Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods directly from a distribution center to the final customer, optimizing speed and convenience in urban and suburban areas. In contrast, hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory in major hubs and uses spokes to route shipments efficiently, reducing transportation costs and increasing network scalability. Explore detailed comparisons and operational strategies to determine the best logistics solution for your business needs.
Why it is important
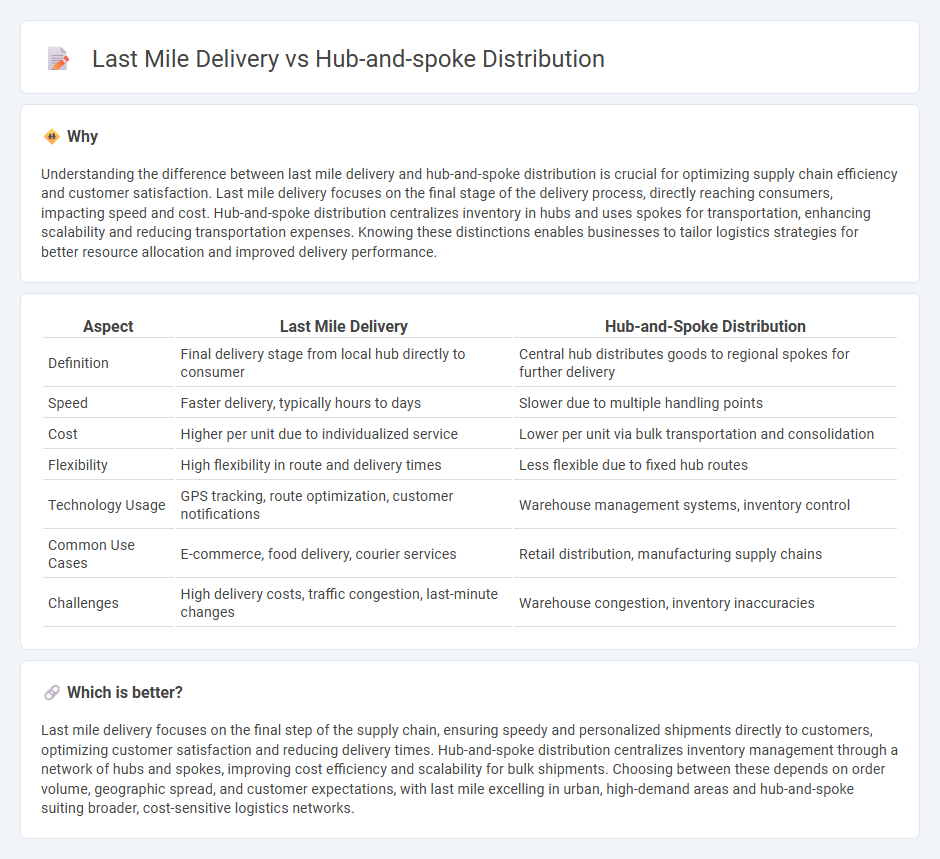
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and hub-and-spoke distribution is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery focuses on the final stage of the delivery process, directly reaching consumers, impacting speed and cost. Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory in hubs and uses spokes for transportation, enhancing scalability and reducing transportation expenses. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to tailor logistics strategies for better resource allocation and improved delivery performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Hub-and-Spoke Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final delivery stage from local hub directly to consumer | Central hub distributes goods to regional spokes for further delivery |
| Speed | Faster delivery, typically hours to days | Slower due to multiple handling points |
| Cost | Higher per unit due to individualized service | Lower per unit via bulk transportation and consolidation |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in route and delivery times | Less flexible due to fixed hub routes |
| Technology Usage | GPS tracking, route optimization, customer notifications | Warehouse management systems, inventory control |
| Common Use Cases | E-commerce, food delivery, courier services | Retail distribution, manufacturing supply chains |
| Challenges | High delivery costs, traffic congestion, last-minute changes | Warehouse congestion, inventory inaccuracies |
Which is better?
Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of the supply chain, ensuring speedy and personalized shipments directly to customers, optimizing customer satisfaction and reducing delivery times. Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory management through a network of hubs and spokes, improving cost efficiency and scalability for bulk shipments. Choosing between these depends on order volume, geographic spread, and customer expectations, with last mile excelling in urban, high-demand areas and hub-and-spoke suiting broader, cost-sensitive logistics networks.
Connection
Last mile delivery relies on the hub-and-spoke distribution model by utilizing centralized hubs to efficiently dispatch parcels to their final destinations, reducing transit time and costs. The hub serves as a consolidation point where goods are sorted and routed through spokes to local delivery points, optimizing route planning and resource allocation. This interconnected system enhances delivery speed and reliability in urban and suburban logistics networks.
Key Terms
Centralized Hub
A Centralized Hub in hub-and-spoke distribution streamlines delivery by consolidating goods before dispatching them to regional spokes, enhancing inventory management and reducing transportation costs. This model contrasts with last mile delivery, which emphasizes direct, localized shipment from hubs or warehouses to the final consumer, often facing challenges like traffic congestion and route optimization. Explore more on how centralized hubs transform supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Spoke Routes
Spoke routes in a hub-and-spoke distribution model streamline the transfer of goods from central hubs to peripheral spokes, enhancing efficiency by consolidating shipments and optimizing delivery schedules. This approach contrasts with last mile delivery, which emphasizes the final leg of transport directly to the customer, often facing greater variability and cost challenges. Explore how optimizing spoke routes can significantly improve overall supply chain performance and reduce delivery times.
Endpoint Delivery
Hub-and-spoke distribution centralizes inventory in a few large warehouses (hubs) from which shipments are dispatched to smaller local centers (spokes) before reaching the endpoint, optimizing transportation costs and efficiency. Last mile delivery addresses the critical final step of transporting goods from the local spoke to the endpoint, focusing on speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction in urban and suburban environments. Explore more about how endpoint delivery innovations are transforming supply chain logistics and enhancing customer experiences.
Source and External Links
Hub and Spoke Model In Logistics And Its Importance - NimbusPost - The hub-and-spoke model centralizes distribution through a main hub, improving delivery planning, reducing costs, optimizing routes, increasing workforce productivity, and ensuring faster deliveries to multiple destinations efficiently.
The Hub and Spoke Distribution Model for SMB's - Ware2Go - This model reduces time in transit, improves service levels by positioning inventory closer to consumers, offsets freight costs, lowers inventory carrying rates, and increases efficiency by centralizing logistics operations.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - The hub-and-spoke system organizes routes as spokes connecting to a central hub, optimizing transport topology; pioneered by Delta Airlines in 1955 and widely adopted in aviation and logistics for efficient network and delivery systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com