Dynamic routing continuously updates path selection based on real-time network conditions to optimize logistics efficiency and reduce delivery times. Adaptive routing adjusts routes in response to changing traffic patterns, weather, and other environmental factors, enhancing supply chain resilience. Explore how these routing strategies transform logistics operations for greater agility and cost savings.
Why it is important
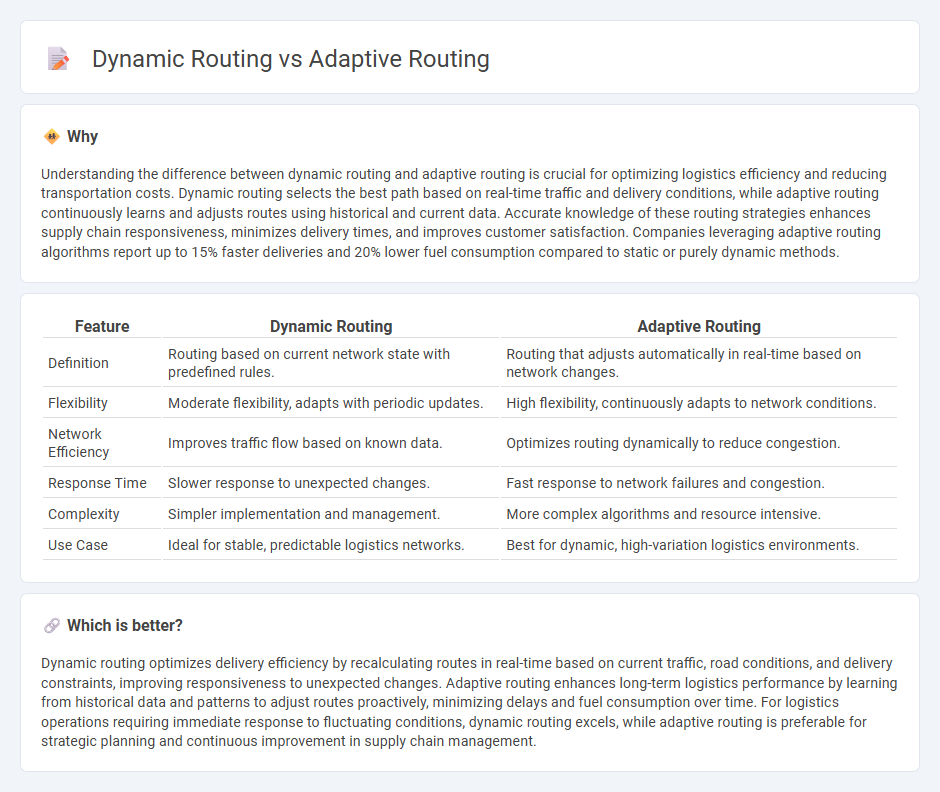
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and adaptive routing is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Dynamic routing selects the best path based on real-time traffic and delivery conditions, while adaptive routing continuously learns and adjusts routes using historical and current data. Accurate knowledge of these routing strategies enhances supply chain responsiveness, minimizes delivery times, and improves customer satisfaction. Companies leveraging adaptive routing algorithms report up to 15% faster deliveries and 20% lower fuel consumption compared to static or purely dynamic methods.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Adaptive Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Routing based on current network state with predefined rules. | Routing that adjusts automatically in real-time based on network changes. |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, adapts with periodic updates. | High flexibility, continuously adapts to network conditions. |
| Network Efficiency | Improves traffic flow based on known data. | Optimizes routing dynamically to reduce congestion. |
| Response Time | Slower response to unexpected changes. | Fast response to network failures and congestion. |
| Complexity | Simpler implementation and management. | More complex algorithms and resource intensive. |
| Use Case | Ideal for stable, predictable logistics networks. | Best for dynamic, high-variation logistics environments. |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing optimizes delivery efficiency by recalculating routes in real-time based on current traffic, road conditions, and delivery constraints, improving responsiveness to unexpected changes. Adaptive routing enhances long-term logistics performance by learning from historical data and patterns to adjust routes proactively, minimizing delays and fuel consumption over time. For logistics operations requiring immediate response to fluctuating conditions, dynamic routing excels, while adaptive routing is preferable for strategic planning and continuous improvement in supply chain management.
Connection
Dynamic routing and adaptive routing are interconnected through their shared goal of optimizing data or delivery paths in real-time based on current network or traffic conditions. Both methods utilize algorithms to continuously analyze variables such as traffic congestion, network failures, or delivery delays to determine the most efficient routes. This synergy enhances overall logistics efficiency by reducing transit times and improving resource allocation.
Key Terms
Real-time Data
Adaptive routing uses real-time data to continuously update routes based on current network conditions, improving traffic flow and reducing congestion. Dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and EIGRP, automatically adjust paths by exchanging routing information but may not rely as heavily on instant data changes. Explore how integrating real-time data enhances network efficiency through adaptive routing.
Route Optimization
Adaptive routing continuously adjusts route selection based on current network conditions, while dynamic routing uses predefined algorithms to update routes as network topology changes. Both methods aim to optimize routes, but adaptive routing focuses more on real-time traffic and congestion for improved performance. Explore the differences and benefits of these routing strategies to enhance network efficiency.
Traffic Conditions
Adaptive routing continuously adjusts paths based on real-time traffic conditions, ensuring optimal data flow and minimizing congestion by dynamically selecting less crowded routes. Dynamic routing updates routing tables using algorithms like OSPF or RIP, reacting primarily to network topology changes rather than immediate traffic load. Explore how these routing technologies impact network performance and scalability.
Source and External Links
What Is Adaptive Routing? Why Do We Need It? - Huawei - Adaptive routing is a technology that dynamically determines network routes based on topology and traffic load, selecting short and uncongested paths to improve throughput, resilience, and reduce latency, especially useful in large supercomputing centers with direct topologies.
What Is Adaptive Routing? Why Is It Needed? | FS Community - Adaptive routing dynamically adjusts routes by assessing network congestion, prioritizing the shortest and least congested paths to optimize bandwidth utilization, latency, and cost in high-performance computing networks.
Difference between Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Routing algorithms - GeeksforGeeks - Adaptive routing algorithms make dynamic decisions based on current network traffic and topology for enhanced performance and congestion control, contrasting with static routing that follows fixed paths regardless of network conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com