Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking through software bots, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing human error. Blockchain logistics, on the other hand, offers a decentralized, transparent ledger that ensures secure data sharing, real-time tracking, and enhanced traceability across the supply chain. Explore the distinct advantages of RPA and blockchain to discover how these technologies revolutionize logistics management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and blockchain in logistics is crucial because RPA streamlines repetitive tasks and improves operational efficiency, while blockchain ensures transparency, security, and traceability in supply chain transactions. RPA automates processes such as inventory management and shipment tracking, boosting speed and accuracy without altering the data's integrity. Blockchain, on the other hand, provides an immutable ledger that enhances trust and reduces fraud by securely recording every transaction across the logistics network. Knowing these distinctions enables logistics professionals to apply the appropriate technology to optimize performance and compliance effectively.
Comparison Table
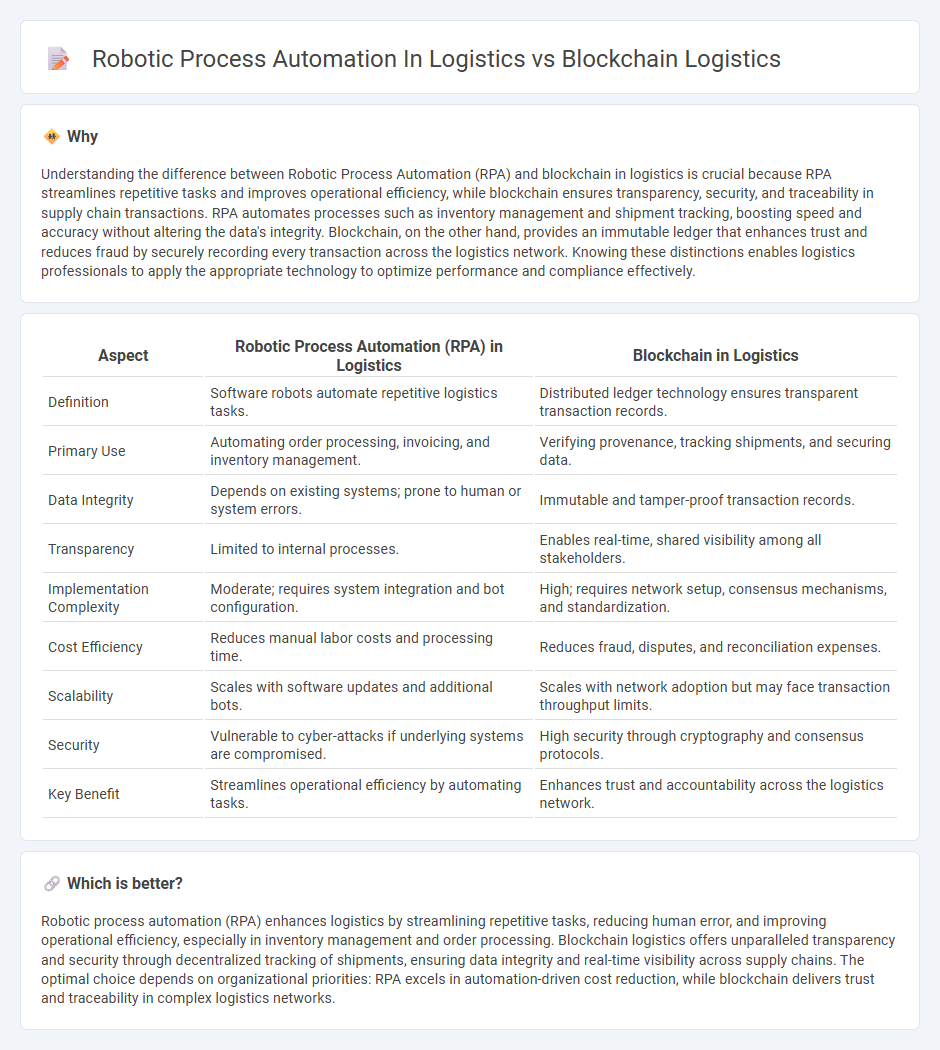
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Blockchain in Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automate repetitive logistics tasks. | Distributed ledger technology ensures transparent transaction records. |
| Primary Use | Automating order processing, invoicing, and inventory management. | Verifying provenance, tracking shipments, and securing data. |
| Data Integrity | Depends on existing systems; prone to human or system errors. | Immutable and tamper-proof transaction records. |
| Transparency | Limited to internal processes. | Enables real-time, shared visibility among all stakeholders. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; requires system integration and bot configuration. | High; requires network setup, consensus mechanisms, and standardization. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces manual labor costs and processing time. | Reduces fraud, disputes, and reconciliation expenses. |
| Scalability | Scales with software updates and additional bots. | Scales with network adoption but may face transaction throughput limits. |
| Security | Vulnerable to cyber-attacks if underlying systems are compromised. | High security through cryptography and consensus protocols. |
| Key Benefit | Streamlines operational efficiency by automating tasks. | Enhances trust and accountability across the logistics network. |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances logistics by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and improving operational efficiency, especially in inventory management and order processing. Blockchain logistics offers unparalleled transparency and security through decentralized tracking of shipments, ensuring data integrity and real-time visibility across supply chains. The optimal choice depends on organizational priorities: RPA excels in automation-driven cost reduction, while blockchain delivers trust and traceability in complex logistics networks.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as inventory management and shipment tracking, increasing efficiency and accuracy. Blockchain logistics enhances transparency and security by providing an immutable ledger for transactions and data sharing across supply chain stakeholders. Integrating RPA with blockchain creates a seamless automated data exchange system, reducing errors and improving real-time visibility in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Smart Contracts
Blockchain logistics leverages decentralized ledgers to enhance transparency and traceability, ensuring secure and immutable transaction records, while Smart Contracts automate these agreements to execute tasks based on predefined conditions. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on streamlining repetitive manual tasks through software bots, improving operational efficiency but lacking the inherent trust and security features provided by blockchain technology. Explore the unique advantages and integrations of Smart Contracts in logistics by learning more about blockchain and RPA applications.
Automated Material Handling
Blockchain logistics enhances transparency and traceability in automated material handling by securely recording each transaction and movement within the supply chain. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks in logistics operations, such as inventory management and order processing, improving efficiency and accuracy without human intervention. Explore further to understand how integrating blockchain and RPA can revolutionize automated material handling in logistics.
Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain logistics enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable, decentralized records of transactions, enabling real-time tracking and reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines routine logistics tasks but relies on existing data systems, offering limited improvement in end-to-end transparency. Explore how integrating blockchain with RPA can revolutionize supply chain visibility and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Blockchain in Logistics: Definition, Role in Logistics, and Benefits - Blockchain technology is transforming logistics by enhancing traceability, improving freight processes, and reducing fraud, with future developments including AI integration, smart contract automation, and improved customs clearance to increase efficiency and transparency.
Leveraging blockchain technology to transform logistics - DHL - Blockchain in logistics offers complete transparency with real-time data access, enhances security via decentralized data protection, automates processes with smart contracts, reduces costs, and improves product traceability from origin to consumer.
Blockchain for supply chain solutions - IBM - IBM's blockchain solutions provide trusted, permissioned shared data across supply chain partners, facilitating near real-time visibility, automated smart contracts, improved onboarding of suppliers, and enhanced resiliency against disruptions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com