Dynamic routing leverages real-time data and algorithms to continuously adjust delivery paths, optimizing efficiency in logistics operations. Heuristic routing relies on predefined rules and approximations to determine routes quickly, offering practical solutions when immediate decisions are needed. Explore the advantages and use cases of both methods to enhance your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and heuristic routing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Dynamic routing uses real-time data to adjust routes based on current traffic and delivery conditions, enhancing responsiveness and flexibility. In contrast, heuristic routing relies on predefined rules and approximations to quickly generate solutions, which can be less adaptive but computationally faster. Selecting the appropriate routing method ensures improved delivery accuracy, customer satisfaction, and operational scalability in logistics management.
Comparison Table
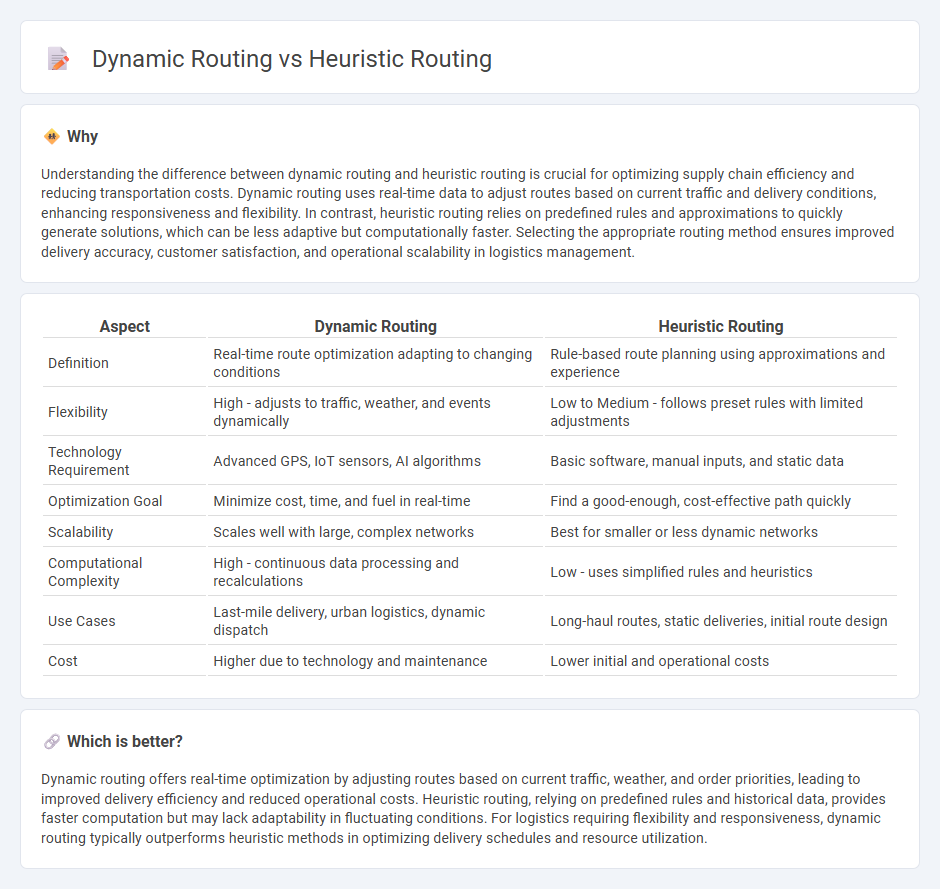
| Aspect | Dynamic Routing | Heuristic Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time route optimization adapting to changing conditions | Rule-based route planning using approximations and experience |
| Flexibility | High - adjusts to traffic, weather, and events dynamically | Low to Medium - follows preset rules with limited adjustments |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced GPS, IoT sensors, AI algorithms | Basic software, manual inputs, and static data |
| Optimization Goal | Minimize cost, time, and fuel in real-time | Find a good-enough, cost-effective path quickly |
| Scalability | Scales well with large, complex networks | Best for smaller or less dynamic networks |
| Computational Complexity | High - continuous data processing and recalculations | Low - uses simplified rules and heuristics |
| Use Cases | Last-mile delivery, urban logistics, dynamic dispatch | Long-haul routes, static deliveries, initial route design |
| Cost | Higher due to technology and maintenance | Lower initial and operational costs |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing offers real-time optimization by adjusting routes based on current traffic, weather, and order priorities, leading to improved delivery efficiency and reduced operational costs. Heuristic routing, relying on predefined rules and historical data, provides faster computation but may lack adaptability in fluctuating conditions. For logistics requiring flexibility and responsiveness, dynamic routing typically outperforms heuristic methods in optimizing delivery schedules and resource utilization.
Connection
Dynamic routing and heuristic routing are connected through their shared goal of optimizing supply chain efficiency by continuously adapting routes based on real-time data and problem-specific algorithms. Dynamic routing adjusts delivery paths in response to changing conditions such as traffic or demand, while heuristic routing employs rule-based approaches to generate near-optimal solutions quickly for complex logistics problems. Together, they enhance route planning by combining adaptive flexibility with computational efficiency, reducing transportation costs and improving service reliability.
Key Terms
Optimization algorithms
Heuristic routing uses rule-based algorithms tailored for specific network conditions, enabling quicker, computationally efficient path selection without exhaustive search. Dynamic routing employs optimization algorithms like Dijkstra's and Bellman-Ford, updating routes based on real-time network state to find shortest or least costly paths dynamically. Discover more about how these optimization techniques impact network performance and reliability.
Real-time data
Heuristic routing uses predefined rules and estimations to make routing decisions, often without relying on current network conditions, leading to less adaptability in real-time scenarios. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and EIGRP, continuously gather and utilize real-time network data like link status and traffic load to optimize path selection and improve network performance. Explore the advantages of real-time data in routing to enhance your network's efficiency and resiliency.
Flexibility
Heuristic routing offers limited flexibility by relying on predefined rules and static parameters, which may not adapt well to changing network conditions. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and EIGRP, enhance flexibility by continuously analyzing and updating routes based on real-time network topology and traffic changes. Explore the advantages of each routing method to determine the best fit for your network's flexibility requirements.
Source and External Links
Heuristic routing - Wikipedia - Heuristic routing uses algorithms to find better, though not always optimal, paths for data delivery especially when network topology problems occur, relying on empirical knowledge and heuristic problem-solving methods rather than purely deterministic algorithms.
A Heuristic Routing Mechanism Using a New Addressing Scheme (PDF) - Introduces the concept of variable addresses in heuristic routing, proposing a flexible mechanism using heuristic solutions, including gene-inspired methods to efficiently address routing challenges in dynamic networks.
Heuristic routing : Notes | PDF - SlideShare - Summarizes heuristic routing as a method in telecommunications and transport networks for selecting alternative paths when network issues arise, leveraging heuristic approaches for problem solving in routing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com