Quick commerce relies on rapid, small-scale deliveries, emphasizing speed and customer convenience through localized inventory and streamlined order processing. Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) serve as compact warehouses situated close to urban areas, optimizing storage density and automation to enable faster fulfillment times. Explore the distinct advantages of quick commerce and micro-fulfillment centers to understand their impact on modern logistics.
Why it is important
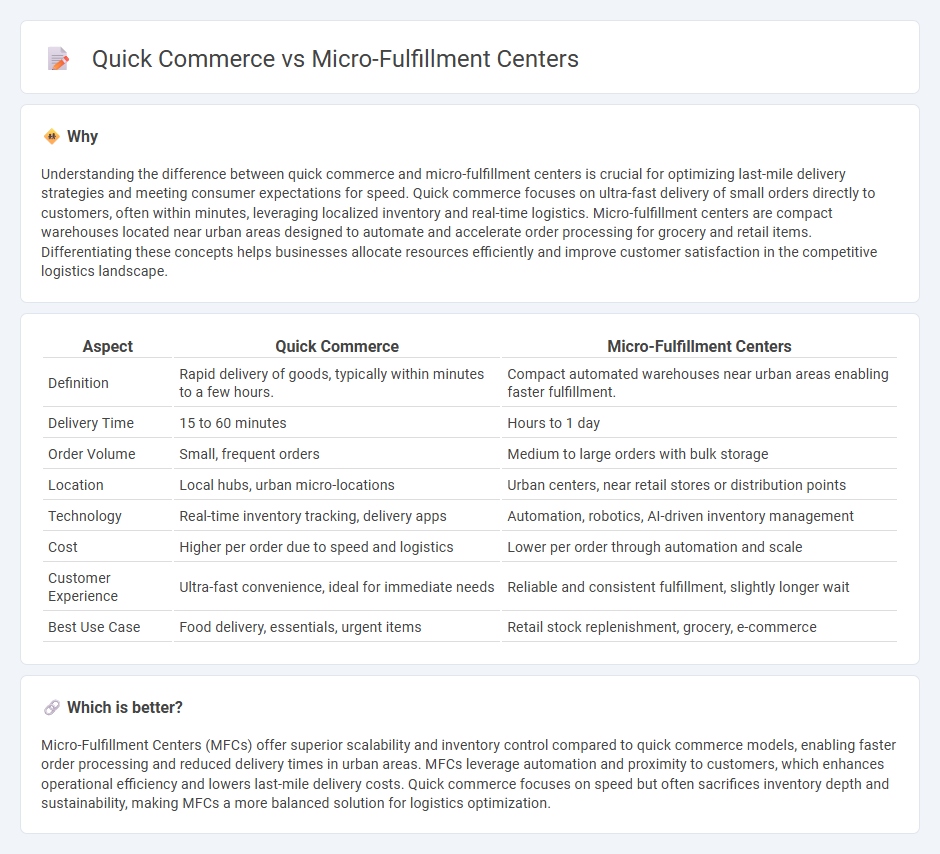
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and micro-fulfillment centers is crucial for optimizing last-mile delivery strategies and meeting consumer expectations for speed. Quick commerce focuses on ultra-fast delivery of small orders directly to customers, often within minutes, leveraging localized inventory and real-time logistics. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact warehouses located near urban areas designed to automate and accelerate order processing for grocery and retail items. Differentiating these concepts helps businesses allocate resources efficiently and improve customer satisfaction in the competitive logistics landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quick Commerce | Micro-Fulfillment Centers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid delivery of goods, typically within minutes to a few hours. | Compact automated warehouses near urban areas enabling faster fulfillment. |
| Delivery Time | 15 to 60 minutes | Hours to 1 day |
| Order Volume | Small, frequent orders | Medium to large orders with bulk storage |
| Location | Local hubs, urban micro-locations | Urban centers, near retail stores or distribution points |
| Technology | Real-time inventory tracking, delivery apps | Automation, robotics, AI-driven inventory management |
| Cost | Higher per order due to speed and logistics | Lower per order through automation and scale |
| Customer Experience | Ultra-fast convenience, ideal for immediate needs | Reliable and consistent fulfillment, slightly longer wait |
| Best Use Case | Food delivery, essentials, urgent items | Retail stock replenishment, grocery, e-commerce |
Which is better?
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) offer superior scalability and inventory control compared to quick commerce models, enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery times in urban areas. MFCs leverage automation and proximity to customers, which enhances operational efficiency and lowers last-mile delivery costs. Quick commerce focuses on speed but often sacrifices inventory depth and sustainability, making MFCs a more balanced solution for logistics optimization.
Connection
Quick commerce relies heavily on micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) to enable rapid delivery of goods within urban areas by optimizing inventory storage close to consumers. These compact warehouses use advanced automation and real-time data analytics to process orders efficiently, reducing last-mile delivery times significantly. The integration of MFCs in the quick commerce model enhances supply chain responsiveness and customer satisfaction by minimizing logistical delays.
Key Terms
Order Fulfillment Speed
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automated storage and retrieval systems to accelerate order fulfillment, reducing processing times to under 30 minutes. Quick commerce relies on hyperlocal inventory and optimized delivery routes to offer speedy last-mile delivery within 15 to 30 minutes. Discover more about how these innovations reshape consumer expectations and supply chain efficiencies.
Inventory Localization
Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) optimize inventory localization by strategically placing goods closer to urban consumers, reducing delivery times and last-mile costs in quick commerce. Quick commerce depends heavily on these compact, technology-driven warehouses to fulfill rapid delivery promises, enabling real-time inventory management and minimizing stockouts. Discover how inventory localization in micro-fulfillment centers revolutionizes quick commerce efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Last-Mile Delivery
Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) streamline last-mile delivery by enabling rapid order processing near urban hubs, reducing delivery times and costs in quick commerce. Quick commerce relies on small, strategically located MFCs to fulfill high-demand, small-basket orders efficiently, enhancing customer satisfaction through faster deliveries. Explore how integrating micro-fulfillment centers optimizes last-mile logistics in the dynamic quick commerce landscape.
Source and External Links
Micro-Fulfillment Explained: Key Benefits and Strategies for Ecommerce Success - Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are small, highly efficient warehouses (3,000-10,000 sq ft) positioned in urban areas to store fast-moving products for rapid shipping, significantly reducing last-mile delivery time and cost while improving supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What Are Micro Fulfillment Centers? - City National Bank - MFCs typically hold up to 15,000 items and use compact designs to store more products per square foot than conventional warehouses, enabling faster order turnaround and higher inventory turnover, especially in grocery retail, which is adopting MFCs rapidly following pandemic-driven demand for contactless shopping.
Micro-Fulfillment: The Next Step to Faster, More Efficient Last-Mile Delivery - Micro-fulfillment places small-scale warehouses close to consumers in dense urban areas or repurposed retail spaces, reducing delivery costs by up to 75% per order and transforming underused real estate into strategic distribution assets, helping brands compete efficiently in the e-commerce market.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com