Urban air mobility offers rapid, congestion-free transport solutions through electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, while electric delivery vans provide eco-friendly ground-based logistics with established infrastructure and lower operational costs. eVTOLs excel in reducing last-mile delivery times in densely populated areas, whereas electric vans remain crucial for heavier payloads and longer routes within urban environments. Explore how integrating both technologies can revolutionize modern logistics networks.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between urban air mobility (UAM) and electric delivery vans is crucial for optimizing last-mile logistics solutions in densely populated cities. UAM offers rapid, airborne transport that bypasses ground traffic congestion, reducing delivery times for urgent goods. In contrast, electric delivery vans provide environmentally friendly, cost-effective ground transportation with established infrastructure and payload capacity. Selecting the appropriate mode depends on factors like delivery speed, payload size, urban infrastructure, and sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
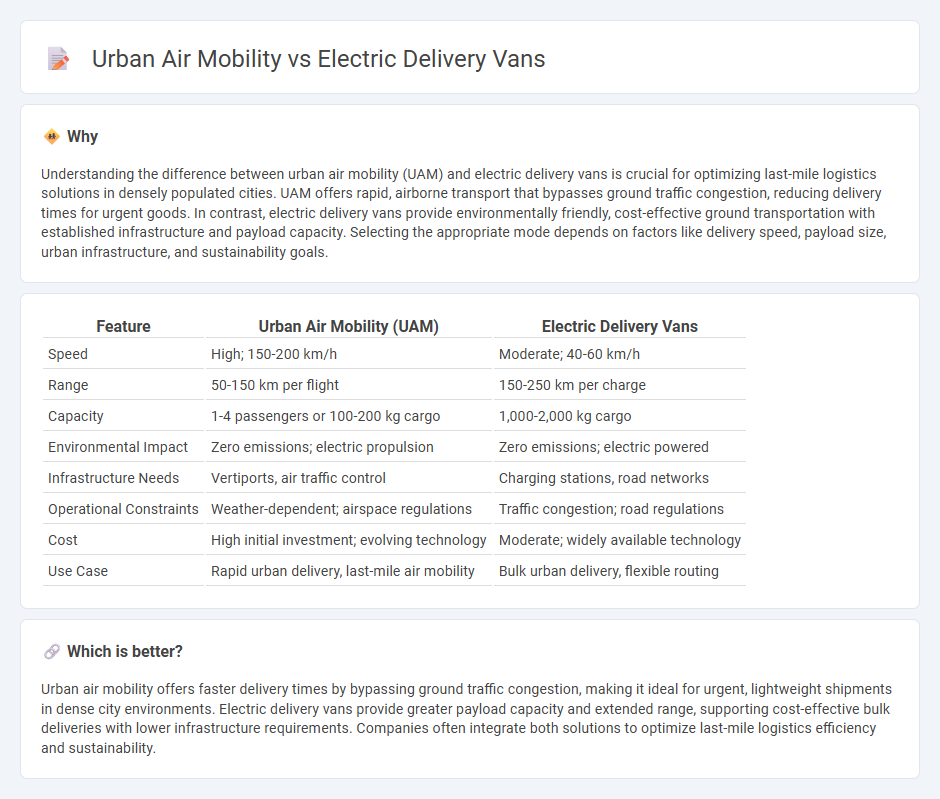
| Feature | Urban Air Mobility (UAM) | Electric Delivery Vans |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High; 150-200 km/h | Moderate; 40-60 km/h |
| Range | 50-150 km per flight | 150-250 km per charge |
| Capacity | 1-4 passengers or 100-200 kg cargo | 1,000-2,000 kg cargo |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions; electric propulsion | Zero emissions; electric powered |
| Infrastructure Needs | Vertiports, air traffic control | Charging stations, road networks |
| Operational Constraints | Weather-dependent; airspace regulations | Traffic congestion; road regulations |
| Cost | High initial investment; evolving technology | Moderate; widely available technology |
| Use Case | Rapid urban delivery, last-mile air mobility | Bulk urban delivery, flexible routing |
Which is better?
Urban air mobility offers faster delivery times by bypassing ground traffic congestion, making it ideal for urgent, lightweight shipments in dense city environments. Electric delivery vans provide greater payload capacity and extended range, supporting cost-effective bulk deliveries with lower infrastructure requirements. Companies often integrate both solutions to optimize last-mile logistics efficiency and sustainability.
Connection
Urban air mobility and electric delivery vans both represent innovative solutions aimed at reducing carbon emissions and traffic congestion in logistics. Electric delivery vans offer sustainable last-mile transportation on roads, while urban air mobility utilizes electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft to expedite parcel delivery across dense urban areas. Integrating these technologies enhances efficiency in supply chains by combining ground and aerial transport for faster, greener urban logistics.
Key Terms
Last-mile delivery
Electric delivery vans reduce urban emissions and optimize last-mile delivery through accessible road networks and established charging infrastructure. Urban Air Mobility (UAM) offers rapid, congestion-free parcel transport by leveraging drones and electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, though regulatory and airspace challenges limit widespread adoption. Explore the latest innovations and detailed comparisons to understand how these technologies are reshaping last-mile delivery.
Zero-emission vehicles
Electric delivery vans produce zero tailpipe emissions and are increasingly adopted for last-mile urban logistics due to their battery efficiency and established infrastructure. Urban air mobility (UAM) promises zero-emission aerial transport by leveraging electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) technology, targeting congestion reduction and rapid delivery in dense metropolitan areas. Explore the future impact of zero-emission vehicles in urban mobility and logistics to understand evolving sustainable transport solutions.
Vertiport infrastructure
Electric delivery vans rely on well-established road networks and charging stations to ensure efficient urban logistics, while urban air mobility demands the development of specialized vertiport infrastructure for takeoff, landing, and charging of electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft. Vertiports must integrate advanced air traffic management systems, rapid charging capabilities, and passenger or cargo handling facilities to support high-frequency operations in dense urban environments. Explore the future of vertiport infrastructure and its critical role in revolutionizing city logistics and urban air mobility.
Source and External Links
Ram Promaster EV | Ram Electric Cargo Van - The 2024 Ram ProMaster EV is a powerful electric cargo van with a 110 kWh battery, offering up to 164 miles of range and a maximum payload of over 3,000 pounds, designed for commercial delivery needs.
Rivian Fleet: Electric Work & Commercial Vans - Rivian offers electric commercial vans built for driver safety and comfort, such as the Delivery 500 and 700 models, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing fleet efficiency for delivery businesses.
Here are 10 good electric vans if you need... a good electric van - A range of electric delivery vans including Renault Kangoo E-Tech with up to 186 miles range, Peugeot e-Partner, and others offering various cargo capacities and features catering to different commercial delivery requirements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com