore more about how these community amenities impact lifestyle and sustainability in different housing models.
Source and External Links
Tiny House Communities - Escalante Village in Durango, Colorado, exemplifies an affordable and customizable tiny home community offering riverfront living near the city with amenities like trails, community gardens, and supportive infrastructure.
Tiny Home Villages: A Rising Community to Reduce Homelessness - Tiny home villages serve as transitional or permanent low-cost housing solutions designed to help reduce homelessness by providing secure shelter, community support, and job opportunities to residents.
Tiny House Village - Low Income Housing Institute - Several tiny house villages in Seattle, such as Rosie's Village and Lake Union Village, provide safe, supported shelter and community services for homeless individuals, combining housing with case management and facilities to aid recovery and stability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com