Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of the supply chain, ensuring packages reach the end customer's doorstep quickly and efficiently, often involving urban areas with high delivery density. Freight forwarding manages the overall movement of goods internationally or domestically, coordinating multiple carriers and handling customs, warehousing, and documentation. Explore how these logistics components differ in scope, challenges, and technologies by learning more about their unique roles in supply chain management.
Why it is important
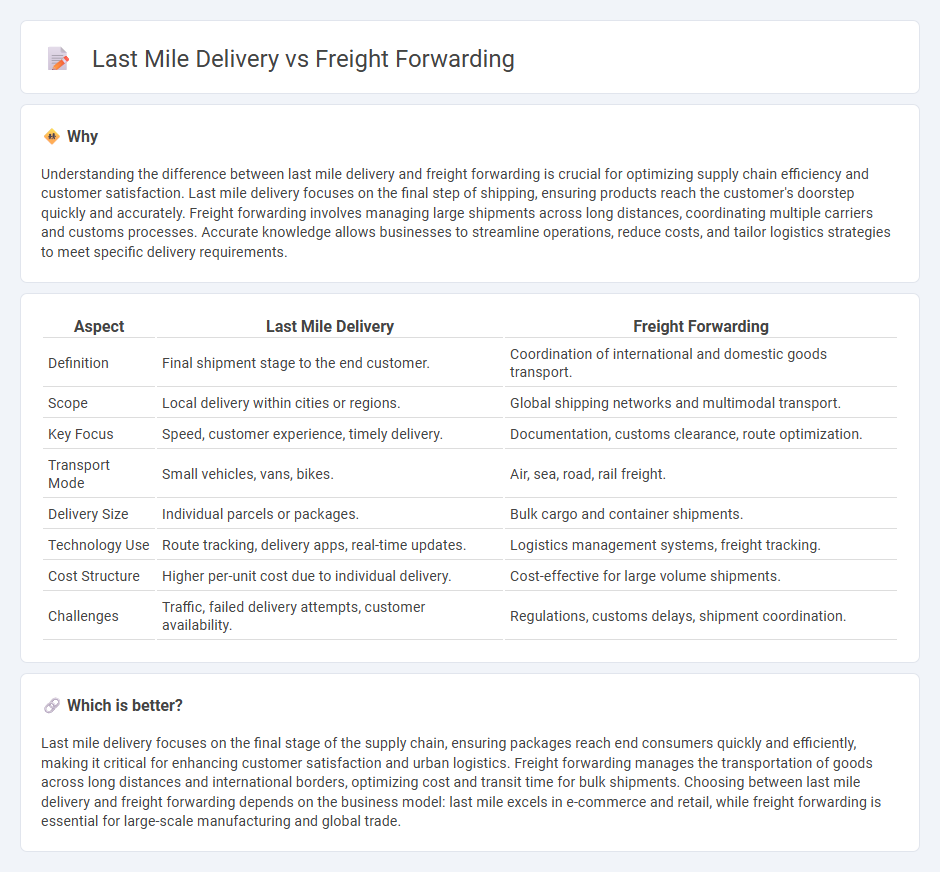
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and freight forwarding is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of shipping, ensuring products reach the customer's doorstep quickly and accurately. Freight forwarding involves managing large shipments across long distances, coordinating multiple carriers and customs processes. Accurate knowledge allows businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and tailor logistics strategies to meet specific delivery requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final shipment stage to the end customer. | Coordination of international and domestic goods transport. |
| Scope | Local delivery within cities or regions. | Global shipping networks and multimodal transport. |
| Key Focus | Speed, customer experience, timely delivery. | Documentation, customs clearance, route optimization. |
| Transport Mode | Small vehicles, vans, bikes. | Air, sea, road, rail freight. |
| Delivery Size | Individual parcels or packages. | Bulk cargo and container shipments. |
| Technology Use | Route tracking, delivery apps, real-time updates. | Logistics management systems, freight tracking. |
| Cost Structure | Higher per-unit cost due to individual delivery. | Cost-effective for large volume shipments. |
| Challenges | Traffic, failed delivery attempts, customer availability. | Regulations, customs delays, shipment coordination. |
Which is better?
Last mile delivery focuses on the final stage of the supply chain, ensuring packages reach end consumers quickly and efficiently, making it critical for enhancing customer satisfaction and urban logistics. Freight forwarding manages the transportation of goods across long distances and international borders, optimizing cost and transit time for bulk shipments. Choosing between last mile delivery and freight forwarding depends on the business model: last mile excels in e-commerce and retail, while freight forwarding is essential for large-scale manufacturing and global trade.
Connection
Last mile delivery and freight forwarding are interconnected components of the logistics supply chain, where freight forwarding manages the transportation and customs clearance of goods from origin to the destination country, and last mile delivery ensures the final distribution from local hubs to end consumers. Efficient coordination between these logistics processes reduces transit times, lowers costs, and improves customer satisfaction by enabling seamless movement of goods across international and urban networks. Advanced tracking technologies and real-time data exchange facilitate synchronization between freight forwarding activities and last mile delivery operations, optimizing route planning and inventory management.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves the coordination and shipment of goods from the point of origin to the final destination, often spanning international borders and utilizing multiple transportation modes such as air, sea, and land. It encompasses services like customs clearance, cargo insurance, and warehousing to ensure efficient global supply chain management. Explore more to understand the critical role of freight forwarding in optimizing logistics and reducing shipping complexities.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding involves managing the international shipment of goods, including customs clearance, where documentation, duties, and regulatory compliance are critical to ensure smooth transit across borders. Last mile delivery focuses on the final movement of goods to the end customer, typically within the domestic market, and rarely handles customs processes directly. Explore how customs clearance intricacies differ between freight forwarding and last mile delivery to optimize your supply chain operations.
Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading is a crucial document in freight forwarding, serving as a receipt, contract, and title for transported goods during international shipping. In last mile delivery, the Bill of Lading's role shifts to confirming receipt and enabling inventory tracking rather than serving as legal ownership proof. Explore the nuances of Bill of Lading management in both freight forwarding and last mile delivery to optimize your logistics operations.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? - Freight forwarding is the strategic coordination of international cargo movement across air, sea, rail, or road, involving planning routes, customs clearance, and handling logistics to ensure goods arrive timely and intact.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key ... - Freight forwarding includes stages like export haulage, customs clearance, and origin handling, with freight forwarders acting as intermediaries between shippers and transport to facilitate safe and legal shipment of goods internationally.
About Freight Forwarding - Freight forwarding encompasses the carriage, consolidation, storage, packing, and distribution of goods, including customs, insurance, and total supply chain management to guarantee cost-effective and timely delivery of international shipments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com