Dynamic routing leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to optimize delivery paths, reducing transit times and operational costs. Multi-modal routing integrates various transportation modes--such as trucks, rail, and ships--to enhance flexibility and efficiency in complex supply chains. Explore the benefits and applications of both strategies to improve your logistics operations.
Why it is important
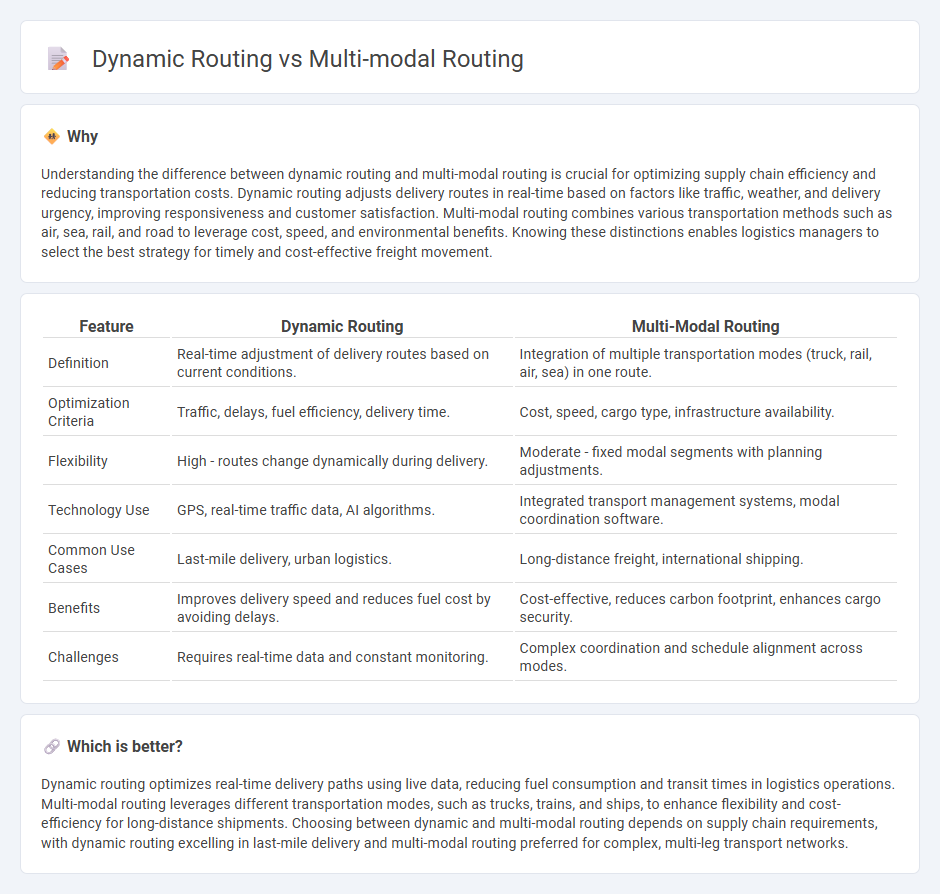
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and multi-modal routing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Dynamic routing adjusts delivery routes in real-time based on factors like traffic, weather, and delivery urgency, improving responsiveness and customer satisfaction. Multi-modal routing combines various transportation methods such as air, sea, rail, and road to leverage cost, speed, and environmental benefits. Knowing these distinctions enables logistics managers to select the best strategy for timely and cost-effective freight movement.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Multi-Modal Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of delivery routes based on current conditions. | Integration of multiple transportation modes (truck, rail, air, sea) in one route. |
| Optimization Criteria | Traffic, delays, fuel efficiency, delivery time. | Cost, speed, cargo type, infrastructure availability. |
| Flexibility | High - routes change dynamically during delivery. | Moderate - fixed modal segments with planning adjustments. |
| Technology Use | GPS, real-time traffic data, AI algorithms. | Integrated transport management systems, modal coordination software. |
| Common Use Cases | Last-mile delivery, urban logistics. | Long-distance freight, international shipping. |
| Benefits | Improves delivery speed and reduces fuel cost by avoiding delays. | Cost-effective, reduces carbon footprint, enhances cargo security. |
| Challenges | Requires real-time data and constant monitoring. | Complex coordination and schedule alignment across modes. |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing optimizes real-time delivery paths using live data, reducing fuel consumption and transit times in logistics operations. Multi-modal routing leverages different transportation modes, such as trucks, trains, and ships, to enhance flexibility and cost-efficiency for long-distance shipments. Choosing between dynamic and multi-modal routing depends on supply chain requirements, with dynamic routing excelling in last-mile delivery and multi-modal routing preferred for complex, multi-leg transport networks.
Connection
Dynamic routing enhances logistics efficiency by continuously adjusting delivery paths based on real-time data, while multi-modal routing optimizes transport by integrating different transportation modes such as trucks, trains, and ships. Combined, these approaches improve supply chain responsiveness and reduce transit times by selecting the most efficient routes and transportation combinations. The synergy between dynamic and multi-modal routing enables smarter decision-making in complex logistics networks, maximizing resource use and minimizing costs.
Key Terms
**Multi-modal routing:**
Multi-modal routing integrates various transportation modes such as walking, cycling, driving, and public transit to create optimal travel routes based on factors like travel time, cost, and environmental impact. It leverages real-time data and sophisticated algorithms to provide seamless transitions between modes, enhancing efficiency and user convenience. Explore further to understand how multi-modal routing transforms urban mobility and transportation planning.
Intermodal transportation
Multi-modal routing integrates various transportation modes such as rail, road, and sea to optimize intermodal transportation efficiency, reducing transit times and costs through synchronized scheduling and asset utilization. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on traffic conditions, delays, or disruptions, enhancing responsiveness but potentially increasing complexity in coordinating intermodal transfers. Explore deeper insights on how these routing strategies transform intermodal logistics for supply chain resilience.
Transshipment
Multi-modal routing integrates multiple transportation modes, optimizing transshipment points to enhance efficiency and reduce transit times in complex supply chains. Dynamic routing adapts in real-time to changing conditions, improving responsiveness at transshipment hubs by minimizing delays and adjusting routes based on demand and disruptions. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each method enhances transshipment strategies in modern logistics networks.
Source and External Links
A MULTI-MODAL ROUTE PLANNING APPROACH WITH AN ... - Multi-modal routing integrates different transport modes like driving, bus, subway, and walking into a layered network connected by transfer nodes and links, to provide optimal and personalized travel routes while maintaining each mode's independence and connectivity.
What is multi-model routing? - UbiOps - Multi-model routing in AI involves linking multiple specialized models either in series or parallel to handle various data types efficiently, enabling modular workflows for complex tasks like prompt enhancement and expert routing.
Multi-Modal Transportation Recommendation with Unified Route ... - Multi-modal routing integrates various transportation networks into a unified directed graph combining hubs and links from different transport modes, optimizing travel routes with constraints like limited mode transfers and spatial-temporal network dynamics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com