Digital twins create dynamic, real-time digital replicas of physical properties, enabling precise monitoring and simulation of building performance, while Geographic Information Systems (GIS) focus on spatial data analysis and mapping across broader geographic areas. In real estate, digital twins enhance asset management and predictive maintenance at the building level, whereas GIS supports strategic decision-making through location intelligence and environmental context. Explore how integrating digital twins with GIS transforms property development and urban planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twins and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is crucial in real estate for accurate property visualization and enhanced decision-making. Digital twins create dynamic, real-time virtual models of physical properties, enabling simulation of building performance and maintenance. GIS maps spatial data like land use, zoning, and infrastructure, providing a strategic perspective on location and environmental context. Combining both improves investment analysis, urban planning, and asset management by leveraging detailed, spatially accurate insights.
Comparison Table
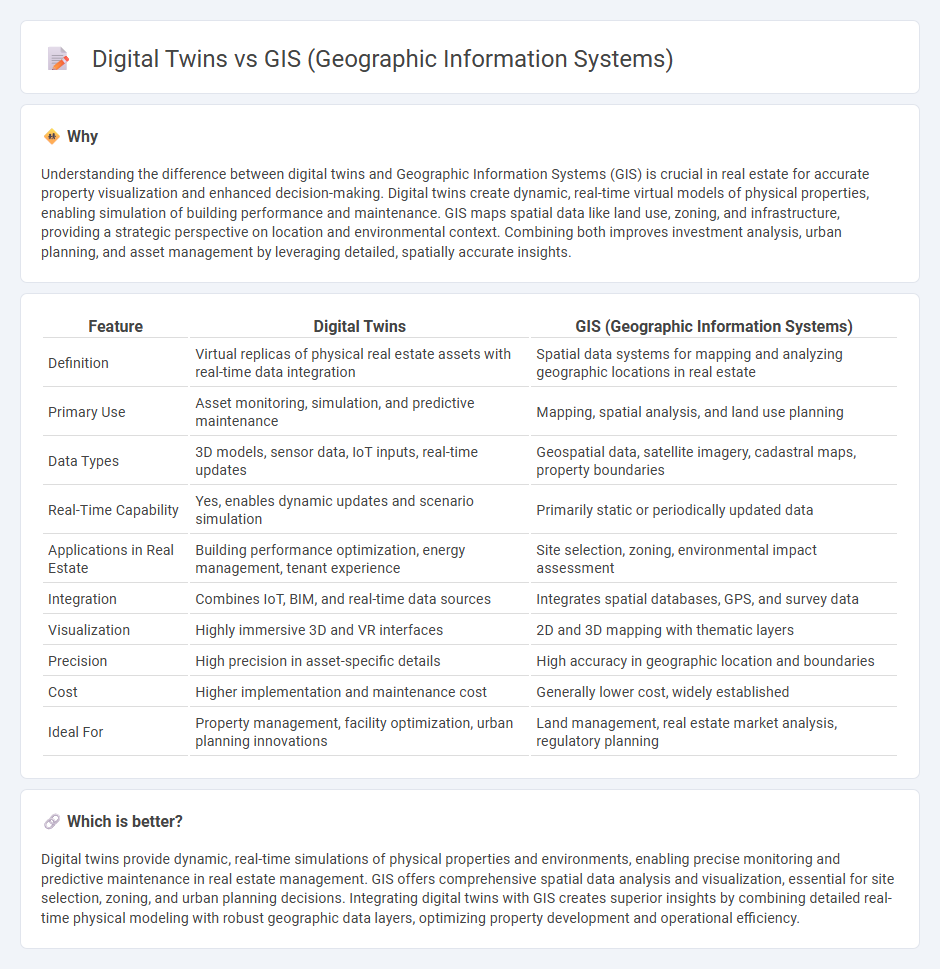
| Feature | Digital Twins | GIS (Geographic Information Systems) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replicas of physical real estate assets with real-time data integration | Spatial data systems for mapping and analyzing geographic locations in real estate |
| Primary Use | Asset monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance | Mapping, spatial analysis, and land use planning |
| Data Types | 3D models, sensor data, IoT inputs, real-time updates | Geospatial data, satellite imagery, cadastral maps, property boundaries |
| Real-Time Capability | Yes, enables dynamic updates and scenario simulation | Primarily static or periodically updated data |
| Applications in Real Estate | Building performance optimization, energy management, tenant experience | Site selection, zoning, environmental impact assessment |
| Integration | Combines IoT, BIM, and real-time data sources | Integrates spatial databases, GPS, and survey data |
| Visualization | Highly immersive 3D and VR interfaces | 2D and 3D mapping with thematic layers |
| Precision | High precision in asset-specific details | High accuracy in geographic location and boundaries |
| Cost | Higher implementation and maintenance cost | Generally lower cost, widely established |
| Ideal For | Property management, facility optimization, urban planning innovations | Land management, real estate market analysis, regulatory planning |
Which is better?
Digital twins provide dynamic, real-time simulations of physical properties and environments, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance in real estate management. GIS offers comprehensive spatial data analysis and visualization, essential for site selection, zoning, and urban planning decisions. Integrating digital twins with GIS creates superior insights by combining detailed real-time physical modeling with robust geographic data layers, optimizing property development and operational efficiency.
Connection
Digital twins integrate GIS data to create dynamic, real-time virtual models of physical properties and environments, enabling enhanced spatial analysis and decision-making in real estate management. Geographic Information Systems provide critical location-based information that digital twins use to simulate property conditions, monitor infrastructure, and optimize land use. The synergy between digital twins and GIS accelerates urban planning, asset management, and risk assessment in real estate development.
Key Terms
Spatial Analysis
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) enables comprehensive spatial analysis by capturing, storing, and visualizing geospatial data for mapping and decision-making purposes. Digital twins extend spatial analysis by integrating real-time sensor data with GIS layers to create dynamic, virtual replicas of physical environments for simulation and predictive modeling. Explore how combining GIS and digital twin technologies enhances spatial insights and operational efficiency.
3D Modeling
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) excel in integrating and analyzing spatial data, providing comprehensive 3D mapping essential for urban planning and environmental monitoring. Digital twins offer dynamic 3D modeling by replicating real-world objects and processes through real-time data, enabling predictive analytics and operational simulations. Explore the unique capabilities and applications of GIS and digital twins in 3D modeling to enhance spatial intelligence and decision-making.
Data Visualization
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) excels in mapping and spatial analysis by integrating various layers of geographic data, enabling robust data visualization through dynamic maps and spatial models. Digital twins create real-time, interactive 3D representations of physical assets or environments by combining IoT data with simulations, offering a more immersive and operational view. Explore how these visualization technologies differ and complement each other to enhance decision-making and spatial understanding.
Source and External Links
Geographic information system - Wikipedia - A GIS consists of integrated hardware and software to store, manage, analyze, edit, and visualize geographic data, linking spatial locations with related information, and is used in many fields like planning, management, and natural sciences.
Geographic Information System (GIS) - NOAA Ocean Exploration - GIS is a computer-based framework that organizes and analyzes spatial data using layers such as points, lines, and polygons, enabling visualization and understanding of Earth's surface and features like ocean bathymetry.
Difference Between GISC and GIS - Online Degrees & Programs - GIS refers to the systems and tools for managing and analyzing spatial information, while GIScience is the study of the methods and techniques behind spatial data processing and analysis across various disciplines.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com