Containerization revolutionizes global trade by standardizing cargo transport, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs through modular containers. Reverse logistics focuses on the return, recycling, and disposal of goods, promoting sustainability and minimizing waste within supply chains. Explore how both strategies optimize logistics operations and contribute to a greener economy.
Why it is important
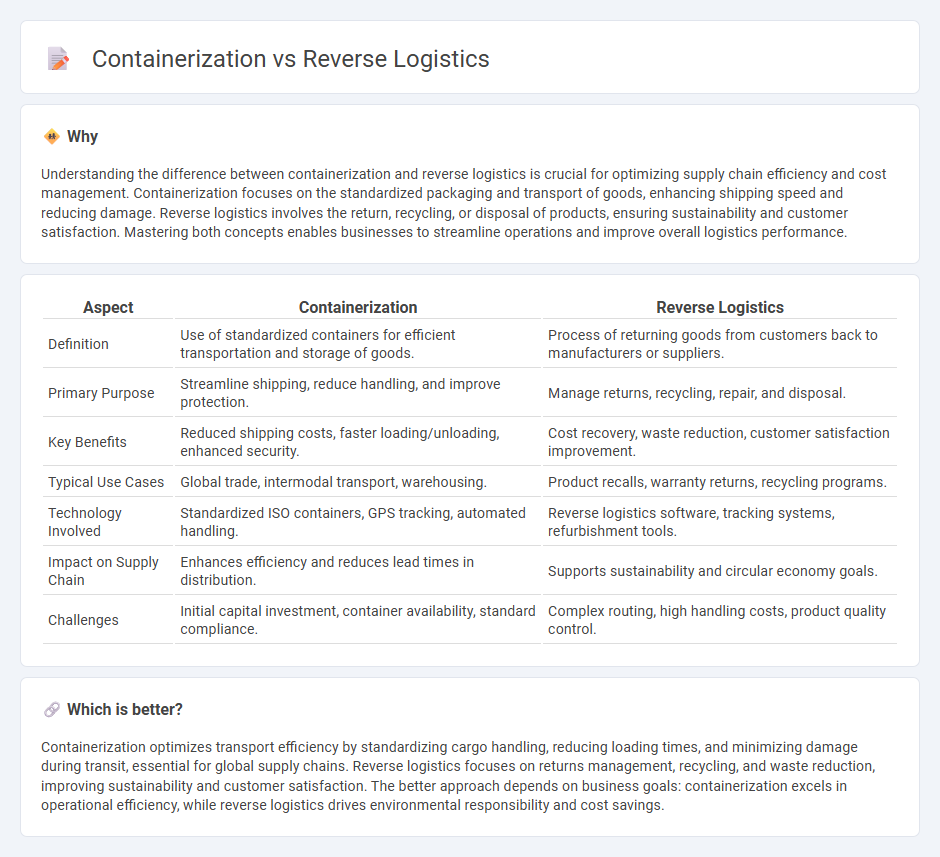
Understanding the difference between containerization and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management. Containerization focuses on the standardized packaging and transport of goods, enhancing shipping speed and reducing damage. Reverse logistics involves the return, recycling, or disposal of products, ensuring sustainability and customer satisfaction. Mastering both concepts enables businesses to streamline operations and improve overall logistics performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Containerization | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of standardized containers for efficient transportation and storage of goods. | Process of returning goods from customers back to manufacturers or suppliers. |
| Primary Purpose | Streamline shipping, reduce handling, and improve protection. | Manage returns, recycling, repair, and disposal. |
| Key Benefits | Reduced shipping costs, faster loading/unloading, enhanced security. | Cost recovery, waste reduction, customer satisfaction improvement. |
| Typical Use Cases | Global trade, intermodal transport, warehousing. | Product recalls, warranty returns, recycling programs. |
| Technology Involved | Standardized ISO containers, GPS tracking, automated handling. | Reverse logistics software, tracking systems, refurbishment tools. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Enhances efficiency and reduces lead times in distribution. | Supports sustainability and circular economy goals. |
| Challenges | Initial capital investment, container availability, standard compliance. | Complex routing, high handling costs, product quality control. |
Which is better?
Containerization optimizes transport efficiency by standardizing cargo handling, reducing loading times, and minimizing damage during transit, essential for global supply chains. Reverse logistics focuses on returns management, recycling, and waste reduction, improving sustainability and customer satisfaction. The better approach depends on business goals: containerization excels in operational efficiency, while reverse logistics drives environmental responsibility and cost savings.
Connection
Containerization streamlines the transportation and storage of goods, enabling efficient handling and tracking throughout the supply chain. Reverse logistics relies on containerization to facilitate the organized return, recycling, or disposal of products, reducing costs and environmental impact. Optimizing container usage in reverse logistics improves resource recovery and accelerates the processing of returned items.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or distribution center for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, aiming to maximize value recovery and reduce environmental impact. Effective reverse logistics systems leverage data analytics, transportation management, and return policies to optimize product lifecycle and inventory management. Explore more about innovative strategies and technologies revolutionizing reverse logistics for improved efficiency and sustainability.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics streamlines Returns Management by efficiently handling product returns, refurbishments, and recycling, reducing costs and environmental impact. Containerization enhances this process by securing goods during transportation and simplifying tracking, ensuring timely and safe delivery of returned items. Explore how integrating reverse logistics and containerization can optimize your Returns Management strategy.
Remanufacturing
Reverse logistics streamlines the return and recovery of used products, which is essential for remanufacturing processes aimed at reducing waste and conserving resources. Containerization optimizes the transportation and storage of these returned goods by using standardized containers, enhancing efficiency and reducing damage during transit. Explore how combining reverse logistics with containerization can significantly improve remanufacturing workflows and sustainability outcomes.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics - This webpage defines reverse logistics as the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics - This guide outlines how reverse logistics works across various industries, handling returns, leases, and refurbishments to optimize supply chain management.
Reverse Logistics - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their typical final destination for capturing value or proper disposal, sometimes involving remanufacturing and refurbishing activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com