Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as order processing and inventory management, significantly improving operational efficiency and accuracy. In contrast, the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances logistics through real-time tracking of shipments, vehicle monitoring, and predictive maintenance by connecting physical assets to the digital network. Explore the nuanced benefits and applications of RPA and IoT in logistics to optimize your supply chain strategies.
Why it is important
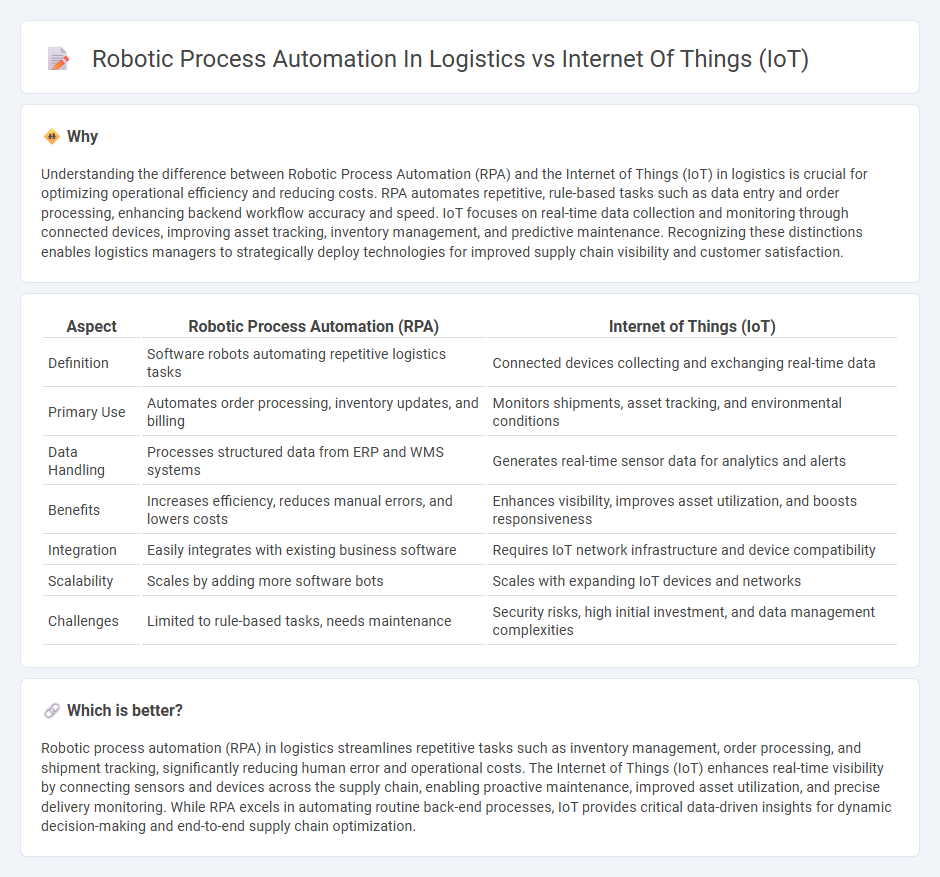
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in logistics is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry and order processing, enhancing backend workflow accuracy and speed. IoT focuses on real-time data collection and monitoring through connected devices, improving asset tracking, inventory management, and predictive maintenance. Recognizing these distinctions enables logistics managers to strategically deploy technologies for improved supply chain visibility and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Internet of Things (IoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive logistics tasks | Connected devices collecting and exchanging real-time data |
| Primary Use | Automates order processing, inventory updates, and billing | Monitors shipments, asset tracking, and environmental conditions |
| Data Handling | Processes structured data from ERP and WMS systems | Generates real-time sensor data for analytics and alerts |
| Benefits | Increases efficiency, reduces manual errors, and lowers costs | Enhances visibility, improves asset utilization, and boosts responsiveness |
| Integration | Easily integrates with existing business software | Requires IoT network infrastructure and device compatibility |
| Scalability | Scales by adding more software bots | Scales with expanding IoT devices and networks |
| Challenges | Limited to rule-based tasks, needs maintenance | Security risks, high initial investment, and data management complexities |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking, significantly reducing human error and operational costs. The Internet of Things (IoT) enhances real-time visibility by connecting sensors and devices across the supply chain, enabling proactive maintenance, improved asset utilization, and precise delivery monitoring. While RPA excels in automating routine back-end processes, IoT provides critical data-driven insights for dynamic decision-making and end-to-end supply chain optimization.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking. The Internet of Things (IoT) provides real-time data from connected devices like sensors, GPS trackers, and smart warehouses, enabling RPA systems to make informed decisions based on accurate, real-time information. The integration of RPA and IoT creates a seamless logistics ecosystem that improves supply chain visibility, reduces errors, and accelerates delivery times.
Key Terms
Real-time Tracking
IoT in logistics offers real-time tracking through interconnected sensors and GPS-enabled devices, providing instant visibility into shipment locations and environmental conditions. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances logistics by automating data processing and exception handling but lacks the sensory capabilities for real-time physical tracking. Explore how integrating IoT and RPA can optimize logistics operations further and deliver comprehensive real-time tracking solutions.
Process Automation
Internet of Things (IoT) integrates sensors and real-time data exchange to optimize inventory tracking, fleet management, and warehouse operations, significantly enhancing process visibility and decision-making in logistics. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based administrative tasks such as order processing, invoicing, and shipment scheduling, reducing human error and increasing operational efficiency. Explore the distinct advantages of IoT and RPA in logistics process automation to identify the best fit for your supply chain needs.
Data Integration
Internet of Things (IoT) in logistics enhances real-time data integration through connected sensors and devices, enabling dynamic tracking and monitoring of assets. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines data processing by automating repetitive tasks and integrating information across multiple legacy systems. Explore the transformative impact of IoT and RPA on optimizing logistics data integration strategies.
Source and External Links
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - IBM - IoT is a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors and connectivity, enabling them to collect and share data autonomously.
What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - AWS - IoT refers to the collective network of billions of internet-connected devices and the technologies that facilitate communication and intelligent responses among these devices.
What is IoT (Internet of Things)? | Definition from TechTarget - IoT is a system of interrelated devices with sensors and software that connect and exchange data with each other and the cloud, encompassing everything from household items to industrial machinery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com