Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as order processing and inventory management through software bots, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) specialize in physical material handling, navigating warehouses independently to transport goods and optimize supply chain operations. Explore how integrating RPA and AMR can transform logistics workflows for improved productivity and cost savings.
Why it is important
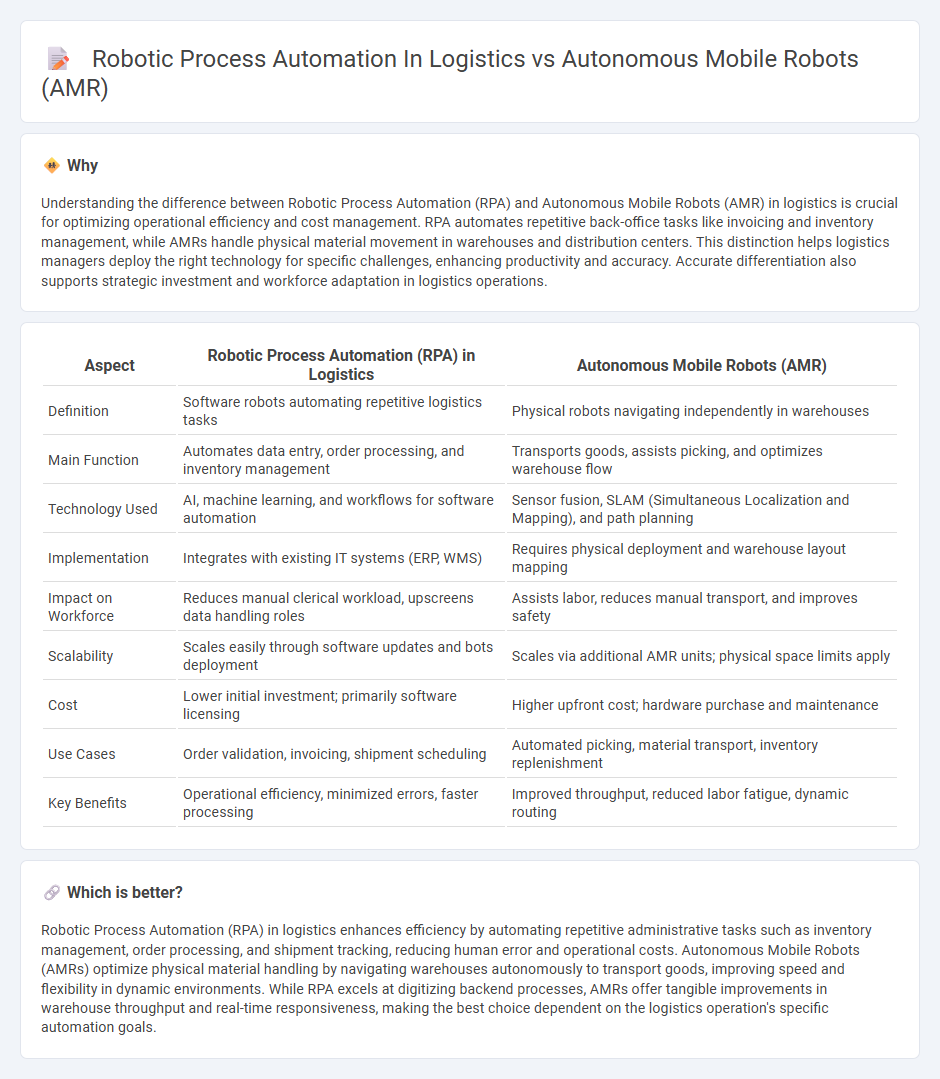
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) in logistics is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and cost management. RPA automates repetitive back-office tasks like invoicing and inventory management, while AMRs handle physical material movement in warehouses and distribution centers. This distinction helps logistics managers deploy the right technology for specific challenges, enhancing productivity and accuracy. Accurate differentiation also supports strategic investment and workforce adaptation in logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive logistics tasks | Physical robots navigating independently in warehouses |
| Main Function | Automates data entry, order processing, and inventory management | Transports goods, assists picking, and optimizes warehouse flow |
| Technology Used | AI, machine learning, and workflows for software automation | Sensor fusion, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and path planning |
| Implementation | Integrates with existing IT systems (ERP, WMS) | Requires physical deployment and warehouse layout mapping |
| Impact on Workforce | Reduces manual clerical workload, upscreens data handling roles | Assists labor, reduces manual transport, and improves safety |
| Scalability | Scales easily through software updates and bots deployment | Scales via additional AMR units; physical space limits apply |
| Cost | Lower initial investment; primarily software licensing | Higher upfront cost; hardware purchase and maintenance |
| Use Cases | Order validation, invoicing, shipment scheduling | Automated picking, material transport, inventory replenishment |
| Key Benefits | Operational efficiency, minimized errors, faster processing | Improved throughput, reduced labor fatigue, dynamic routing |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics enhances efficiency by automating repetitive administrative tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking, reducing human error and operational costs. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) optimize physical material handling by navigating warehouses autonomously to transport goods, improving speed and flexibility in dynamic environments. While RPA excels at digitizing backend processes, AMRs offer tangible improvements in warehouse throughput and real-time responsiveness, making the best choice dependent on the logistics operation's specific automation goals.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances logistics by streamlining data management, order processing, and inventory control, enabling Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) to operate with real-time, accurate information. Integration of RPA systems with AMRs facilitates seamless coordination in warehouse environments, improving efficiency in tasks such as goods picking, sorting, and transportation. This synergy reduces human error, accelerates throughput, and optimizes supply chain workflows, driving cost savings and operational agility.
