Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property prices based on market demand, competition, and buyer behavior, enabling sellers to maximize revenue through flexible pricing strategies. Auction pricing, on the other hand, allows bidders to compete openly, often leading to faster sales and transparent price discovery. Explore more about how these pricing models impact real estate transactions and investment outcomes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dynamic pricing and auction pricing is crucial in real estate as dynamic pricing adjusts property values based on real-time market demand and trends, whereas auction pricing relies on competitive bidding to determine the final sale price. Dynamic pricing allows sellers to optimize revenue by reacting quickly to market fluctuations, while auction pricing provides transparency and urgency, often leading to higher sale prices in competitive markets. Accurate knowledge of these strategies enables investors and sellers to select the most effective pricing mechanism, maximizing returns and minimizing time on market. Choosing the appropriate pricing model aligns property valuation with market behavior and buyer engagement patterns.
Comparison Table
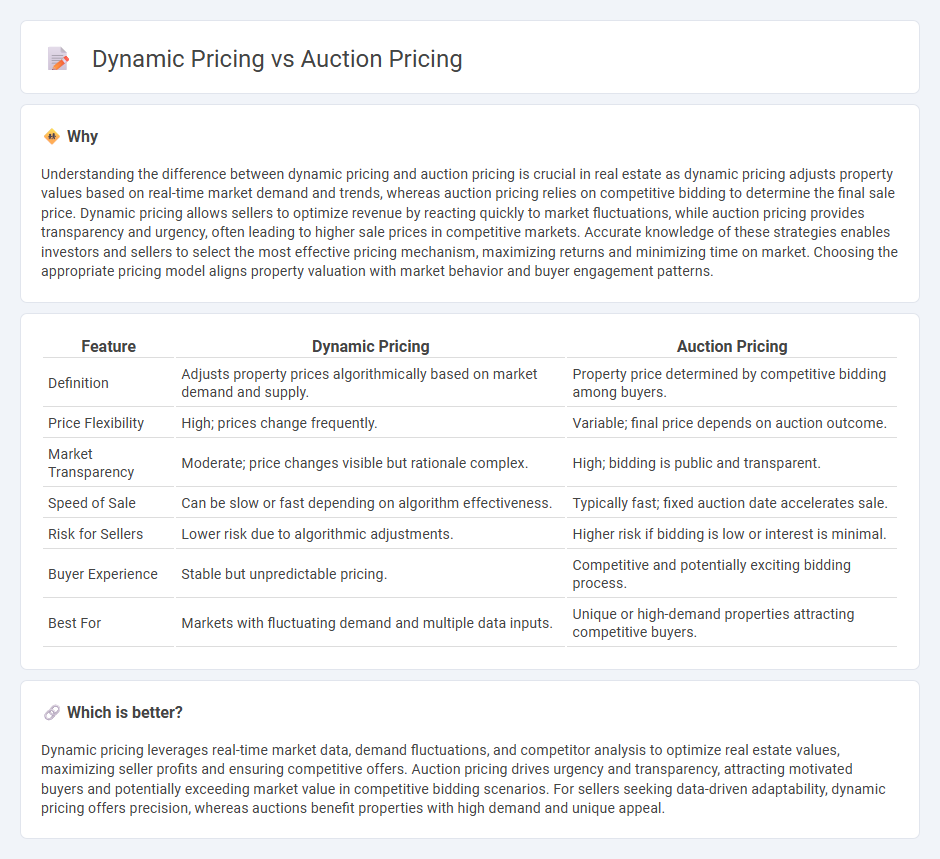
| Feature | Dynamic Pricing | Auction Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusts property prices algorithmically based on market demand and supply. | Property price determined by competitive bidding among buyers. |
| Price Flexibility | High; prices change frequently. | Variable; final price depends on auction outcome. |
| Market Transparency | Moderate; price changes visible but rationale complex. | High; bidding is public and transparent. |
| Speed of Sale | Can be slow or fast depending on algorithm effectiveness. | Typically fast; fixed auction date accelerates sale. |
| Risk for Sellers | Lower risk due to algorithmic adjustments. | Higher risk if bidding is low or interest is minimal. |
| Buyer Experience | Stable but unpredictable pricing. | Competitive and potentially exciting bidding process. |
| Best For | Markets with fluctuating demand and multiple data inputs. | Unique or high-demand properties attracting competitive buyers. |
Which is better?
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time market data, demand fluctuations, and competitor analysis to optimize real estate values, maximizing seller profits and ensuring competitive offers. Auction pricing drives urgency and transparency, attracting motivated buyers and potentially exceeding market value in competitive bidding scenarios. For sellers seeking data-driven adaptability, dynamic pricing offers precision, whereas auctions benefit properties with high demand and unique appeal.
Connection
Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property values based on real-time market demand, while auction pricing determines final sale prices through competitive bidding. Both strategies leverage market fluctuations and buyer behavior to optimize property valuation and maximize seller revenue. Integrating dynamic pricing with auction methods enhances pricing accuracy and market responsiveness in real estate transactions.
Key Terms
Reserve Price
Auction pricing often incorporates a reserve price, which is the minimum acceptable bid set by the seller to protect the item's value from dropping too low. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, with no fixed minimum, allowing more flexibility but less price protection. Discover how setting an effective reserve price can optimize your auction's revenue potential.
Market Demand
Auction pricing adjusts prices based on real-time bids, directly reflecting immediate market demand fluctuations and buyer competition, often leading to higher prices in high-demand scenarios. Dynamic pricing employs algorithms that analyze various market signals such as consumer behavior, competitor pricing, and inventory levels to continuously optimize prices in response to shifting demand patterns. Explore more on how these pricing strategies leverage market demand for revenue maximization.
Price Adjustment
Auction pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on competitive bids, creating a transparent market-driven value for each item sold. Dynamic pricing uses algorithms to modify prices continuously based on factors like demand, customer behavior, and inventory levels, ensuring optimal revenue capture. Explore how businesses leverage these strategies to maximize profitability and market efficiency.
Source and External Links
How to Price Silent Auction Items: Complete Guide for 2025 - Winspire - Provides a four-step model for pricing auction items including fair market value, starting bid, minimum bid increase, and buy now option, with distinctions between silent and live auction pricing strategies such as live auctions starting at 25-30% FMV and higher bid flexibility.
How to Price Silent Auction Items (& Raise More) in 5 Steps - Recommends setting bidding increments at about 10% of the item's fair market value to keep bidding momentum, adjusting increments based on item popularity and past data, and rounding increments for bidder convenience.
How to Price Silent Auction Items: 12 Tips from an Expert - Emphasizes strategic starting bids around 30% FMV, competitive pricing for popular items like gift cards, adapting pricing during the event based on bidder interest, and conducting thorough market and past auction research for optimal pricing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com