Cross docking minimizes storage time by quickly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing handling costs. Direct shipping bypasses intermediate warehousing, delivering products straight from supplier to customer, which improves delivery speed but may increase transportation complexity. Explore in-depth comparisons to determine the best logistics strategy for your business needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cross docking and direct shipping is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Cross docking minimizes inventory holding by transferring products directly from inbound to outbound transportation, speeding up delivery times. Direct shipping sends products straight from the supplier to the customer, which can save on handling but may increase transportation costs. Knowing when to use each method enhances logistics planning and improves customer satisfaction.
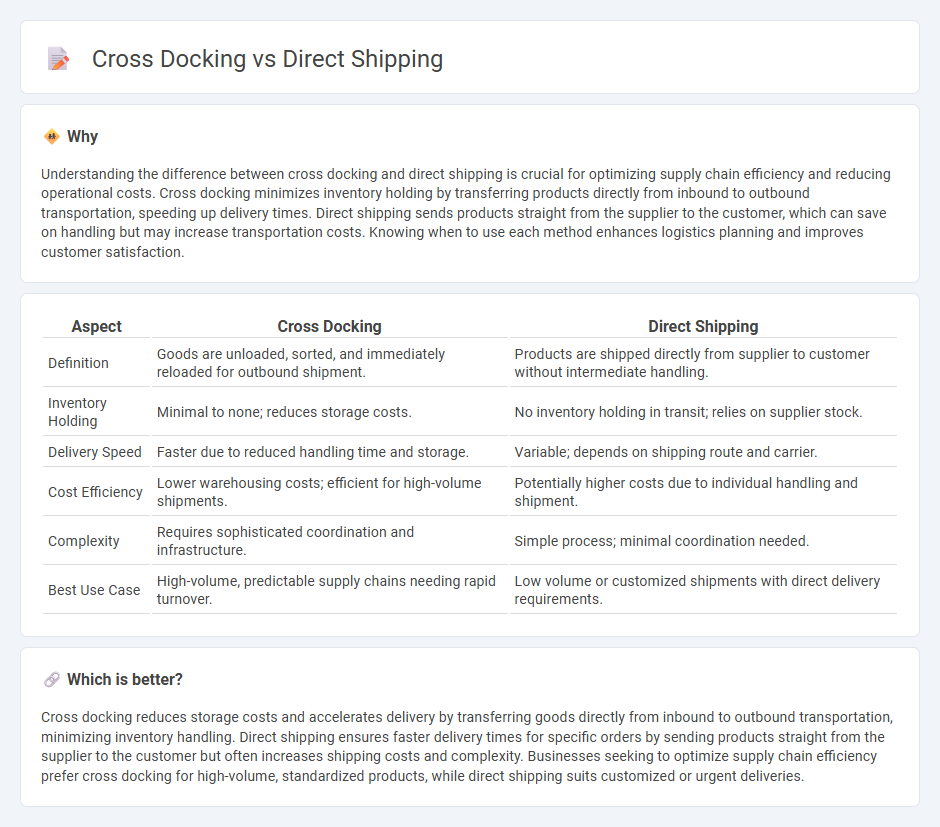
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cross Docking | Direct Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goods are unloaded, sorted, and immediately reloaded for outbound shipment. | Products are shipped directly from supplier to customer without intermediate handling. |
| Inventory Holding | Minimal to none; reduces storage costs. | No inventory holding in transit; relies on supplier stock. |
| Delivery Speed | Faster due to reduced handling time and storage. | Variable; depends on shipping route and carrier. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower warehousing costs; efficient for high-volume shipments. | Potentially higher costs due to individual handling and shipment. |
| Complexity | Requires sophisticated coordination and infrastructure. | Simple process; minimal coordination needed. |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, predictable supply chains needing rapid turnover. | Low volume or customized shipments with direct delivery requirements. |
Which is better?
Cross docking reduces storage costs and accelerates delivery by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing inventory handling. Direct shipping ensures faster delivery times for specific orders by sending products straight from the supplier to the customer but often increases shipping costs and complexity. Businesses seeking to optimize supply chain efficiency prefer cross docking for high-volume, standardized products, while direct shipping suits customized or urgent deliveries.
Connection
Cross docking and direct shipping streamline logistics by minimizing storage time and accelerating delivery processes. Both methods reduce inventory handling, with cross docking transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, while direct shipping sends products straight from supplier to customer. These strategies enhance supply chain efficiency by cutting down lead times and lowering operational costs.
Key Terms
Lead Time
Direct shipping reduces lead time by delivering goods straight from the supplier to the customer, minimizing handling and transit delays. Cross docking consolidates shipments at a warehouse for immediate redistribution, which can shorten lead time for large volume deliveries but may increase handling time for smaller orders. Explore more to determine which method optimizes lead time for your supply chain needs.
Inventory Holding
Direct shipping minimizes inventory holding by sending products straight from suppliers to customers, reducing storage needs and associated costs. Cross docking involves brief storage at a distribution center to consolidate shipments, lowering inventory holding time but requiring efficient coordination. Explore the differences further to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Distribution Center
Direct shipping involves sending products directly from suppliers to customers, minimizing handling time but increasing transportation costs and potential delays. Cross docking at a Distribution Center (DC) streamlines inventory by unloading inbound shipments and immediately loading them for outbound delivery, reducing storage needs and accelerating order fulfillment. Explore more about how optimizing DC operations with cross docking can enhance supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
Direct Shipping: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages - Direct shipping is a method where goods are delivered directly from the supplier to the customer without passing through intermediary warehouses or seller facilities, saving logistics costs but risking quality control and affecting the seller's reputation.
What Is Direct Shipping? Pros and Cons of Direct Shipping - Direct shipping is an in-house fulfillment method where sellers manage inventory and ship products directly to customers, enabling faster deliveries and closer customer relationships by bypassing third-party warehouses.
Direct Shipping: A Comprehensive Guide - Direct shipping involves manufacturers or wholesalers shipping orders directly to customers on behalf of retailers, offering reduced storage costs and better control over branding compared to dropshipping, but requiring upfront inventory purchases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com