Vertical farming real estate involves specialized agricultural buildings designed for indoor crop production using advanced hydroponic and aeroponic systems, maximizing space efficiency and sustainability. Commercial real estate, by contrast, encompasses properties intended for business operations such as office buildings, retail centers, and warehouses, focusing on revenue generation through tenant leasing and location value. Explore the evolving dynamics between vertical farming real estate and traditional commercial properties to understand emerging investment opportunities.
Why it is important
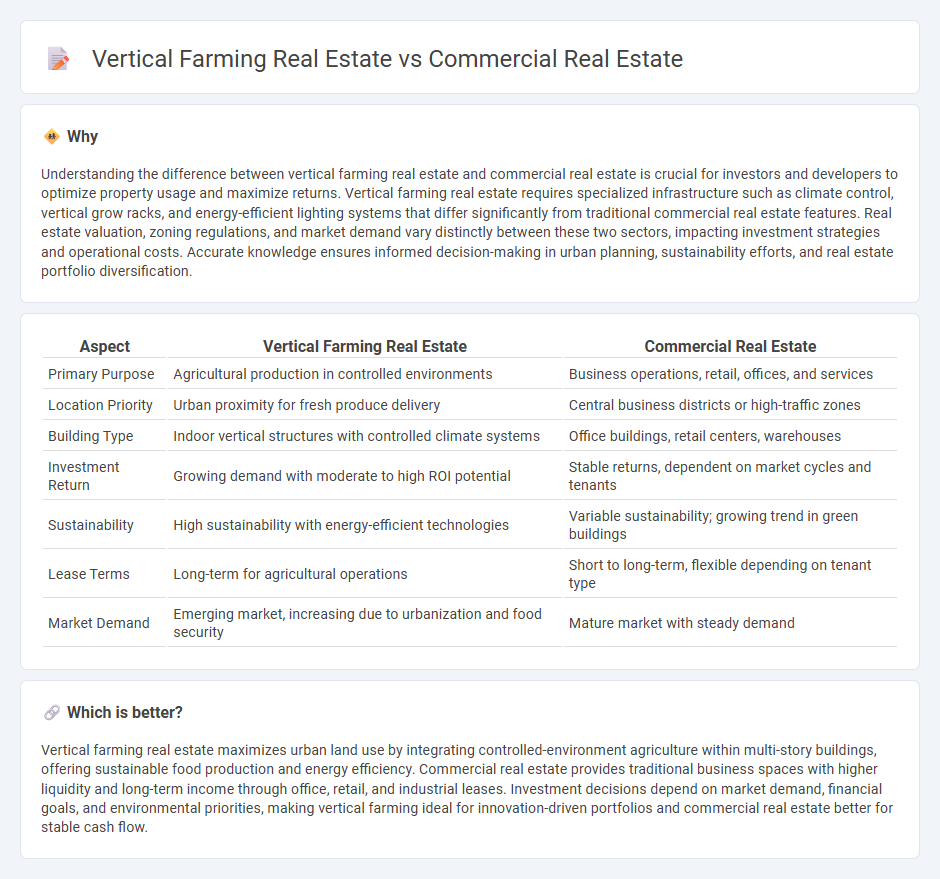
Understanding the difference between vertical farming real estate and commercial real estate is crucial for investors and developers to optimize property usage and maximize returns. Vertical farming real estate requires specialized infrastructure such as climate control, vertical grow racks, and energy-efficient lighting systems that differ significantly from traditional commercial real estate features. Real estate valuation, zoning regulations, and market demand vary distinctly between these two sectors, impacting investment strategies and operational costs. Accurate knowledge ensures informed decision-making in urban planning, sustainability efforts, and real estate portfolio diversification.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Real Estate | Commercial Real Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Agricultural production in controlled environments | Business operations, retail, offices, and services |
| Location Priority | Urban proximity for fresh produce delivery | Central business districts or high-traffic zones |
| Building Type | Indoor vertical structures with controlled climate systems | Office buildings, retail centers, warehouses |
| Investment Return | Growing demand with moderate to high ROI potential | Stable returns, dependent on market cycles and tenants |
| Sustainability | High sustainability with energy-efficient technologies | Variable sustainability; growing trend in green buildings |
| Lease Terms | Long-term for agricultural operations | Short to long-term, flexible depending on tenant type |
| Market Demand | Emerging market, increasing due to urbanization and food security | Mature market with steady demand |
Which is better?
Vertical farming real estate maximizes urban land use by integrating controlled-environment agriculture within multi-story buildings, offering sustainable food production and energy efficiency. Commercial real estate provides traditional business spaces with higher liquidity and long-term income through office, retail, and industrial leases. Investment decisions depend on market demand, financial goals, and environmental priorities, making vertical farming ideal for innovation-driven portfolios and commercial real estate better for stable cash flow.
Connection
Vertical farming real estate and commercial real estate intersect through the adaptive reuse of urban spaces, optimizing high-value locations for sustainable agriculture. Investors increasingly integrate vertical farms within commercial properties to enhance property value and support local food supply chains. This fusion leverages commercial real estate's infrastructure, promoting environmentally friendly developments and boosting urban land efficiency.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations for commercial real estate typically emphasize retail, office, and industrial uses with restrictions based on location, building height, and floor area ratio, while vertical farming real estate often falls under agricultural or mixed-use zoning categories requiring allowances for controlled-environment agriculture. Vertical farming operations must comply with specific regulations involving water usage, energy consumption, and waste management, which differ significantly from traditional commercial real estate requirements. Explore detailed zoning law comparisons to optimize property selection for your real estate investment or development project.
Lease structure
Commercial real estate lease structures typically involve triple net leases where tenants pay rent along with property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs, ensuring stable income for landlords. Vertical farming real estate leases may include specialized clauses addressing utility expenses, crop-related liabilities, and modifications for climate control systems to accommodate agricultural operations. Explore detailed comparisons of lease structures to optimize investment strategies in these distinct real estate sectors.
Infrastructure requirements
Commercial real estate demands extensive infrastructure such as robust structural frameworks, advanced HVAC systems, and scalable utilities to support diverse business operations. Vertical farming real estate prioritizes specialized infrastructure including controlled environment agriculture technology, hydroponic or aeroponic systems, LED grow lighting, and precise climate control mechanisms to optimize crop yield. Explore the unique infrastructure needs shaping these real estate sectors for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
CENTURY 21 Commercial Real Estate - Offers commercial properties for sale or lease, helping investors find the right investment opportunities.
Commercial Property on Wikipedia - Provides an overview of commercial property, including types like office buildings and retail stores.
LoopNet - A leading marketplace for commercial real estate listings, offering both sale and lease options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com