Reverse logistics focuses on managing product returns, recycling, and waste disposal to optimize resource recovery and reduce environmental impact. Last-mile delivery prioritizes the efficient transportation of goods from distribution centers to the final consumer, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and minimize delivery times. Explore the key differences and strategic benefits of reverse logistics versus last-mile delivery to improve your supply chain effectiveness.
Why it is important
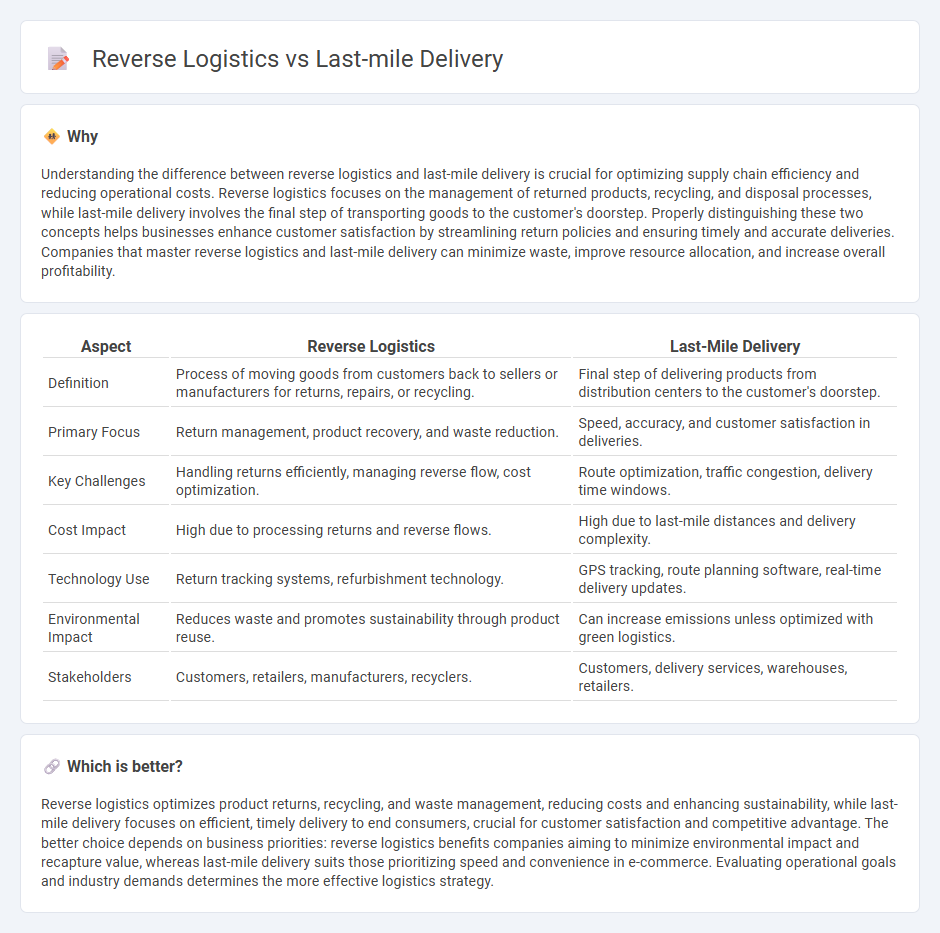
Understanding the difference between reverse logistics and last-mile delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Reverse logistics focuses on the management of returned products, recycling, and disposal processes, while last-mile delivery involves the final step of transporting goods to the customer's doorstep. Properly distinguishing these two concepts helps businesses enhance customer satisfaction by streamlining return policies and ensuring timely and accurate deliveries. Companies that master reverse logistics and last-mile delivery can minimize waste, improve resource allocation, and increase overall profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Logistics | Last-Mile Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of moving goods from customers back to sellers or manufacturers for returns, repairs, or recycling. | Final step of delivering products from distribution centers to the customer's doorstep. |
| Primary Focus | Return management, product recovery, and waste reduction. | Speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction in deliveries. |
| Key Challenges | Handling returns efficiently, managing reverse flow, cost optimization. | Route optimization, traffic congestion, delivery time windows. |
| Cost Impact | High due to processing returns and reverse flows. | High due to last-mile distances and delivery complexity. |
| Technology Use | Return tracking systems, refurbishment technology. | GPS tracking, route planning software, real-time delivery updates. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and promotes sustainability through product reuse. | Can increase emissions unless optimized with green logistics. |
| Stakeholders | Customers, retailers, manufacturers, recyclers. | Customers, delivery services, warehouses, retailers. |
Which is better?
Reverse logistics optimizes product returns, recycling, and waste management, reducing costs and enhancing sustainability, while last-mile delivery focuses on efficient, timely delivery to end consumers, crucial for customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. The better choice depends on business priorities: reverse logistics benefits companies aiming to minimize environmental impact and recapture value, whereas last-mile delivery suits those prioritizing speed and convenience in e-commerce. Evaluating operational goals and industry demands determines the more effective logistics strategy.
Connection
Reverse logistics and last-mile delivery are interconnected through their shared focus on the efficient movement of goods between end consumers and supply chains. Effective reverse logistics relies on last-mile delivery infrastructure to handle returns, repairs, and recycling, minimizing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction. Optimizing both processes reduces delivery times, lowers transportation expenses, and improves sustainability in the overall logistics network.
Key Terms
**Last-mile delivery:**
Last-mile delivery, the final step in the supply chain, involves transporting goods from a distribution center to the customer's doorstep, optimizing speed and efficiency to meet rising consumer expectations for fast shipping. Technologies such as route optimization software, real-time tracking, and autonomous delivery vehicles significantly enhance last-mile delivery operations by reducing costs and improving accuracy. Explore innovative strategies and tools shaping the future of last-mile delivery to stay ahead in logistics management.
Route optimization
Last-mile delivery centers on efficient route optimization to ensure timely parcel arrival at customer doorsteps, minimizing transportation costs and fuel consumption. Reverse logistics uses route optimization to streamline the return process, reducing lead time and enhancing resource allocation for product returns and recycling. Explore how advanced route optimization technologies revolutionize both last-mile delivery and reverse logistics operations.
Delivery windows
Last-mile delivery emphasizes precise delivery windows to meet customer expectations for timely arrival, often within narrow timeframes ranging from one to two hours. Reverse logistics schedules are typically more flexible but still require clear communication to facilitate efficient pickups and returns, balancing convenience with operational cost. Explore more insights on optimizing delivery windows in last-mile and reverse logistics operations.
Source and External Links
Last mile delivery: solutions for your business | DHL Discover - Last-mile delivery, also known as final mile, is the final leg of moving goods from a local distribution center to the consumer's doorstep using vehicles or drop-off points, focusing on speed, cost, and reliability as key factors for customer satisfaction and brand interaction.
Last Mile Delivery Logistics, Trends and Data for Retailers Explained | eMarketer - Last-mile delivery is the crucial last phase where goods move from warehouse to customer, often being the most expensive and time-consuming part, but essential for customer satisfaction, driving sales by enabling faster delivery and convenience.
What is a Last Mile? Complete Guide to Last Mile Delivery & Logistics | FarEye - Last mile delivery is the final step bringing products to end users, and leveraging technology like route planning, real-time tracking, and communication tools can optimize efficiency and reduce time and costs of deliveries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com