Grey market shipping involves the import and sale of genuine products through unauthorized channels, often leading to lower prices but potential warranty and quality assurance risks. Drop shipping, in contrast, enables retailers to sell products directly from suppliers to customers without holding inventory, minimizing upfront costs and stock management challenges. Explore the key differences and strategic advantages of grey market shipping versus drop shipping to optimize your logistics approach.
Why it is important
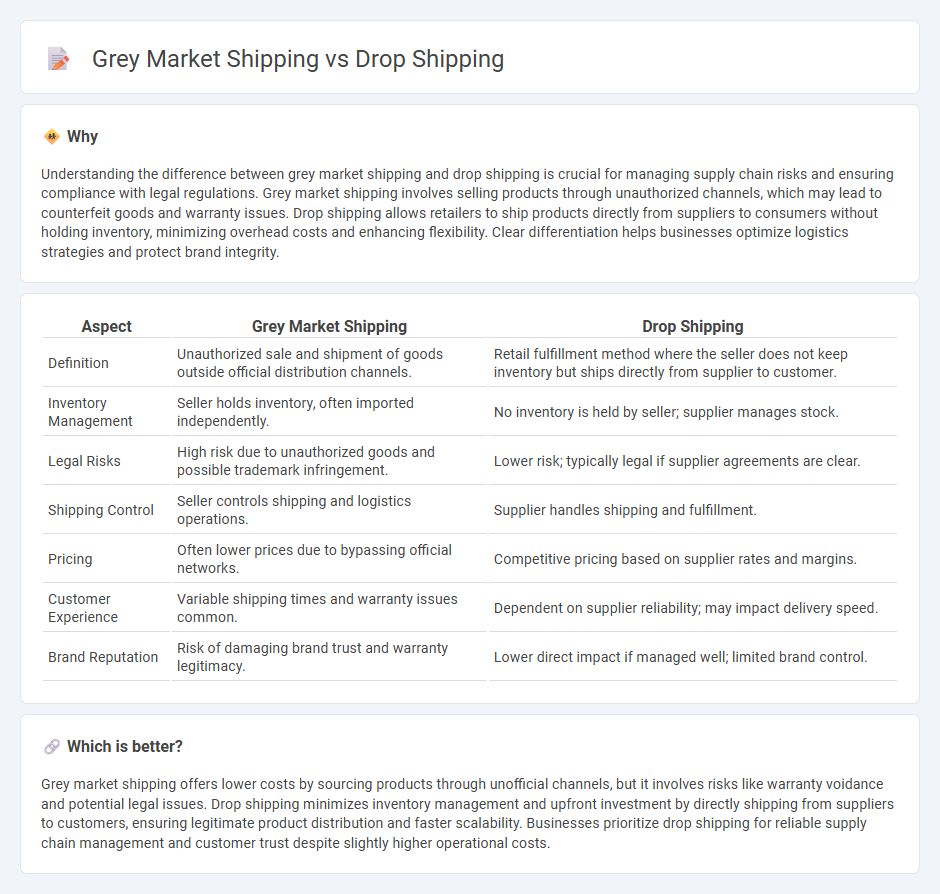
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and drop shipping is crucial for managing supply chain risks and ensuring compliance with legal regulations. Grey market shipping involves selling products through unauthorized channels, which may lead to counterfeit goods and warranty issues. Drop shipping allows retailers to ship products directly from suppliers to consumers without holding inventory, minimizing overhead costs and enhancing flexibility. Clear differentiation helps businesses optimize logistics strategies and protect brand integrity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Shipping | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized sale and shipment of goods outside official distribution channels. | Retail fulfillment method where the seller does not keep inventory but ships directly from supplier to customer. |
| Inventory Management | Seller holds inventory, often imported independently. | No inventory is held by seller; supplier manages stock. |
| Legal Risks | High risk due to unauthorized goods and possible trademark infringement. | Lower risk; typically legal if supplier agreements are clear. |
| Shipping Control | Seller controls shipping and logistics operations. | Supplier handles shipping and fulfillment. |
| Pricing | Often lower prices due to bypassing official networks. | Competitive pricing based on supplier rates and margins. |
| Customer Experience | Variable shipping times and warranty issues common. | Dependent on supplier reliability; may impact delivery speed. |
| Brand Reputation | Risk of damaging brand trust and warranty legitimacy. | Lower direct impact if managed well; limited brand control. |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping offers lower costs by sourcing products through unofficial channels, but it involves risks like warranty voidance and potential legal issues. Drop shipping minimizes inventory management and upfront investment by directly shipping from suppliers to customers, ensuring legitimate product distribution and faster scalability. Businesses prioritize drop shipping for reliable supply chain management and customer trust despite slightly higher operational costs.
Connection
Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of products, often bypassing official supply chains, while drop shipping relies on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers without holding inventory. Both methods circumvent traditional logistics processes, reducing overhead but increasing risks such as lower product authenticity control and longer delivery times. Efficient logistics management is crucial to mitigate challenges in tracking shipments and ensuring customer satisfaction within these non-traditional shipping models.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Ownership
Dropshipping involves suppliers directly shipping products to customers without the retailer holding inventory, resulting in limited supply chain ownership by the retailer. Grey market shipping refers to the distribution of genuine products through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official supply chains and warranty provisions, creating complexities in supply chain control. Explore the key differences in supply chain ownership between dropshipping and grey market shipping to optimize your logistics strategy.
Authorized Distribution
Authorized distribution ensures products are sourced from official manufacturers or licensed distributors, maintaining product authenticity and warranty coverage. In dropshipping, sellers ship products directly from authorized distributors or manufacturers, preserving legitimate product flow, while grey market shipping involves unauthorized channels that may bypass manufacturer controls, potentially voiding warranties and risking counterfeit goods. Explore the distinctions in supply chain integrity and consumer protection to make informed purchasing decisions.
Product Authenticity
Product authenticity is a critical factor distinguishing drop shipping and grey market shipping, with drop shipping typically sourcing products directly from authorized suppliers ensuring genuine items. Grey market shipping often involves importing branded products through unauthorized channels at lower prices, increasing the risk of counterfeit or tampered goods. Explore the nuances of product authenticity to make informed decisions between drop shipping and grey market shipping strategies.
Source and External Links
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail method where the seller takes orders without stocking goods and forwards them to a supplier who ships directly to customers, allowing low overhead but with less control over product quality and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping is a business model where an online retailer sells products it does not stock; when a customer orders, the retailer forwards the order to a supplier who handles fulfillment and shipment directly to the customer.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping outsources production, warehousing, and shipping to suppliers, letting retailers focus on marketing and sales while suppliers ship products directly to customers on demand.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com