Urban logistics hubs streamline last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory within city centers, reducing transit times and traffic congestion. Satellite depots complement these hubs by extending storage and distribution capabilities to peripheral areas, enhancing flexibility and coverage. Explore how integrating urban logistics hubs with satellite depots can optimize supply chain efficiency and sustainable urban mobility.
Why it is important
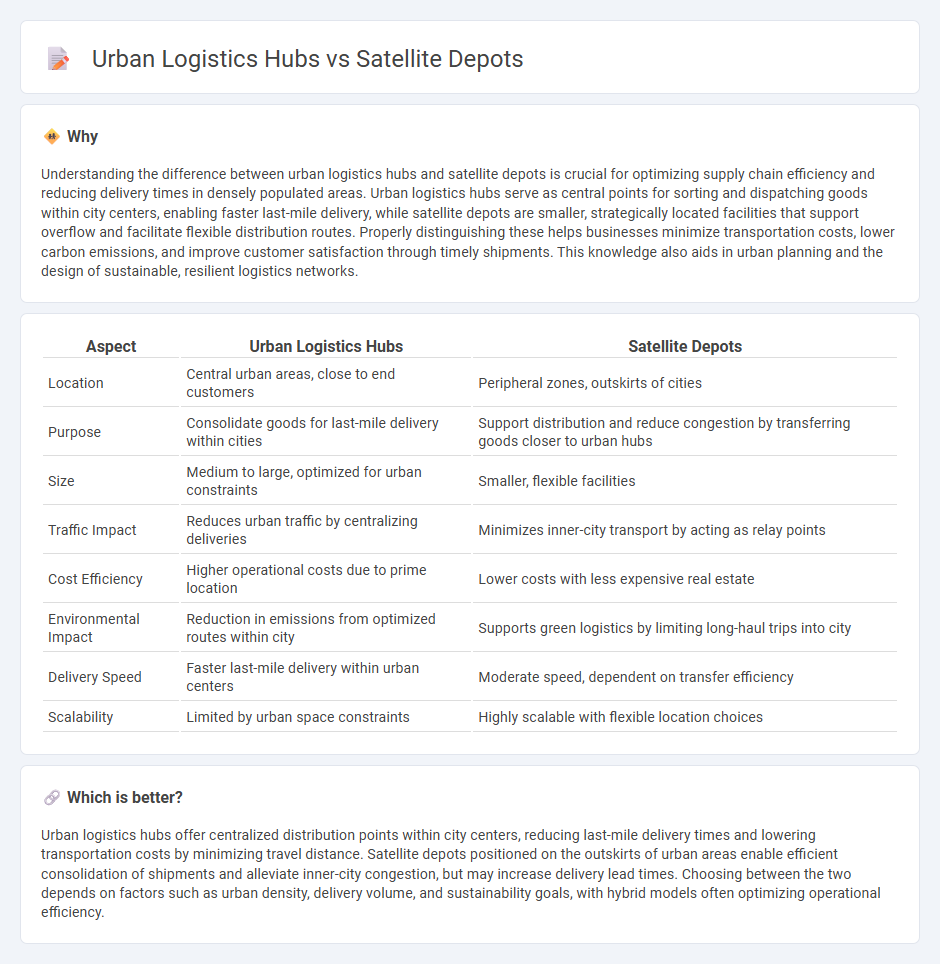
Understanding the difference between urban logistics hubs and satellite depots is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing delivery times in densely populated areas. Urban logistics hubs serve as central points for sorting and dispatching goods within city centers, enabling faster last-mile delivery, while satellite depots are smaller, strategically located facilities that support overflow and facilitate flexible distribution routes. Properly distinguishing these helps businesses minimize transportation costs, lower carbon emissions, and improve customer satisfaction through timely shipments. This knowledge also aids in urban planning and the design of sustainable, resilient logistics networks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Logistics Hubs | Satellite Depots |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Central urban areas, close to end customers | Peripheral zones, outskirts of cities |
| Purpose | Consolidate goods for last-mile delivery within cities | Support distribution and reduce congestion by transferring goods closer to urban hubs |
| Size | Medium to large, optimized for urban constraints | Smaller, flexible facilities |
| Traffic Impact | Reduces urban traffic by centralizing deliveries | Minimizes inner-city transport by acting as relay points |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to prime location | Lower costs with less expensive real estate |
| Environmental Impact | Reduction in emissions from optimized routes within city | Supports green logistics by limiting long-haul trips into city |
| Delivery Speed | Faster last-mile delivery within urban centers | Moderate speed, dependent on transfer efficiency |
| Scalability | Limited by urban space constraints | Highly scalable with flexible location choices |
Which is better?
Urban logistics hubs offer centralized distribution points within city centers, reducing last-mile delivery times and lowering transportation costs by minimizing travel distance. Satellite depots positioned on the outskirts of urban areas enable efficient consolidation of shipments and alleviate inner-city congestion, but may increase delivery lead times. Choosing between the two depends on factors such as urban density, delivery volume, and sustainability goals, with hybrid models often optimizing operational efficiency.
Connection
Urban logistics hubs and satellite depots are interconnected through advanced transportation networks and real-time data exchange systems that optimize last-mile delivery efficiency. These facilities leverage IoT technology and AI-driven route planning to synchronize inventory levels, reduce delivery times, and minimize traffic congestion within city centers. Integration of electric vehicles and automated loading systems further enhances sustainable urban logistics operations while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Satellite depots enable decentralization by positioning smaller distribution centers closer to urban demand points, reducing last-mile delivery times and congestion. Urban logistics hubs consolidate freight volumes within city boundaries while optimizing space utilization and supporting sustainable delivery methods such as cargo bikes and electric vehicles. Explore how decentralization through satellite depots and urban hubs transforms urban freight efficiency and environmental impact.
Last-mile delivery
Satellite depots optimize last-mile delivery by storing inventory closer to urban centers, reducing delivery times and vehicle emissions. Urban logistics hubs concentrate multiple transportation modes and consolidate shipments, enhancing efficiency in dense city environments. Explore the benefits and strategic differences between satellite depots and urban logistics hubs for optimized last-mile delivery solutions.
Inventory positioning
Satellite depots and urban logistics hubs optimize inventory positioning by balancing proximity to end customers with storage capacity. Satellite depots typically hold smaller inventories closer to demand centers to enable rapid last-mile delivery, while urban logistics hubs serve as larger storage points facilitating efficient consolidation and distribution. Explore how inventory strategies differ between these models to enhance urban supply chain performance.
Source and External Links
Satellite Depot - Lark - A satellite depot is a mini-warehouse or satellite facility strategically located near end consumers to reduce delivery times and costs, enhance inventory turnover, and provide more localized service, especially used in the food and beverage industry for efficient distribution and supply chain management.
Benefits of Cross-Docking Facilities & Satellite Depots | CRS UK - A satellite depot often functions as a cross-docking facility, where goods are quickly transferred without long storage, improving delivery times and reducing transport costs, and is commonly used for temperature-sensitive products and in urban areas with space constraints.
A new model for Last-Mile Delivery and Satellite Depots management - Satellite depots play a significant role in urban freight logistics by enabling efficient last-mile delivery systems, optimizing city logistics including demand disruptions and the integration of crowdsourcing technologies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com