Dynamic routing optimizes delivery routes in real-time using data such as traffic patterns, weather conditions, and order urgency to minimize transit times and fuel consumption. Zone-based routing assigns deliveries to predefined geographic areas, simplifying logistics management but potentially sacrificing route efficiency. Explore the advantages and applications of these routing strategies to enhance your supply chain performance.
Why it is important
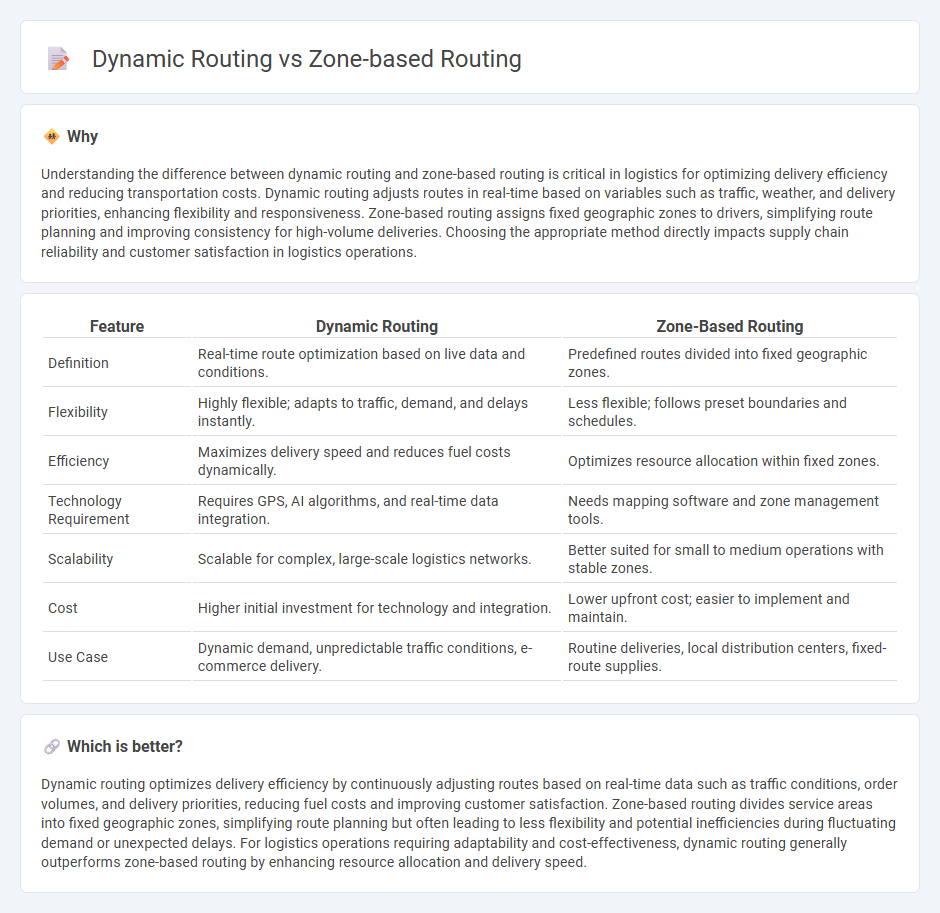
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and zone-based routing is critical in logistics for optimizing delivery efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Dynamic routing adjusts routes in real-time based on variables such as traffic, weather, and delivery priorities, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. Zone-based routing assigns fixed geographic zones to drivers, simplifying route planning and improving consistency for high-volume deliveries. Choosing the appropriate method directly impacts supply chain reliability and customer satisfaction in logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Zone-Based Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time route optimization based on live data and conditions. | Predefined routes divided into fixed geographic zones. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; adapts to traffic, demand, and delays instantly. | Less flexible; follows preset boundaries and schedules. |
| Efficiency | Maximizes delivery speed and reduces fuel costs dynamically. | Optimizes resource allocation within fixed zones. |
| Technology Requirement | Requires GPS, AI algorithms, and real-time data integration. | Needs mapping software and zone management tools. |
| Scalability | Scalable for complex, large-scale logistics networks. | Better suited for small to medium operations with stable zones. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for technology and integration. | Lower upfront cost; easier to implement and maintain. |
| Use Case | Dynamic demand, unpredictable traffic conditions, e-commerce delivery. | Routine deliveries, local distribution centers, fixed-route supplies. |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing optimizes delivery efficiency by continuously adjusting routes based on real-time data such as traffic conditions, order volumes, and delivery priorities, reducing fuel costs and improving customer satisfaction. Zone-based routing divides service areas into fixed geographic zones, simplifying route planning but often leading to less flexibility and potential inefficiencies during fluctuating demand or unexpected delays. For logistics operations requiring adaptability and cost-effectiveness, dynamic routing generally outperforms zone-based routing by enhancing resource allocation and delivery speed.
Connection
Dynamic routing enhances logistics efficiency by continuously adjusting delivery paths based on real-time data, while zone-based routing divides a service area into defined sectors for optimized resource allocation. Integrating dynamic routing within each zone allows logistics providers to respond swiftly to traffic conditions, order changes, and customer demands. This connection reduces delivery times, lowers operational costs, and improves overall supply chain agility.
Key Terms
**Zone-based routing:**
Zone-based routing segments a network into security zones, applying policies that control traffic flow between these zones to enhance security and simplify management. This method enables granular control by grouping interfaces into zones, where intra-zone traffic is typically unrestricted while inter-zone traffic is carefully filtered based on predefined rules. Explore the benefits and configurations of zone-based routing to strengthen your network's security posture effectively.
Fixed Zones
Fixed zone-based routing organizes network paths by dividing the area into predetermined zones, enhancing scalability and management in large networks compared to dynamic routing, which adjusts routes in real-time. This approach minimizes routing overhead and simplifies path determination within static boundaries, making it ideal for networks with predictable traffic patterns. Explore more about how fixed zones boost network efficiency and reduce latency in complex routing environments.
Predefined Routes
Zone-based routing relies on predefined routes configured according to specific network zones, enabling precise control over traffic flow and security policies within segmented areas. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF or EIGRP, automatically adjust routes based on current network conditions without relying on predefined paths, offering flexibility and scalability. Explore how predefined routes impact performance and security in zone-based routing to optimize your network design.
Source and External Links
Dynamic Operations and Zone-Based Routing - Wise Systems - Zone-based routing divides geographic areas into zones assigned to specific drivers for servicing stops, enabling dynamic and efficient routing while maintaining familiar territories for drivers.
Zone-Based Routing - Introw - Zone-based routing assigns leads or deals to reps based on geographic or industry zones to ensure quick responses and local expertise, commonly used in regional sales or partnership programs.
Understand the Zone-Based Policy Firewall Design - Cisco - In network security, zone-based routing defines traffic boundaries to apply policies between zones, controlling how traffic flows through security zones in firewalls and routers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com