Urban logistics hubs streamline last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory and distribution within city centers, reducing transportation costs and emissions. Shared logistics spaces optimize resource utilization by enabling multiple businesses to collaborate on warehousing and delivery operations, enhancing efficiency and scalability. Discover how integrating urban logistics hubs with shared logistics spaces can transform urban supply chains and sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between urban logistics hubs and shared logistics spaces is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing last-mile delivery costs in congested city environments. Urban logistics hubs serve as centralized points for sorting and distribution tailored to dense metropolitan areas, while shared logistics spaces offer flexible, multi-user warehousing solutions that enhance resource utilization. Proper identification of each type improves inventory management, accelerates delivery times, and supports sustainable urban mobility practices. Businesses leveraging this knowledge can strategically position their operations to meet customer demands while minimizing environmental impact.
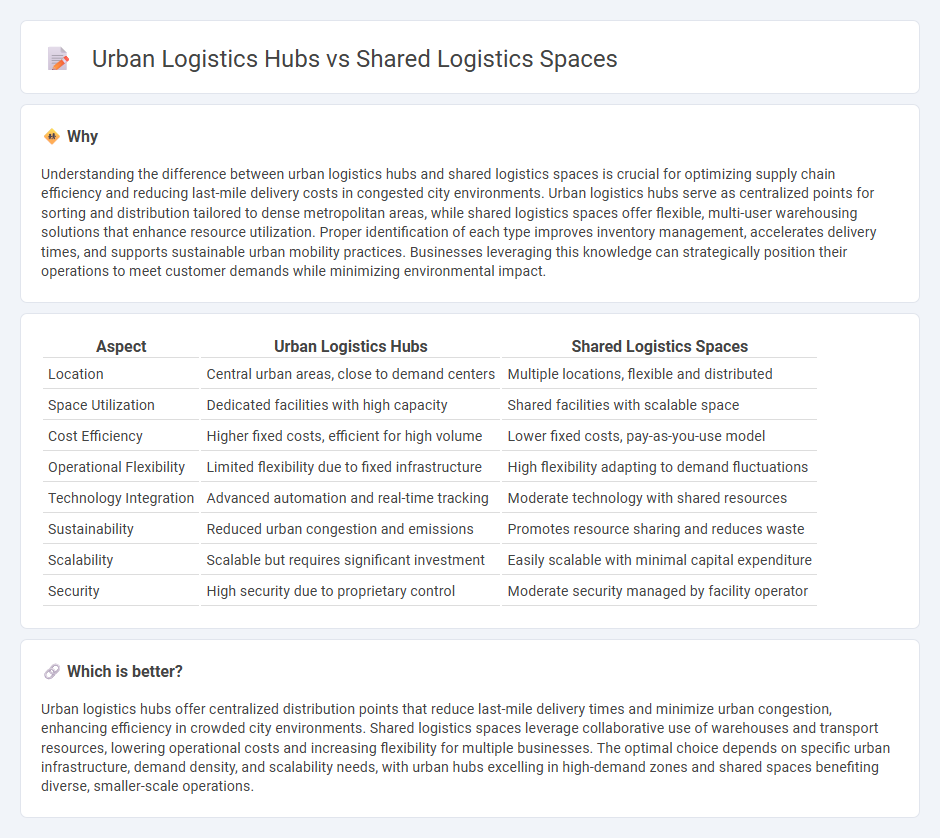
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Logistics Hubs | Shared Logistics Spaces |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Central urban areas, close to demand centers | Multiple locations, flexible and distributed |
| Space Utilization | Dedicated facilities with high capacity | Shared facilities with scalable space |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher fixed costs, efficient for high volume | Lower fixed costs, pay-as-you-use model |
| Operational Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to fixed infrastructure | High flexibility adapting to demand fluctuations |
| Technology Integration | Advanced automation and real-time tracking | Moderate technology with shared resources |
| Sustainability | Reduced urban congestion and emissions | Promotes resource sharing and reduces waste |
| Scalability | Scalable but requires significant investment | Easily scalable with minimal capital expenditure |
| Security | High security due to proprietary control | Moderate security managed by facility operator |
Which is better?
Urban logistics hubs offer centralized distribution points that reduce last-mile delivery times and minimize urban congestion, enhancing efficiency in crowded city environments. Shared logistics spaces leverage collaborative use of warehouses and transport resources, lowering operational costs and increasing flexibility for multiple businesses. The optimal choice depends on specific urban infrastructure, demand density, and scalability needs, with urban hubs excelling in high-demand zones and shared spaces benefiting diverse, smaller-scale operations.
Connection
Urban logistics hubs centralize goods distribution within city environments, enhancing efficiency by reducing delivery times and congestion. Shared logistics spaces integrate multiple stakeholders, such as carriers, retailers, and couriers, fostering resource optimization and collaborative inventory management. This interconnected approach streamlines last-mile delivery, minimizes environmental impact, and supports scalable urban supply chains.
Key Terms
Co-location
Shared logistics spaces maximize efficiency by enabling multiple businesses to access common warehousing, loading, and distribution facilities, reducing costs and environmental impact. Urban logistics hubs, strategically located within city centers, prioritize last-mile delivery speed and minimize traffic congestion, benefiting from co-location to streamline operations across retailers, couriers, and suppliers. Discover more about how co-location in shared spaces and hubs revolutionizes urban supply chains and sustainability.
Last-mile delivery
Shared logistics spaces improve last-mile delivery efficiency by consolidating multiple carriers and reducing empty runs through collaborative use of urban warehouses. Urban logistics hubs, strategically located close to dense populations, enable faster delivery times with enhanced load capacity and real-time inventory management. Explore how these models transform same-day delivery and reduce urban congestion for smarter city logistics.
Cross-docking
Shared logistics spaces optimize urban freight distribution by enabling multiple businesses to use a common facility, reducing transportation costs and delivery times. Urban logistics hubs specifically facilitate cross-docking operations by swiftly transferring goods from inbound to outbound vehicles without long-term storage, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. Explore how cross-docking in shared logistics spaces and urban hubs revolutionizes last-mile delivery solutions.
Source and External Links
Dedicated vs Shared Warehousing: 12 Key Points - EP Logistics - Shared warehousing involves multiple businesses sharing warehouse space, resources, and costs, offering a cost-effective, scalable, pay-as-you-go model ideal for small businesses to minimize overhead while accessing high-quality storage and services.
A Comprehensive Guide to Shared Warehouse Space - Shared warehouse spaces provide benefits such as cost-effectiveness, customization for branding, 24/7 accessibility, and foster a community environment that encourages collaboration and networking among businesses.
The Power of Shared Warehousing in Modern Supply Chains - This logistics model enables businesses to share warehouse facilities and operational resources, offering flexibility, reduced costs, real-time inventory visibility, advanced security, and suitability especially for SMEs, seasonal businesses, and those entering new markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com