Reverse logistics focuses on the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer for returns, recycling, or disposal, optimizing cost and environmental impact. Production logistics involves the planning and management of materials and workflow within manufacturing facilities to ensure efficient production and timely delivery. Explore the key differences and benefits of reverse logistics versus production logistics to enhance your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
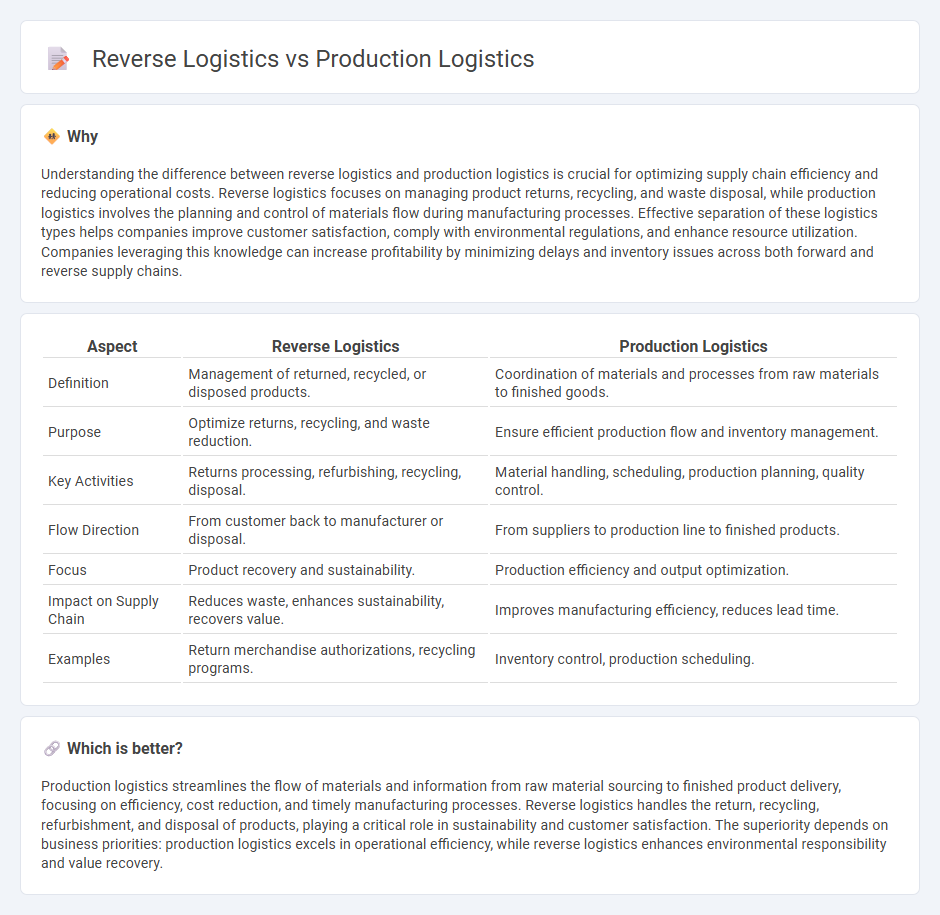
Understanding the difference between reverse logistics and production logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Reverse logistics focuses on managing product returns, recycling, and waste disposal, while production logistics involves the planning and control of materials flow during manufacturing processes. Effective separation of these logistics types helps companies improve customer satisfaction, comply with environmental regulations, and enhance resource utilization. Companies leveraging this knowledge can increase profitability by minimizing delays and inventory issues across both forward and reverse supply chains.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Logistics | Production Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of returned, recycled, or disposed products. | Coordination of materials and processes from raw materials to finished goods. |
| Purpose | Optimize returns, recycling, and waste reduction. | Ensure efficient production flow and inventory management. |
| Key Activities | Returns processing, refurbishing, recycling, disposal. | Material handling, scheduling, production planning, quality control. |
| Flow Direction | From customer back to manufacturer or disposal. | From suppliers to production line to finished products. |
| Focus | Product recovery and sustainability. | Production efficiency and output optimization. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Reduces waste, enhances sustainability, recovers value. | Improves manufacturing efficiency, reduces lead time. |
| Examples | Return merchandise authorizations, recycling programs. | Inventory control, production scheduling. |
Which is better?
Production logistics streamlines the flow of materials and information from raw material sourcing to finished product delivery, focusing on efficiency, cost reduction, and timely manufacturing processes. Reverse logistics handles the return, recycling, refurbishment, and disposal of products, playing a critical role in sustainability and customer satisfaction. The superiority depends on business priorities: production logistics excels in operational efficiency, while reverse logistics enhances environmental responsibility and value recovery.
Connection
Reverse logistics and production logistics are interconnected through the efficient management of materials flow, where reverse logistics handles the return, recycling, and disposal of products, feeding valuable components back into production logistics processes. This integration minimizes waste and reduces production costs by ensuring a continuous supply of recyclable materials and reusable parts. Advanced data analytics and real-time tracking systems optimize the coordination between reverse and production logistics, enhancing overall supply chain sustainability and efficiency.
Key Terms
**Production Logistics:**
Production logistics involves managing the flow of raw materials, components, and finished goods within the manufacturing process to ensure efficient production scheduling, inventory control, and timely delivery. It encompasses supply chain coordination, warehouse management, and just-in-time inventory techniques to minimize costs and maximize operational efficiency. Explore more to understand how optimized production logistics drive competitive advantage in manufacturing.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Production logistics optimizes materials flow and inventory management to support Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery of components. Reverse logistics manages the return, recycling, and disposal processes to recover value from used products or materials, enhancing sustainability in the supply chain. Explore more to understand how integrating JIT principles in both logistics types can improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Material Flow
Production logistics manages the efficient flow of raw materials and components through manufacturing processes to final product assembly, optimizing inventory levels and minimizing production delays. Reverse logistics handles the return flow of finished products, including returns, recycling, and disposal, ensuring sustainability and cost recovery. Explore detailed strategies and technologies to enhance both production and reverse logistics efficiencies.
Source and External Links
Production Logistics Definition and Meaning - Production logistics involves planning, coordinating, and managing the flow of materials and products during production to optimize resource use, reduce delays, and maintain efficient manufacturing processes.
Production logistics: the heart of controlled efficient production - BITO - Production logistics ensures the smooth flow of items from raw materials through production to finished goods, focusing on reducing lead times and integrating Industry 4.0 technologies for automation and networked production systems.
What is Supply Chain and Production Logistics? - AsstrA - Production logistics coordinates the internal production processes by managing inventory, order, transport, and production planning to optimize efficiency and maintain a smooth supply chain within manufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com