Key Terms
Navigation Systems
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) in logistics employ advanced navigation systems incorporating LiDAR, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and AI-driven path planning to adapt dynamically to warehouse environments and optimize route efficiency. In contrast, robotic process automation (RPA) focuses on software-based automation of repetitive back-office tasks without physical navigation capabilities, enhancing data processing and operational workflows. Explore detailed comparisons of navigation technologies and operational impact to understand how AMRs and RPA transform logistics efficiency.
Workflow Automation
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) enhance logistics by automating physical tasks such as goods transportation and inventory management, leveraging sensors and AI for real-time navigation and obstacle avoidance. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) optimizes workflow automation by automating repetitive digital tasks, such as order processing, shipment tracking, and data entry, increasing efficiency and accuracy in supply chain management. Explore how integrating AMR and RPA can create seamless, end-to-end workflow automation to maximize logistics productivity.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) enhance logistics efficiency by dynamically navigating environments and collaborating directly with human workers for tasks like inventory management and order fulfillment, whereas Robotic Process Automation (RPA) optimizes backend operations by automating repetitive digital workflows such as data entry and shipment tracking. Human-Robot Collaboration in logistics leverages AMRs' physical interaction capabilities alongside RPA's digital automation to create seamless end-to-end process integration. Explore how these technologies synergize to revolutionize human-robot teamwork in modern supply chain management.
Source and External Links
A Guide to Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) - AutoStore - AMRs are intelligent robots capable of autonomous navigation and real-time decision-making using advanced sensors and intelligent software, unlike AGVs that follow fixed paths, making AMRs highly versatile for warehouses, manufacturing, and logistics.
AMR vs AGV: Key Differences Explained - Mobile Industrial Robots - AMRs offer agile, flexible, and intelligent navigation with 3D cameras and LiDAR, enabling them to dynamically avoid obstacles and comply with safety standards, unlike AGVs which follow fixed routes and require manual intervention for obstacles.
Automated & Autonomous Mobile Robots | Robotnik(r) - Robotnik's AMRs use advanced SLAM technology to navigate freely in dynamic and unstructured environments, adaptable across industries for tasks like logistics transport, assembly assistance, quality inspection, and scalable deployment without complex setups.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com