Infill development focuses on utilizing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas to create compact, walkable communities, reducing the need for extensive infrastructure expansion. Urban sprawl, characterized by low-density, peripheral expansion, often leads to increased traffic congestion, higher infrastructure costs, and loss of green spaces. Explore the benefits and challenges of infill development compared to urban sprawl to understand sustainable urban growth strategies.
Why it is important
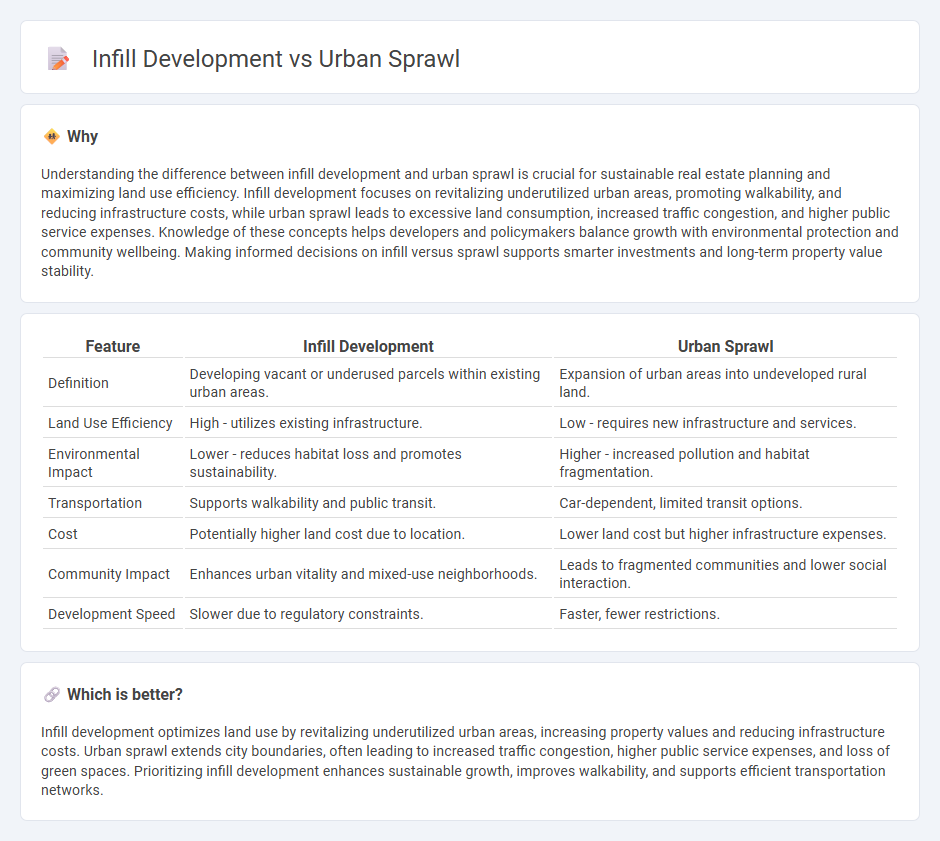
Understanding the difference between infill development and urban sprawl is crucial for sustainable real estate planning and maximizing land use efficiency. Infill development focuses on revitalizing underutilized urban areas, promoting walkability, and reducing infrastructure costs, while urban sprawl leads to excessive land consumption, increased traffic congestion, and higher public service expenses. Knowledge of these concepts helps developers and policymakers balance growth with environmental protection and community wellbeing. Making informed decisions on infill versus sprawl supports smarter investments and long-term property value stability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Infill Development | Urban Sprawl |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Developing vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas. | Expansion of urban areas into undeveloped rural land. |
| Land Use Efficiency | High - utilizes existing infrastructure. | Low - requires new infrastructure and services. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower - reduces habitat loss and promotes sustainability. | Higher - increased pollution and habitat fragmentation. |
| Transportation | Supports walkability and public transit. | Car-dependent, limited transit options. |
| Cost | Potentially higher land cost due to location. | Lower land cost but higher infrastructure expenses. |
| Community Impact | Enhances urban vitality and mixed-use neighborhoods. | Leads to fragmented communities and lower social interaction. |
| Development Speed | Slower due to regulatory constraints. | Faster, fewer restrictions. |
Which is better?
Infill development optimizes land use by revitalizing underutilized urban areas, increasing property values and reducing infrastructure costs. Urban sprawl extends city boundaries, often leading to increased traffic congestion, higher public service expenses, and loss of green spaces. Prioritizing infill development enhances sustainable growth, improves walkability, and supports efficient transportation networks.
Connection
Infill development targets underutilized urban areas to increase density and reduce the need for outward expansion, directly counteracting urban sprawl. Urban sprawl occurs when cities expand into peripheral rural land, resulting in increased infrastructure costs, habitat loss, and longer commutes. By promoting infill development, cities can optimize land use, enhance walkability, and minimize the environmental and economic impacts associated with sprawling growth patterns.
Key Terms
Land Use
Urban sprawl leads to the inefficient use of land by expanding development over large areas, often resulting in increased infrastructure costs, habitat loss, and longer commutes. Infill development prioritizes the use of vacant or underutilized land within existing urban areas, promoting higher density, reducing environmental impact, and improving access to amenities. Explore more about sustainable land use strategies that balance growth and conservation.
Density
Urban sprawl leads to low-density, fragmented development that expands city boundaries and increases reliance on automobiles, contributing to higher infrastructure costs and environmental degradation. Infill development prioritizes higher density by utilizing vacant or underused urban land, promoting efficient land use, reducing commute times, and supporting public transportation systems. Discover how density impacts sustainable urban growth and the balance between these development strategies.
Infrastructure
Urban sprawl typically leads to higher infrastructure costs due to the extended networks of roads, utilities, and public services required to support dispersed development patterns. Infill development maximizes existing infrastructure by repurposing underutilized land within established urban areas, reducing the need for costly expansions and promoting efficient resource use. Explore more about the impact of infrastructure planning on sustainable urban growth.
Source and External Links
14.3 The Impacts of Urban Sprawl - Urban sprawl is the unplanned extension of low-density residential, commercial, and industrial development beyond city boundaries, characterized by dispersed development, high automobile dependence, habitat fragmentation, and negative effects on energy use, environment, and health.
Urban sprawl | Definition, Examples, Problems, Causes, & ... - Urban sprawl refers to the rapid geographic expansion of cities, often linked to population increases and lifestyle choices, resulting in significant increases in the spatial footprint of metropolitan areas despite varying levels of population growth.
What Is Urban Sprawl? - Urban sprawl is the outward expansion of cities characterized by low-density residential housing and single-use zoning, which leads to increased car dependency and environmental degradation including habitat loss and pollution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com