Urban air mobility offers rapid, flexible delivery solutions by leveraging drone technology to bypass ground traffic congestion, enhancing last-mile freight efficiency in densely populated cities. Underground freight transport systems utilize subterranean tunnels to move goods securely and continuously, minimizing surface-level disruptions and reducing carbon emissions. Explore how these innovative logistics models reshape urban freight delivery for smarter, sustainable cities.
Why it is important
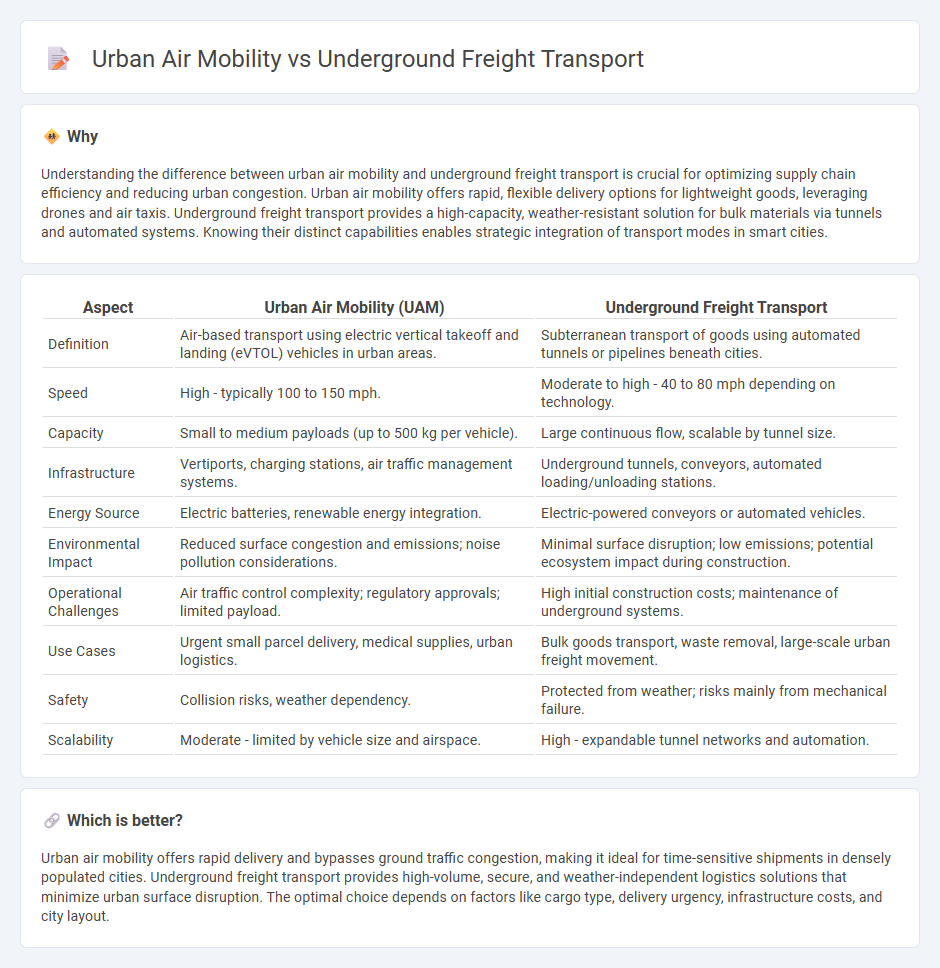
Understanding the difference between urban air mobility and underground freight transport is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing urban congestion. Urban air mobility offers rapid, flexible delivery options for lightweight goods, leveraging drones and air taxis. Underground freight transport provides a high-capacity, weather-resistant solution for bulk materials via tunnels and automated systems. Knowing their distinct capabilities enables strategic integration of transport modes in smart cities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Urban Air Mobility (UAM) | Underground Freight Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Air-based transport using electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) vehicles in urban areas. | Subterranean transport of goods using automated tunnels or pipelines beneath cities. |
| Speed | High - typically 100 to 150 mph. | Moderate to high - 40 to 80 mph depending on technology. |
| Capacity | Small to medium payloads (up to 500 kg per vehicle). | Large continuous flow, scalable by tunnel size. |
| Infrastructure | Vertiports, charging stations, air traffic management systems. | Underground tunnels, conveyors, automated loading/unloading stations. |
| Energy Source | Electric batteries, renewable energy integration. | Electric-powered conveyors or automated vehicles. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced surface congestion and emissions; noise pollution considerations. | Minimal surface disruption; low emissions; potential ecosystem impact during construction. |
| Operational Challenges | Air traffic control complexity; regulatory approvals; limited payload. | High initial construction costs; maintenance of underground systems. |
| Use Cases | Urgent small parcel delivery, medical supplies, urban logistics. | Bulk goods transport, waste removal, large-scale urban freight movement. |
| Safety | Collision risks, weather dependency. | Protected from weather; risks mainly from mechanical failure. |
| Scalability | Moderate - limited by vehicle size and airspace. | High - expandable tunnel networks and automation. |
Which is better?
