Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized import and distribution of goods outside official channels, often bypassing manufacturer warranties and regional restrictions. Freight forwarding, on the other hand, is a legitimate logistics service that manages the transportation and delivery of goods through authorized carriers and compliant routes. Explore the key differences between grey market shipping and freight forwarding to understand their impacts on supply chain efficiency and legal considerations.
Why it is important
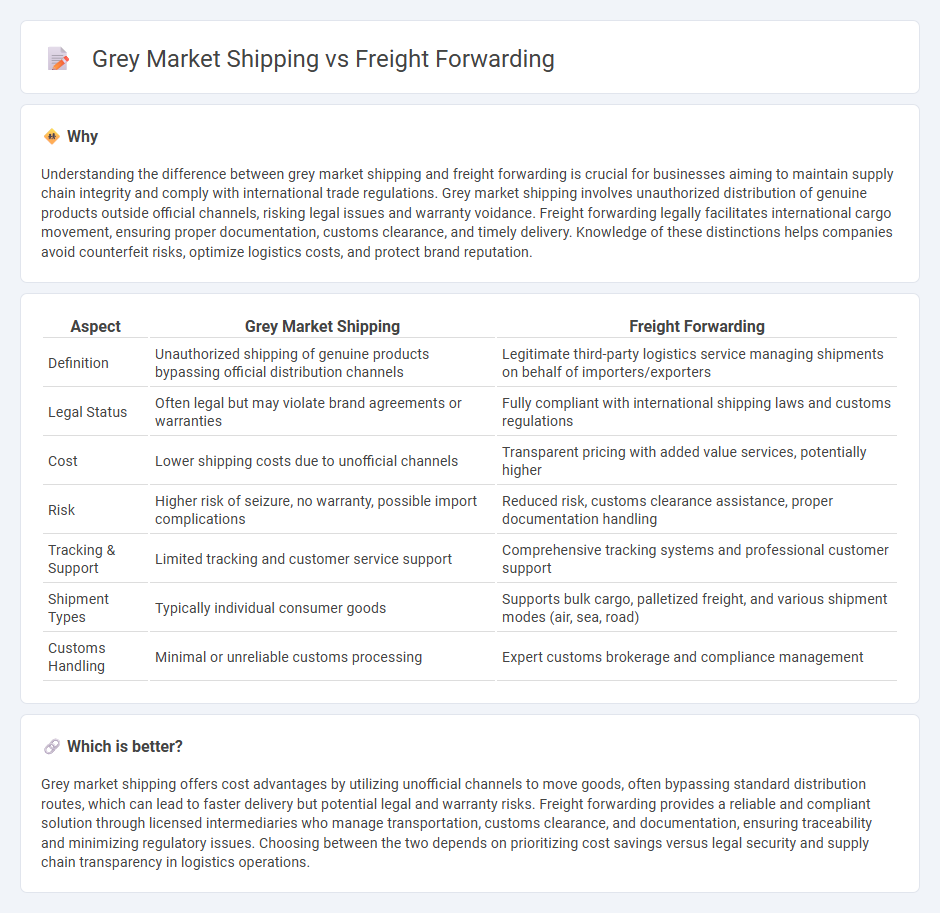
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and freight forwarding is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain supply chain integrity and comply with international trade regulations. Grey market shipping involves unauthorized distribution of genuine products outside official channels, risking legal issues and warranty voidance. Freight forwarding legally facilitates international cargo movement, ensuring proper documentation, customs clearance, and timely delivery. Knowledge of these distinctions helps companies avoid counterfeit risks, optimize logistics costs, and protect brand reputation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Shipping | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized shipping of genuine products bypassing official distribution channels | Legitimate third-party logistics service managing shipments on behalf of importers/exporters |
| Legal Status | Often legal but may violate brand agreements or warranties | Fully compliant with international shipping laws and customs regulations |
| Cost | Lower shipping costs due to unofficial channels | Transparent pricing with added value services, potentially higher |
| Risk | Higher risk of seizure, no warranty, possible import complications | Reduced risk, customs clearance assistance, proper documentation handling |
| Tracking & Support | Limited tracking and customer service support | Comprehensive tracking systems and professional customer support |
| Shipment Types | Typically individual consumer goods | Supports bulk cargo, palletized freight, and various shipment modes (air, sea, road) |
| Customs Handling | Minimal or unreliable customs processing | Expert customs brokerage and compliance management |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping offers cost advantages by utilizing unofficial channels to move goods, often bypassing standard distribution routes, which can lead to faster delivery but potential legal and warranty risks. Freight forwarding provides a reliable and compliant solution through licensed intermediaries who manage transportation, customs clearance, and documentation, ensuring traceability and minimizing regulatory issues. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing cost savings versus legal security and supply chain transparency in logistics operations.
Connection
Grey market shipping often involves the unauthorized distribution of goods through unofficial channels, challenging standard logistics and supply chain protocols. Freight forwarding plays a critical role in this ecosystem by facilitating the movement of shipments across borders, sometimes without full adherence to legal regulations or brand authorizations. The intersection of these two sectors highlights vulnerabilities in global logistics networks, impacting customs compliance and supply chain transparency.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves the organized coordination of shipments from the manufacturer to the final destination, ensuring compliance with customs regulations, proper documentation, and efficient transportation modes. It offers transparency, legal protection, and tracking capabilities that are essential for international trade and smooth delivery processes. Explore the advantages of freight forwarding services for a reliable global shipping experience.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding involves professional handling of customs clearance, ensuring legal compliance and documentation accuracy to avoid delays or penalties. Grey market shipping bypasses authorized channels, often resulting in customs complications, seizures, and additional duties due to misdeclared or uncertified goods. Explore detailed customs clearance processes and risks in both shipping models to make informed decisions.
Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading (BOL) serves as a critical legal document in freight forwarding, providing proof of shipment, details of the cargo, and terms of carriage, ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. In grey market shipping, the Bill of Lading often lacks transparency and authenticity, risking shipment seizures and legal disputes due to unauthorized distribution channels. Explore the nuances of Bill of Lading management to safeguard your international shipments effectively.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding is the strategic planning and coordination of the international movement of goods via multiple modes of transportation, where freight forwarders act as intermediaries arranging logistics, customs clearance, and ensuring timely delivery without physically moving the cargo themselves.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key Stages - Freight forwarding involves key stages such as export haulage, customs clearance, and origin handling, with freight forwarders ensuring goods move safely and legally from origin to destination.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding facilitates international trade by managing carriage, consolidation, storage, packing, customs, insurance, and supply chain management services, aiming for goods to arrive at the right place, time, condition, and cost.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com