Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of transporting goods from a distribution center to the end customer, emphasizing speed and accuracy for individual shipments. Freight forwarding involves managing the complex logistics of large shipments across multiple transportation modes, optimizing route planning and customs clearance. Explore deeper insights into how these crucial logistics components boost supply chain efficiency.
Why it is important
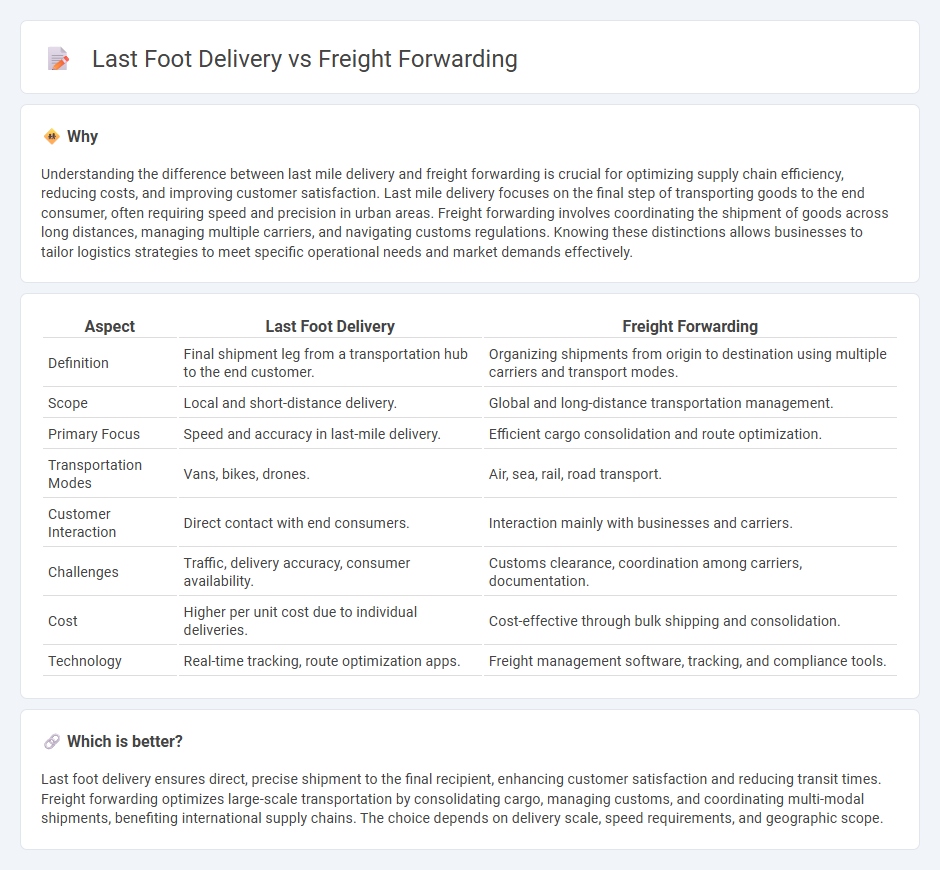
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and freight forwarding is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of transporting goods to the end consumer, often requiring speed and precision in urban areas. Freight forwarding involves coordinating the shipment of goods across long distances, managing multiple carriers, and navigating customs regulations. Knowing these distinctions allows businesses to tailor logistics strategies to meet specific operational needs and market demands effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Foot Delivery | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final shipment leg from a transportation hub to the end customer. | Organizing shipments from origin to destination using multiple carriers and transport modes. |
| Scope | Local and short-distance delivery. | Global and long-distance transportation management. |
| Primary Focus | Speed and accuracy in last-mile delivery. | Efficient cargo consolidation and route optimization. |
| Transportation Modes | Vans, bikes, drones. | Air, sea, rail, road transport. |
| Customer Interaction | Direct contact with end consumers. | Interaction mainly with businesses and carriers. |
| Challenges | Traffic, delivery accuracy, consumer availability. | Customs clearance, coordination among carriers, documentation. |
| Cost | Higher per unit cost due to individual deliveries. | Cost-effective through bulk shipping and consolidation. |
| Technology | Real-time tracking, route optimization apps. | Freight management software, tracking, and compliance tools. |
Which is better?
Last foot delivery ensures direct, precise shipment to the final recipient, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing transit times. Freight forwarding optimizes large-scale transportation by consolidating cargo, managing customs, and coordinating multi-modal shipments, benefiting international supply chains. The choice depends on delivery scale, speed requirements, and geographic scope.
Connection
Last foot delivery and freight forwarding are interconnected components of the logistics supply chain, crucial for ensuring timely and efficient movement of goods. Freight forwarding manages the transportation of shipments across multiple modes and international borders, facilitating customs clearance and cargo tracking, while last foot delivery focuses on the final stage of transporting goods from a local distribution hub directly to the end customer's doorstep. Integrating freight forwarding with last foot delivery optimizes order fulfillment, reduces transit times, and enhances overall customer satisfaction in e-commerce and retail logistics.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves managing the shipment of goods across international borders, coordinating transportation, customs clearance, and documentation to ensure timely delivery. This process includes selecting carriers, negotiating freight rates, and optimizing supply chain logistics for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Explore the benefits and intricacies of freight forwarding to enhance your global shipping strategy.
Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading (BOL) is a critical document in freight forwarding, serving as a contract and receipt between the shipper and carrier, outlining shipment details and ownership transfer. In last foot delivery, the BOL's role is less prominent, as this final stage focuses on local distribution and customer receipt rather than international transport documentation. Explore the nuanced differences in documentation and responsibilities between freight forwarding and last foot delivery for a comprehensive understanding.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding involves comprehensive logistics management, including customs clearance, where documentation and compliance with international trade regulations are critical to avoid delays and penalties. Last foot delivery primarily focuses on the final leg of the supply chain, ensuring packages reach the customer's doorstep but often relies on the prior completion of customs clearance by freight forwarders. Explore how efficient customs processes impact both freight forwarding and last foot delivery solutions to optimize your global shipping strategy.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? Everything you need to know - Freight forwarding is the process of moving imports and exports through the supply chain, where freight forwarders act as intermediaries managing cargo movement, documentation, and customs clearance from origin to destination.
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding is the strategic planning and coordination of international goods movement via multiple transport modes, with freight forwarders arranging shipments, customs clearance, and logistics on behalf of clients.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding involves managing the international transport, consolidation, storage, handling, customs, insurance, and supply chain services to ensure goods arrive timely, safely, and cost-effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com