Urban air mobility offers rapid delivery and bypasses ground traffic congestion, making it ideal for time-sensitive shipments in densely populated cities. Underground freight transport provides high-volume, secure, and weather-independent logistics solutions that minimize urban surface disruption. The optimal choice depends on factors like cargo type, delivery urgency, infrastructure costs, and city layout.
Connection
Urban air mobility and underground freight transport represent innovative solutions addressing urban congestion by utilizing three-dimensional space--air corridors and subterranean tunnels--for efficient cargo movement. Both systems leverage advanced automation, real-time data analytics, and smart infrastructure to optimize last-mile delivery, reduce surface traffic, and lower carbon emissions. Integration of these modalities can create a seamless logistics network enhancing urban freight capacity while mitigating environmental and spatial constraints in densely populated cities.
Key Terms
Underground Freight Transport:
Underground freight transport offers a resilient and efficient solution for urban logistics by utilizing subterranean tunnels to bypass surface traffic congestion and reduce emissions, making it ideal for transporting goods in densely populated cities. This mode leverages automated electric vehicles and advanced infrastructure to enable continuous, high-capacity deliveries, contributing to lower urban pollution and road wear. Explore the latest technological advancements and urban planning strategies driving the future of underground freight transport.
Cargo tunnels
Cargo tunnels in underground freight transport offer high-capacity, weather-independent solutions that reduce urban congestion and carbon emissions compared to traditional road freight. Urban air mobility for cargo relies on drones and air taxis, providing faster delivery but facing limitations in payload capacity and regulatory challenges. Explore the advantages and technical details of cargo tunnels for efficient urban logistics innovation.
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in underground freight transport offer scalable solutions for heavy cargo movement with reduced traffic congestion and enhanced safety in urban environments. Urban Air Mobility (UAM), by contrast, emphasizes rapid delivery over complex aerial routes but faces challenges in payload capacity and regulatory frameworks. Explore the latest advancements and comparative benefits of AGVs and UAM for optimized urban logistics.
Source and External Links
Underground freight transport - FOT - Switzerland is developing a private sector funded, fully-automatic underground freight transport system called Cargo Sous Terrain (CST) to reduce environmental impact and relieve road and rail congestion by moving part of its freight underground between major urban centers on the Swiss Plateau.
Tunnel vision: exploring the future of underground freight transport - Underground freight tunnels, enabled by modern infrastructure and technology, aim to reduce road congestion and emissions while improving delivery reliability by moving cargo underground, though challenges such as high costs and regulations remain.
Cargo Sous Terrain - This Swiss underground logistics system plans automated, flexible transport and storage of various cargo types through tunnels linking production and logistics sites, using renewable energy and environmentally friendly urban distribution vehicles in cooperation with major Swiss retailers; it is designed to alleviate city traffic and waste disposal issues.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com